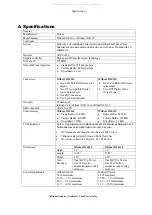
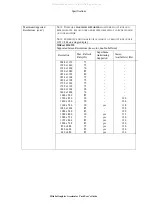
Terms and Definitions
3Dlabs Graphics Accelerator Card User's Guide
Heidi
The API developed by Autodesk to work with its products, such as 3D Studio MAX and AutoCAD.
MIP-Mapping (for texture processing)
A feature that delivers photo-realistic images by wrapping 2D bitmaps around 3D objects closely
matching the texture to the object. MIP-Mapping allows different versions of a texture to be used for
objects of different sizes. It also enables faster performance as textures do not need to be scaled in real
time.
Multiple Resolution Support
The ability to support multiple resolutions on the screen.
OpenGL
The industry standard library of advanced 3D graphics functions developed by Silicon Graphics, Inc.
Perspective Correction
A function that allows an object to maintain its 3D textural features as it moves away from the viewer,
into the background.
Pipelining
A basic hardware tool for accelerating processes.
Pixel
The smallest addressable element of a cathode ray tube display. More simply put, the individual dots that
make up the screen image.
Point Sampling
The basic method of adding texture to an object. Point sampling does not include any filtering of textures.
RAMDAC
The final component in the graphics subsystem that translates a digital image into an analog
representation.
Rasterization
A method to fill in colors for all pixels bound by vertices.
Rendering
The final and most rigorous stage in the 3D pipeline where an object undergoes shading, texturing, etc.
RISC
Reduced Instruction Set Computing.
SDRAM
Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory (SDRAM) is a cost-effective solution to improve
bandwidth to and from memory, resulting in increased graphics performance.
SGRAM
Synchronous Graphics Random Access Memory allows data to be written in a single operation, rather
than a (slower) sequence of operations. It also handles background and foreground image fills effectively.
SDTP
Super Desktop Publishing. SDTP runs at 1600 x 1200.
All manuals and user guides at all-guides.com