User Guide
7
The A, B, X, Y notation used in the labelling of the SDM-SIO1 follows
the practice of the driver chip manufacturer (Maxim Inc.) used in this
product. Unfortunately, the convention of A/B and X/Y labelling differs
between different designers of RS485 products. If you cannot get the
connection to work with another device, or the data is completely
corrupted, please first check the polarity of the connections (see below)
for the SDM-SIO1 relative to the device it is being used with as they give
a more certain indicator of the correct connection than the A/B notation.
If the polarity is not indicated then reversing the A relative to B
connections (and the X and Y if used) can be done to check for the
correct connection with no risk of damage to either device.
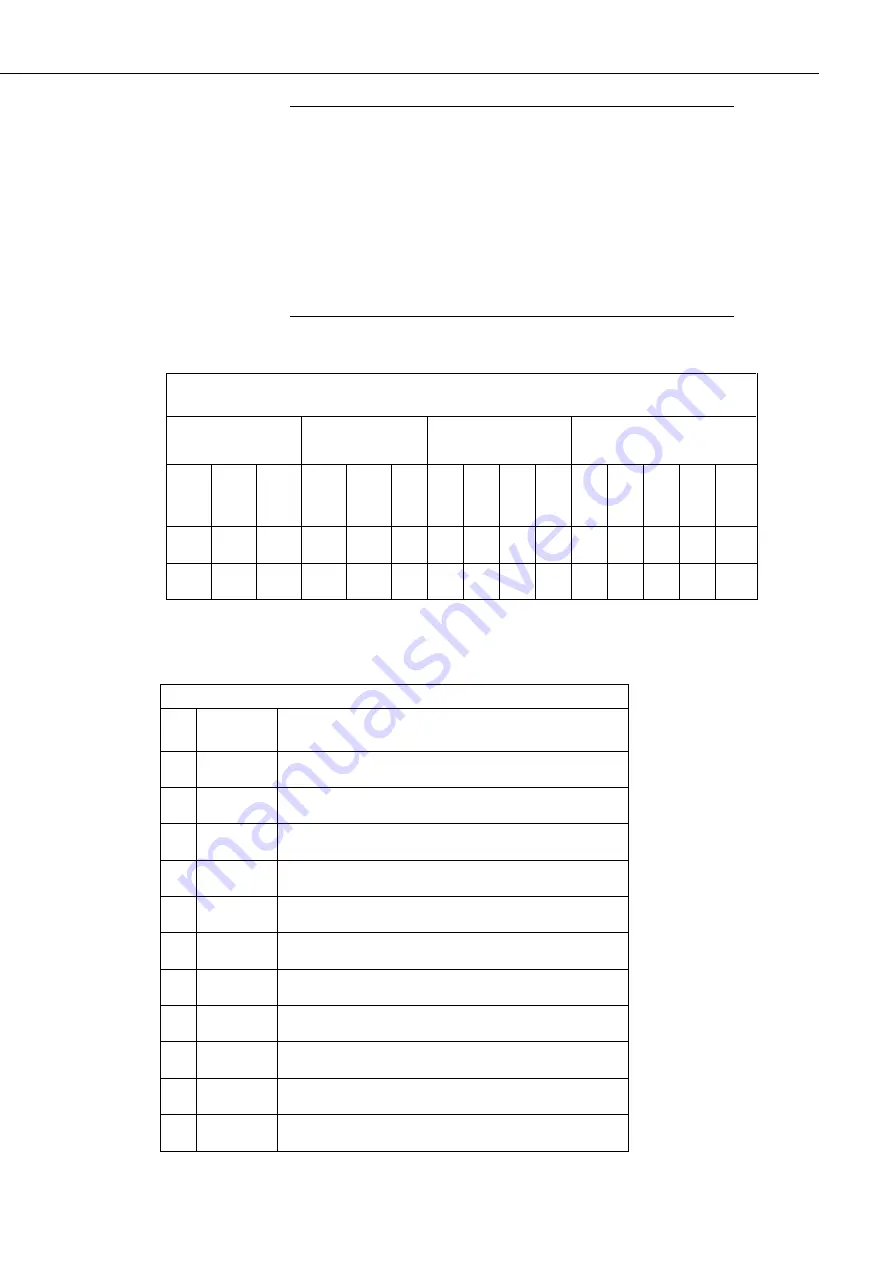
Table 3-2. SDM-SIO1 connections (left to right as viewed from the front
of the unit)
SDM
Power
connections
RS-232 connections
RS-485/RS422
C1
C2
C3
G
+1
2
V
G
RX
-A
C
T
S
-B
R
T
S
-Y
TX
-Z
0V
Z
Y
B
A
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
15
14
13
12
10
9
8
7
Note: Italic numbers indicate which pins are connected internally (for use with RS-485 termination
resistors etc.). For example the signals present on pin 7 will also be present on pin 15.
Table 3-3. SDM-SIO1 Functional description of the connections
N
Case text
Description
1
C1
SDM data line – connect to datalogger SDM C1
2
C2
SDM clock line – connect to datalogger SDM C2
3
C3
SDM
enable
line – connect to datalogger SDM C3
4
G
Connect to the datalogger power ground (G)
(1)
5
+12V
Main power supply – connect to logger 12V
6
G
RS-232 0V reference/second G connection
(2)
7
RX-A
RS-232 receive line
8
CTS-B
RS-232 CTS hardware handshaking line / output
9
RTS-Y
RS-232 RTS hardware handshaking / input
10
TX-Z
RS-232 transmit line
11
0V
RS-485 0V reference line
(3)
NOTE
















































