EMAC to FPGA PHY Interface
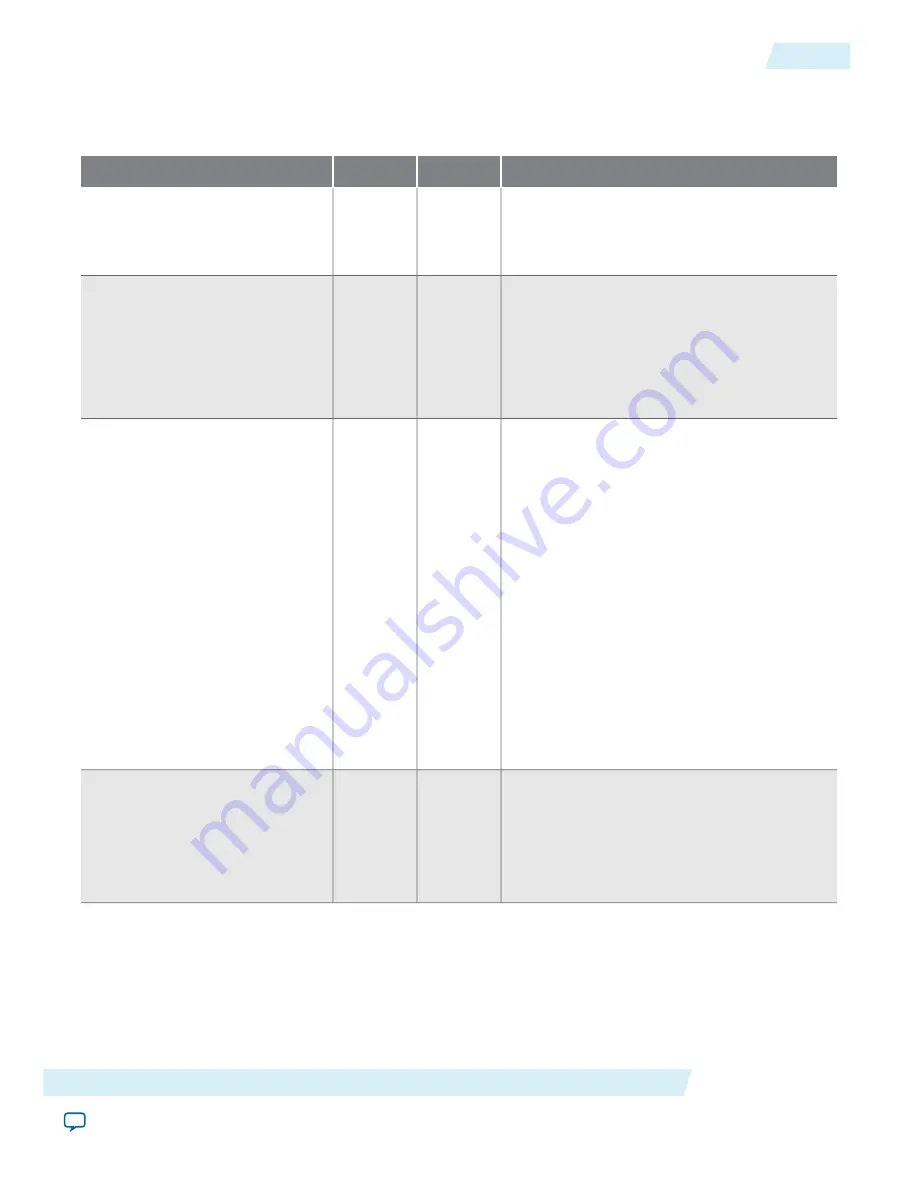
Table 17-2: EMAC to FPGA PHY Interface Signals
Description
Width
In/Out
Signal Name
Transmit Clock. This is the transmit clock (2.5
MHz/25 MHz) provided by the MII PHYs only.
This clock comes from the FPGA Interface and
is used for TX data capture.
1
In
phy_tx_i
Transmit clock output to the PHY to sample
data.
For MII this clock is unused.
For GMII (1G - 125 MHz) and RGMII (125/
25/2.5 MHz), this clock is derived from the
clk_ref_i 250 MHz input.
1
Out
phy_txclk_o
PHY Transmit Data. These are a group of eight
transmit data signals driven by the MAC.
Unused bits in the RGMII interface configura-
tion are driven low. The following functions
depend on which PHY interface is selected:
• GMII: All eight bits provide the GMII
transmit data byte. For the lower speed MII
operation, only the low 4 bits are used. The
validity of the data is qualified with
phy_txen_o and phy_txer_o. Synchronous
to: phy_ clk_tx_o.
• RGMII: Bits [3:0] provide the RGMII
transmit data. The data bus changes with
both rising and falling edges of the transmit
clock (clk_tx_o). The validity of the data is
qualified with phy_txen_o. Synchronous to:
phy_clk_tx_o (both the rising and falling
edges).
8
Out
phy_txd_o
PHY Transmit Data Enable: This signal is
driven by the EMAC component and has the
following function listed below:
• GMII: When high, indicates that valid data
is being transmitted on the phy_txd bus.
Synchronous to: clk_tx_o
1
Out
phy_txen_o
Altera Corporation
Ethernet Media Access Controller
17-5
EMAC to FPGA PHY Interface
cv_54017
2013.12.30
















































