Chapter 2 IPv6 Address Configuration
accept these packets in the same way as it receives packets from external nodes,
and transmits them back to the protocol stack.
The loopback function is used for software test and configuration. Except the
lowest bit, all the other bits of an IPv6 loopback address are 0, that is, a loopback
address can be expressed as 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1 or ::1.
à
IPv6 address embedded with IPv4 address
IPv6 provides two kinds of addresses. One is the IPv4-compatible address, which
allows the IPv6 node to access IPv4 nodes that do not support IPv6.. The other is
the IPv4-mapping address, which allows the IPv6 router to transmit IPv6 packets
over the IPv4 network in tunnel mode, where the nodes understand both IPv4
and IPv6.
The high-order 80 bits of these two kinds of addresses are all set to zeros, and
the low-order 32 bits contain the IPv4 address. If the middle 16 bits of an address
are set to FFFF, it indicates that this address is the IPv6 address mapping to IPv4
address.
lists the address structures of these two kinds of addresses.
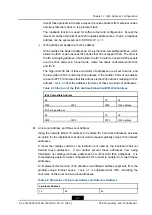
Table 2-3 Structure of the IPv6 Address Embedded With IPv4 Address
IPv4 Compatible Address
80
16
32
0000.................................0000
0000
IPv4 address
IPv4 image address
80
16
32
0000.................................0000
FFFF
IPv4 address
l
Link Local Address and Site-Local Address
Using the network Model 10 address to translate IPv4 network addresses provides
an option for the institutions that do not want to request globally unique IPv4 network
addresses.
A router that resides outside of an institution but used by the institution shall not
forward these addresses.
It can neither prevent these addresses from being
forwarded, nor distinguish these addresses from other valid IPv4 addresses. It is
comparatively easier to make configurations for a router to enable it to forward these
addresses.
To implement this function, IPv6 allocates two different address segments from the
globally unique Internet space.
is originated from RFC, indicating the
structures of link-local and site-local addresses.
Table 2-4 Structures of Link-local Address and Site-local Address
Link-local Address
10
54
64
2-7
SJ-20140504150128-018|2014-05-10 (R1.0)
ZTE Proprietary and Confidential