Operating Manual for
FAN Press Screw Separator PSS 1.1-300
19
9
TEST FOR SEPARATION CAPABILITY
In order to test the separation capability of the medium supplied to the separator, you can perform a
simple suitability test. Take some of the medium intended for separation into your hand and try to press
it out. If the medium is a very fine-grained solid and seeps through your fingers during this test, it cannot
be mechanically separated without reducing the viscosity.
However, if liquid escapes through your fingers and solid matter remains in your hand when opened,
then this medium can be separated in the separator.
You can also perform this test with the effluent of the separator to determine whether further separation
in the separator is possible by using screens with lower gap widths. For example, if the first separator is
operated with a gap width of 0.75 mm, the effluent can be introduced to a separator with a gap width of
0.25 mm and so on.
To determine the possible dry matter content for your application using the separator, perform a screen
test, such as with a screen of gap width 0.50 mm. The dry matter content when using the separator will
always be higher than your test result since the solids are filtered by the solid cake, meaning that even
solids with a size smaller than 0.50 mm will be captured in the cake.
10
LIQUID CLEANING
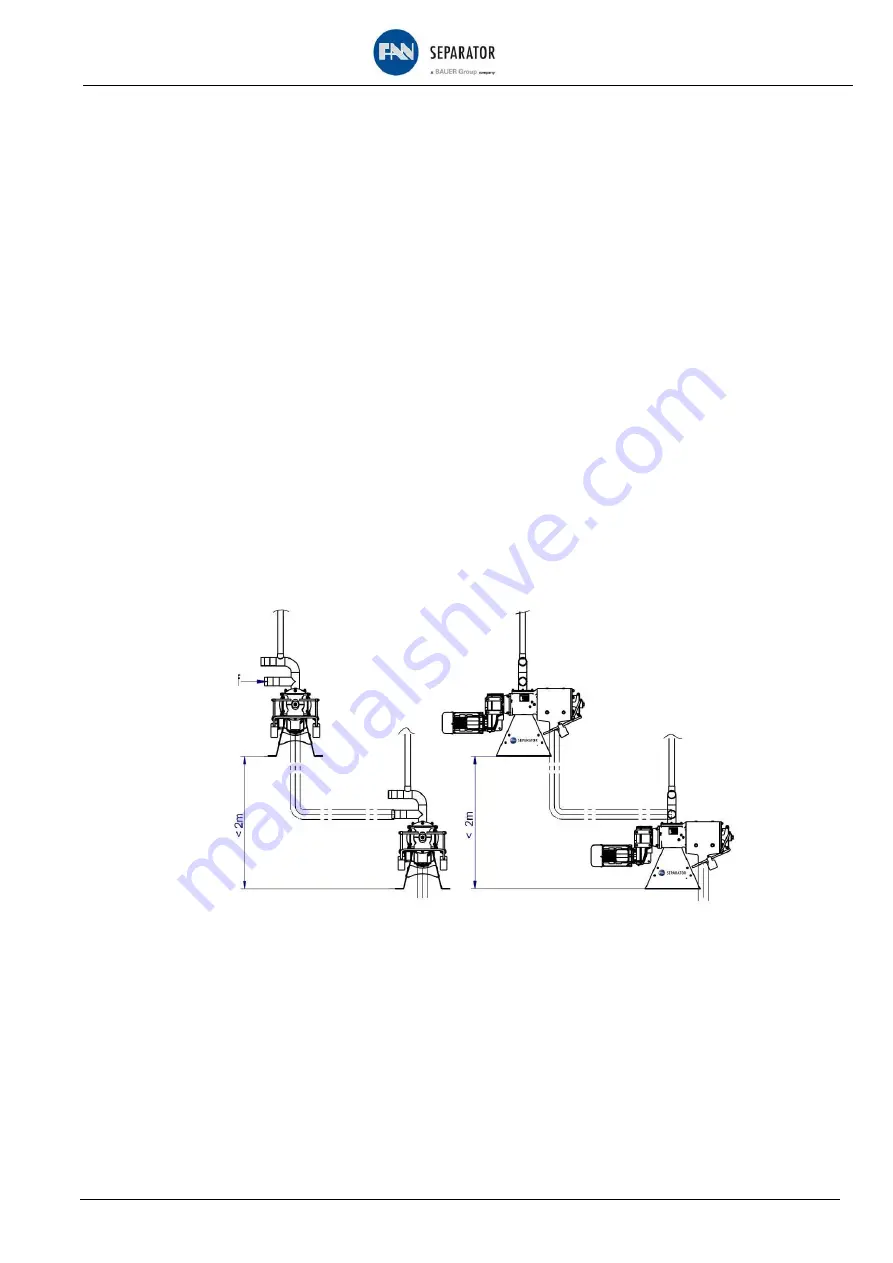
Fig. 10-1 illustrates the arrangement of 2 separators in series, where the effluent of the first separator is
supplied to the second separator. The second separator is equipped with screens of a smaller gap width
than the first separator in order to achieve a further clarifying of the liquid.
Fig. 10-1 Typical arrangement for the operation of 2 separators in series
Inflow






























