Industrial
Electronic Devices
ADFweb.com S.r.l.
User Manual
Modbus Slave / Modbus TCP Master
Document code: MN67510_ENG Revision 2.100 Page 22 of 33
E
XAMPLE
1:
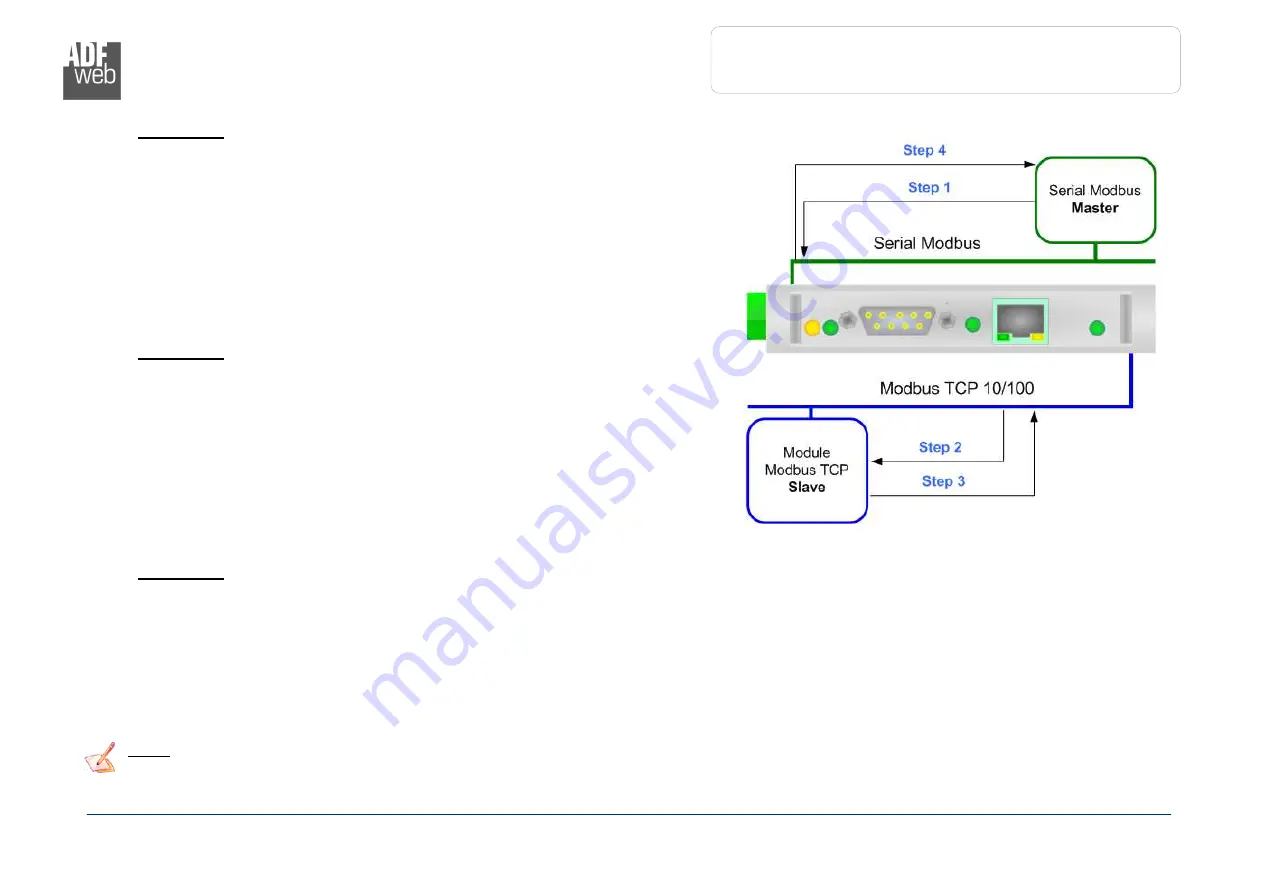
Taking the first row of Figure 4:
Step 1
: A serial Modbus master do the request to the Converter to read the “Coil
Status” address 100 for 5 consecutive points;
Step 2
: The Converter sends to the TCP Slave 192.168.0.18 the read request of
“Coil Status” address 150 for 5 consecutive points;
Step 3
: The slave TCP replies to the Converter with the data;
Step 4
: The Converter sends back the data on serial.
E
XAMPLE
2:
Taking the second row of Figure 4:
Step 1
: A serial Modbus master do the request to the Converter to read the “Input
Status” address 110;
Step 2
: The Converter sends to the TCP Slave 192.168.0.19 the read request of
“Input Status” address 100;
Step 3
: The slave TCP replies to the Converter with the data;
Step 4
: The Converter sends back the data on serial.
E
XAMPLE
3:
Taking the third row of Figure 4:
Step 1
: A serial Modbus master do the request to the Converter to read the “Holding Register” address 91 for 6 consecutive points;
Step 2
: The Converter sends to the TCP Slave 192.168.0.18 the read request of “Holding Register” address 81 for 6 consecutive points;
Step 3
: The slave TCP replies to the Converter with the data;
Step 4
: The Converter sends back the data on serial.
Note:
If the TCP slave responds with an exception, that exception code will be transmitted to the serial master. If the TCP slave does not
respond within the estimated time defined by the Timeout parameter, an exception response will be given: error code $36.
Figure 5: Chart of Request data from serial Modbus












































