Communication extension card
-52-
Function
code
Word
Value range
Default
value
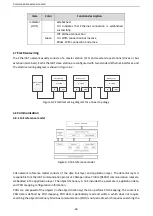
25: State word
26: HDIB frequency value (×100, kHz)
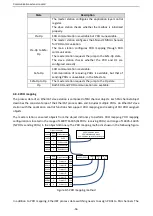
PKW zone
PKW zone (parameter identification flag PKW1
––
numerical zone): The PKW zone describes the processing
mode of the parameter identification interface. A PKW interface is not a physical interface but a mechanism
that defines the transmission mode (such reading and writing a parameter value) of a parameter between
two communication ends.
Parameter
identification (PKW)
Process data
PKW1
PKW2
PKW3
PKW4
CW
SW
PZD2
PZD2
Request
No.
Response
No.l
Parameter
address
Parameter
value error
No.
Parameter
value
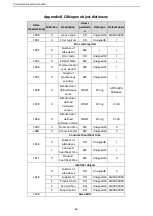
Figure 4-5 Parameter identification zone
In the periodic communication, the PKW zone consists of four 16-bit words. The following table describes
the definition of each word.
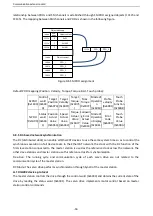
First word PKW1 (16 bits)
Bits 15
–
00
Task or response identification flag
0
–
7
Second word PKW2 (16 bits)
Bits 15
–
00
Basic parameter address
0
–
247
Third word PKW3 (16 bits)
Bits 15
–
00
Value (most significant word) of a
parameter or error code of the returned
value
00
Fourth word PKW4 (16 bits)
Bits 15
–
00
Value (least significant word) of a
parameter
0
–
65535
Note:
If the master station requests the value of a parameter, the values in PKW3 and PKW4 of the packet
that the master station transmits to the VFD are no longer valid.
Task request and response: When transmitting data to a slave, the master uses a request number, and the
slave uses a response number to accept or reject the request.
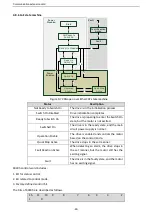
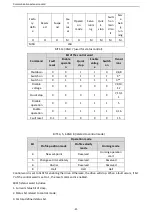
Table 4-9 Task identification flag PKW1
Request No. (from the master to a slave)
Response signal
Request
No.
Function
Acceptance Rejection
0
No task
0
—
1
Requesting the value of a parameter
1, 2
3
2
Modifying a parameter value (one word)
[modifying the value only on RAM]
1
3 or 4