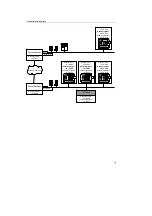
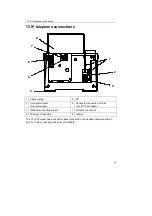
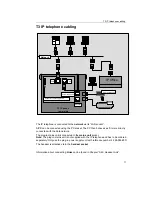
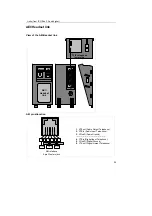
General explanations
9
Codecs, bandwidth, delay, jitter and jitter buffer
Codec
Both the IP telephone and IP Office must have an audio Codec. This codes the voice
signals from the microphone for transfer via the transmitting terminal, and decodes the
received audio signals sent to the loudspeaker/receiver of the terminal.
G.711 and G.729 are supported in the IP telephone.
Process
Nominal data rate
Codec generates its
output data with…
Packetisation
delay
Pass through the
Codec
Short description
G.711A
64 kBit/s
1 ms
No compression, voice quality
comparable with ISDN, European
process for audio digitisation
G.711 ì
64 kBit/s
1 ms
As for G.711A, except a US
process for audio digitisation
G.729
8 kBit/s
25 ms
Best voice quality of the
compressing
process
Bandwidth
•
Data flow depends on the Codec and the configured delay.
•
Voice data are not transferred via the packet-oriented TCP/IP protocol on a
continuous basis.
•
The Codec compiles the voice data into a packet during a specific period of
time, 10ms for the IP telephone.
•
IP packets consist of a variable percentage of user data and a fixed
percentage of management information.
•
For small packets the ratio between user and management data is very
unfavourable for the required bandwidth but there is only a short voice delay.
Section of data transfer
The user data header is 40 bytes.
RTP-Datagram
UDP
Header
8 bytes
RTP
Header
12 bytes
RTP
Payload (user data
)
8 bytes
IP
Header
20 bytes
Содержание T3 Comfort
Страница 73: ...Index 73 Your notes ...