42
ENGLISH
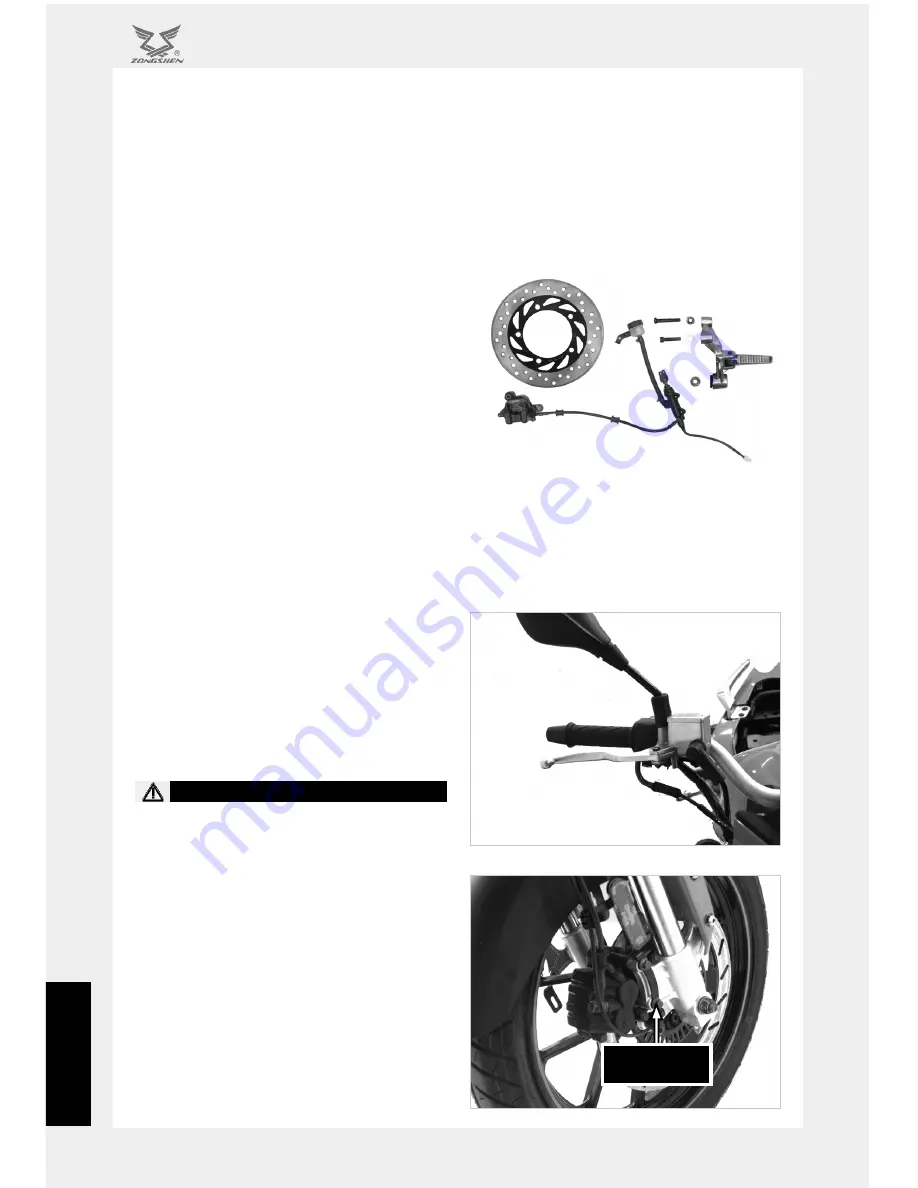
盘式制动器的结构图
Section 12 Brake
1. Structure and Working Principles of Brakes
Motorcycles often slow down to stop in the drive. This requires the brake on the wheel to exert a force
or torque to prevent its rotation, for the purpose of deceleration or parking. For an average motorcycle, the
right hand manipulates the front wheel brake and the right foot operates the rear wheel brake. For some
models using automatic clutch engines, such as mopeds or motor scooters, the rear wheel is operated by
the left hand. Motorcycle brakes can be divided into drum brakes and disc brakes. The motorcycle is a
front and rear disc brakes.
Disc brakes include mechanical and hydraulic
types. Most motorcycles are currently equipped
with hydraulic disc brakes. A hydraulic disc brake
generally include a braking grip (brake pedal),
brake master cylinder, oil storage cylinder (the oil
storage cylinder and the brake master cylinder
are generally made as one in the front brake),
brake caliper, brake disc, brake pipe and other
components. When braking is applied, the brake
grip compresses the master cylinder to raise the
pressure in the hydraulic system and urge the main
piston in the caliper, which presses the friction
plate against the brake disc so that the brake
disc fixed to the wheel gets the braking torque.
Disc brake is characterized by gentle operation,
automatic cleaning and scare failures.
2. Demolition and Maintenance of a Brake
[1] Hold the front brake grip by the right hand and
check the braking performance of the front brake.
The standard free stroke of the front brake grip is:
10mm ~ 20mm.
If the front brake grip can not reach the standard
value of 10m m ~ 20mm, it must readjusted.
注意
Caution
[2] Remove the front brake caliper lock bolts and
take down the front brake caliper.
Front brake
caliper lock bolts
















































