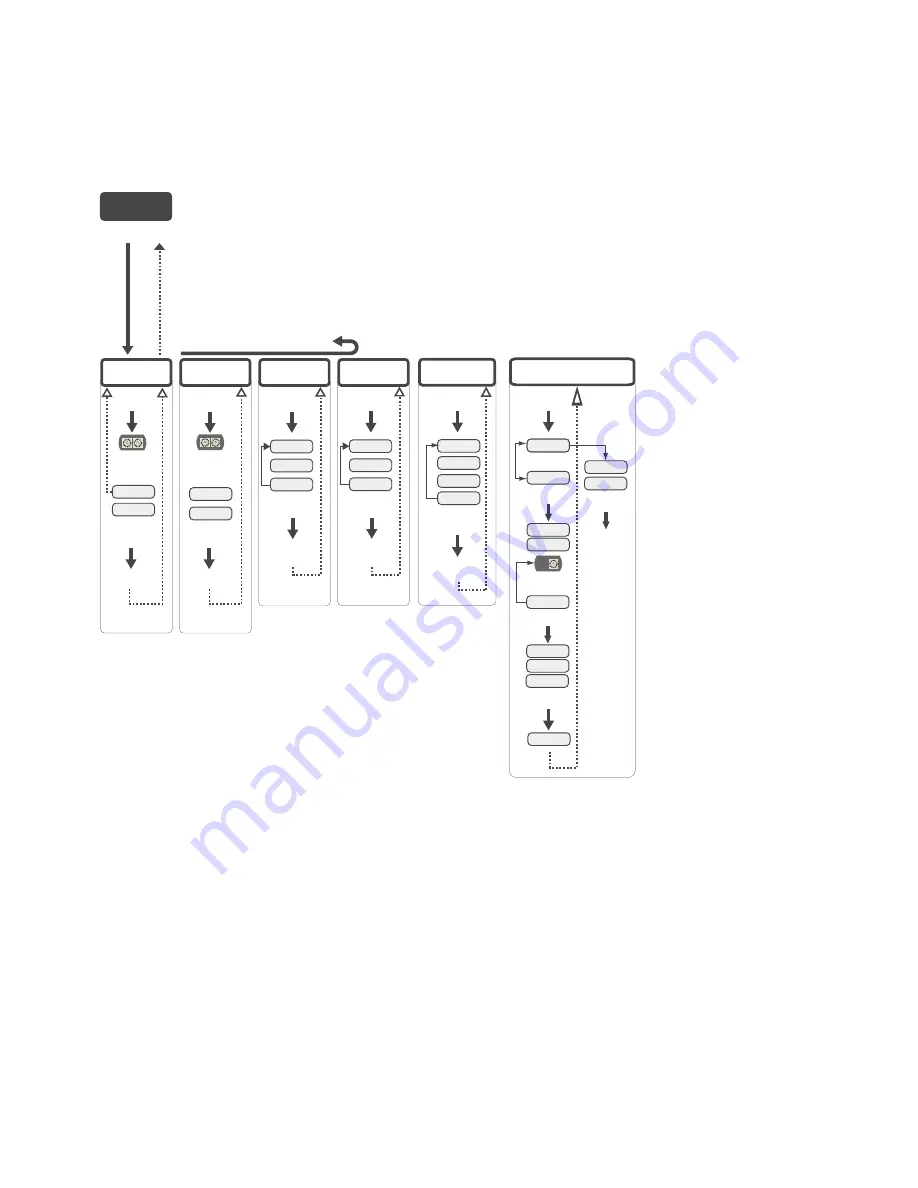
5.1.5 DVCFG (Device Configuration) Menu
On Gateways, the DVCFG menu allows users to set various device-specific parameters, including the network ID (NID),
slave ID (SLID), baud rate, and parity. In extended address mode, use this menu to also set the maximum number of radio
devices (MAXN) within the network and the extended address binding code (XADR).
*
DVCFG
Single-click
Button 2
Double-click Button 2
Even
None
Odd
Single-click
Button 2
Single-click
Button 2
SAVES
DISPLAYED
VALUE
Single-click B1
19200
9600
38400
Single-click
Button 2
Single-click
Button 2
SAVES
DISPLAYED
VALUE
NEW XX
Single-click
Button 2
Single-click
Button 2
adjust rotary switches
to set the network ID
SAVES NEW
VALUES
CUR XX
Single-click
Button 2
Single-click
Button 2
adjust rotary switches
to set slave ID, using
button 1 to select the
digits
SAVES NEW
VALUES
(NID)
(SLID)
(BAUD)
(PRTY)
Network ID
Slave ID
Baud Rate
Parity
Single-click B1
NEW XX
Single-click Button 1 to advance through menu
CUR XX
Double-click Button 2
Double-click
Button 2
* Set to 000000 to use the serial number.
Device Config
16
8
32
Single-click
Button 2
Single-click
Button 2
SAVES
DISPLAYED
VALUE
Single-click B1
(MAXN)
Timing
48
MANUAL
AUTO
AUTO
SET
Single-click
Button 2
Single-click
Button 2
Single-click B1
(XADR)
Extended Addressing
XADR
ADJUST ROTARY
SWITCH TO
SET XADR
Single-click
Button 2
XXXXXX
Single-click B1
Single-click
Button 2
CONFRM
XADR
XXXXX
NETWRK
Single-click
Button 2
BINDNG
Single-click
Button 1 or 2
Reboot
SAVED
*
Gateway
• Baud and Parity. The options for baud rate are: 19200, 38400, or 9600. For parity, select None, Even, or Odd.
• Extended Address (Binding) Code. Binding Nodes to a Gateway ensures the Nodes only exchange data with the
Gateway they are bound to. After a Gateway enters binding mode, the Gateway automatically generates and
transmits a unique extended addressing (XADR), or binding, code to all Nodes within range that are also in binding
mode. The extended addressing (binding) code defines the network, and all radios within a network must use the
same code.
• Max Nodes. Selecting the maximum number of system radio devices (Gateway and all Nodes) changes the timing
for the wireless network. For example, if you are running four Nodes in your wireless network, set the system's
maximum device count to 8. This allows up to 8 radio devices, including the Gateway, in the wireless network and
offers the highest throughput, 62.5 milliseconds, for each Node. The choices are 8, 16, 32, and 48 devices.
• Network ID. The Network ID (NID) is a unique identifier you assign to each wireless network to minimizes the
chances of two collocated networks interfering with each other. Assigning different NIDs to different networks
improves collocation performance in dense installations.
• Slave ID. The slave ID is an identifying number used for devices within a Modbus system. By default, Gateways are
set to Modbus Slave ID 1. When using more than one Modbus slave, assign each slave a unique ID number.
On Nodes, use the DVCFG to set the network ID (NID) and extended address binding code (XADR). The Node address
(NADR), also referred to as a Node ID or device address, is only functional on some models.
Sure Cross
®
Performance DX80 Wireless I/O Networks
www.bannerengineering.com - Tel: + 1 888 373 6767
35
















































