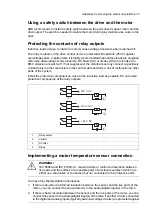
If the cabling is in a metal conduit, it reduces the electromagnetic emission of the whole
drive system.
The protective conductor must always have an adequate conductivity. Unless local wiring
regulations state otherwise, the cross-sectional area of the protective conductor must agree
with the conditions that require automatic disconnection of the supply required in 411.3.2.
of IEC 60364-4-41:2005 and be capable of withstanding the prospective fault current during
the disconnection time of the protective device. The cross-sectional area of the protective
conductor can either be selected from the table below or calculated according to 543.1 of
IEC 60364-5-54.
This table shows the minimum cross-sectional area of the protective conductor related to
the phase conductor size according to IEC 61800-5-1 when the phase conductor and the
protective conductor are made of the same metal. If this is not so, the cross-sectional area
of the protective earthing conductor shall be determined in a manner which produces a
conductance equivalent to that which results from the application of this table.
Minimum cross-sectional area of the corresponding
protective conductor
S
p
(mm
2
)
Cross-sectional area of the phase conductors
S (mm
2
)
S
1)
,
2)
S ≤ 16
16
16 < S ≤ 35
S/2
35 < S
1) Drive safety standard IEC/EN 61800-5-1:
• use a protective earth conductor with a cross-section of at least 10 mm
2
(8 AWG) Cu or 16 mm
2
(6 AWG) Al, or
• use a second protective earth conductor of the same cross-sectional area as the original protective earthing conductor,
or
• use a device which automatically disconnects the supply if the protective earth conductor breaks.
2) Drive safety standard IEC/EN 61800-5-1: If the protective earth conductor is separate (ie, it does not form part of the input
power cable or the input power cable enclosure), the cross section must be at least:
• 2.5 mm
2
(14 AWG) when the conductor is mechanically protected, or
• 4 mm
2
(12 AWG) when the conductor is not mechanically protected.
■
Typical power cable sizes
See the technical data of the drive (or unit).
Guidelines for planning the electrical installation 63
Содержание ACS880-37LC
Страница 1: ... ABB INDUSTRIAL DRIVES ACS880 37LC drives Hardware manual ...
Страница 2: ......
Страница 4: ......
Страница 78: ...78 ...
Страница 116: ...116 ...
Страница 134: ...5 Set the real time clock 134 Maintenance ...
Страница 144: ...144 ...
Страница 167: ... Dimension drawing examples ACS880 37LC 0390A 7 with main contactor Dimensions 167 ...
Страница 169: ...ACS880 37LC 1270A 7 with common motor terminal cubicle Dimensions 169 ...
Страница 170: ...ACS880 37LC 1940A 7 with common motor terminal cubicle 170 Dimensions ...
Страница 171: ...Cabinet height and depth Marine construction option C121 IP42 side view Non marine IP42 side view Dimensions 171 ...
Страница 172: ...Location and size of input terminals Contact ABB for details 172 Dimensions ...
Страница 174: ...Inverter module cubicle with two R8i modules bottom cable exit 174 Dimensions ...
Страница 175: ...Inverter module cubicle with three R8i modules bottom cable exit Dimensions 175 ...
Страница 176: ...Brake chopper cubicle D150 176 Dimensions ...
Страница 177: ... Units with common motor terminal cubicle H359 Cubicle width 300 mm bottom cable exit Dimensions 177 ...
Страница 178: ...Cubicle width 300 mm top cable exit 178 Dimensions ...
Страница 179: ...Cubicle width 400 mm bottom cable exit Dimensions 179 ...
Страница 180: ...Cubicle width 400 mm top cable exit 180 Dimensions ...
Страница 181: ...Cubicle width 600 mm bottom cable exit Dimensions 181 ...
Страница 182: ...Cubicle width 600 mm top cable exit 182 Dimensions ...
Страница 198: ...198 ...
Страница 200: ...200 ...