ABB i-bus
®
KNX
Planning and application
FCC/S 1.X.X.1 | 2CDC 508 200 D0211 Rev A 364
Proportional valve drives are controlled via an analog signal, e.g. 0…10 V. 2 or 3-point valve drives
are controlled via switching of the supply voltage.
2-point valve drives are controlled via the values Open and Close. The valve knows only the states
"Open" and "Closed". 2-point valves are controlled via a 2-point control or pulse width modulation
(PWM).
3-point valve drives are connected via three connecting cables. The opening and closing lines are
connected to terminals A and B. Using 3-point control value drives, the valve can be opened by
any desired percentage and this position can be retained without further energy expenditure. If the
valve does not move, no voltage is applied to the motor.
The control usually used in most cases is continuous control.
12.3.2
Electrothermal Valve Drives
Electrothermal Valve Drives are adjusted due to heat expansion of a material caused by a flow of
electric current. Electrothermal Valve Drives are controlled by pulse width modulation or two-point
control.
Electrothermal Valve Drives are offered in the de-energized closed and de-energized open vari-
ants. Depending on the variant, the valve is opened when voltage is applied and closed when no
voltage is applied, or vice versa.
Electrothermal Valve Drives are connected via two connection cables to the device.
12.3.3
Compatibility with different drive types
For information about the compatibility of individual device variants with the respective drive types,
see Product Overview, Page 11.
12.3.4
Control types
The following control types are commonly used for the control of valves in heating, air-conditioning
and ventilation applications:
•
Continuous control
•
Pulse width modulation (PWM)
•
2-point control
12.4
Priorities
12.4.1
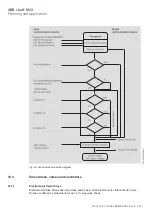
Controller mode
Valve
a) Bus voltage failure
b) Operating mode overridden
c) Safety (dew point or filling level sensor or window contact)
d) Forced operation
e) i-bus Tool
f)
Direct operation via membrane keypad (only FCC/S 1.x.2.1)
g) Manual valve override
h) Normal mode Control (operating mode normal/presence)
i)
Bus voltage recovery
Fan
a) Bus voltage failure
b) Operating mode overridden
c) Safety (dew point or filling level sensor or window contact)