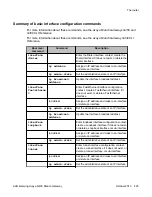
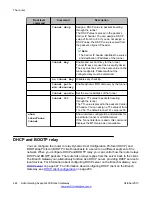
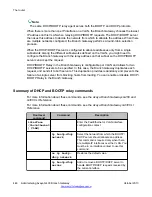
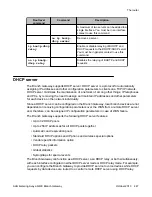
Prevention of nested tunneling in GRE tunnels
Nested tunneling occurs when the tunnel’s next hop for its destination is another tunnel, or the
tunnel itself. When the next hop is the tunnel itself, a tunnel loop occurs. This is also known
as recursive routing.
When the Branch Gateway recognizes nested tunneling, it brings down the Tunnel interface
and produces a message that the interface is temporarily disabled due to nested tunneling.
The tunnel remains down until the tunnel is re-configured to eliminate the nested tunneling.
In addition to checking for nested tunneling, the Branch Gateway prevents loops in connection
with GRE tunnels by preventing the same packet from being encapsulated more than once in
the Branch Gateway.
Related topics:
Reasons for nested tunneling in a GRE tunnel
Recommendations on avoiding nested tunneling
on page 437
Reasons for nested tunneling in a GRE tunnel
• A static route exists on the source tunnel endpoint that tells the tunnel to route packets
addressed to the receiving tunnel endpoint via the tunnel itself
• The local endpoint of the tunnel learns the tunnel as a route to the tunnel’s remote
endpoint via OSPF or RIP
• A combination of static routes via parallel tunnels lead to a situation in which each tunnel
is routing packets via another tunnel. For example:
Gxxx-001(super)# interface tunnel 1
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 1)# tunnel source x.x.x.x
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 1)# tunnel destination 1.0.0.1
Done!
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 1)# exit
Gxxx-001(super)# interface tunnel 2
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 2)# tunnel source x.x.x.x
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 2)# tunnel destination 2.0.0.1
Done!
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 2)# exit
Gxxx-001(super)# interface tunnel 3
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 3)# tunnel source x.x.x.x
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 3)# tunnel destination 3.0.0.1
Done!
Gxxx-001(super-if:Tunnel 3)# exit
Gxxx-001(super)# ip route 1.0.0.1 tunnel 2
Done!
Gxxx-001(super)# ip route 2.0.0.1 tunnel 3
Done!
Gxxx-001(super)# ip route 3.0.0.1 tunnel 1
Done!
Using the network shown in
on page 437 as an illustration, if Router
1 has an entry in its routing table regarding the tunnel’s receiving endpoint, this will cause an
The router
436 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway
October 2013
Содержание G430
Страница 1: ...Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway Release 6 3 03 603228 Issue 5 October 2013 ...
Страница 12: ...12 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 ...
Страница 214: ...Ethernet ports 214 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 232: ...System logging 232 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 246: ...VoIP QoS 246 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 250: ...Modems and the Branch Gateway 250 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 302: ...Emergency Transfer Relay ETR 302 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 556: ...IPSec VPN 556 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 604: ...Policy based routing 604 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 610: ...Synchronization 610 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...
Страница 668: ...Traps and MIBs 668 Administering Avaya G430 Branch Gateway October 2013 Comments infodev avaya com ...