ZXR10 ZSR V2 Configuration Guide (IPv6)
Codes
: K: kernel, I1: isis-l1, SFN: sf-nat64, R: ripng, AF: aftr, B: bgp,
D: direct, I2: isis-l2, SLN: sl-nat64, O: ospfv3, D6: dhcp, P: ppp,
S: static, N: nd, V: vrrp, A: address, M: multicast, UI: user-ipaddr;
Dest
Owner
Metric
Interface
Pri
Gw
3555::/64
I1
20
gei-0/3
115
fe80:2e::2d0:d0ff:fe78:99dd
R2#ping6 3555::52
sending 5,100-byte ICMP echoes to 3555::52,timeout is 2 seconds.
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent(5/5),round-trip min/avg/max= 0/0/0 ms.
7.3.2 Multi-Area IS-ISv6 Configuration Example
Configuration Description
For a large-scale network, the use of multiple areas shall be considered in IS-IS. Set the
near routers to be in one area according to their positions and functions because area
division is helpful to decrease the demand for memory, and the routers in each area only
need to maintain a smaller link state database.
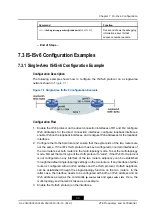
shows a multi-area IS-IS instance. R1 is in Area 1, R2 in Area 0, and R3 and
R4 in Area 2. On R1, perform route aggregation for the network segments in Area 1. The
static routes are redistributed to the IS-IS on R4.
Figure 7-2 Multi-Area IS-ISv6 Configuration Example
Configuration Flow
1.
Enable the IPv6 protocol on the interfaces, configure IPv6 addresses for these
interfaces, configure loopback interfaces, enable IPv6 on the loopback interfaces,
and configure IPv6 addresses for the loopback interfaces.
2.
Configure the IS-ISv6 protocol and ensure that the system-ids of the routers are not
the same. Establish L2 neighbors between R2 and R1/R3, and establish L1 neighbors
between R3 and R4. Here, the multi-topology environment is taken as an example.
3.
Enable the IS-ISv6 protocol on the interfaces.
7-14
SJ-20140504150128-018|2014-05-10 (R1.0)
ZTE Proprietary and Confidential