4
IM05C01E12-01E
IMPORTANT
To use dynamic auto tune control,
(1) be sure to turn on the final control element, such as a heater, before starting the control, and
(2) make sure the controlled loop is a closed loop.
If you do not follow these precautions, improper PID constants may be written into the controller. If this occurs,
carry out the following:
• Set the parameter CTL at PID.
• Set the PID constants at the factory-set defaults (P = (upper range-limit - lower range-limit)
×
5%; I = 240 s.; and D = 60 s.)
• Set the parameter CTL at SLF.
If the control still doesn’t work properly, stop using the dynamic auto tune control function. Change the param-
eter CTL setting to PID and execute auto-tuning to obtain the PID constants.
Note: The alarms numbered 1 to 10 have no waiting
action, while alarms 11 to 20 have a waiting
action.
The waiting action turns off the PV and deviation
alarms that occur from the start of the control
operation until a stable state is reached.
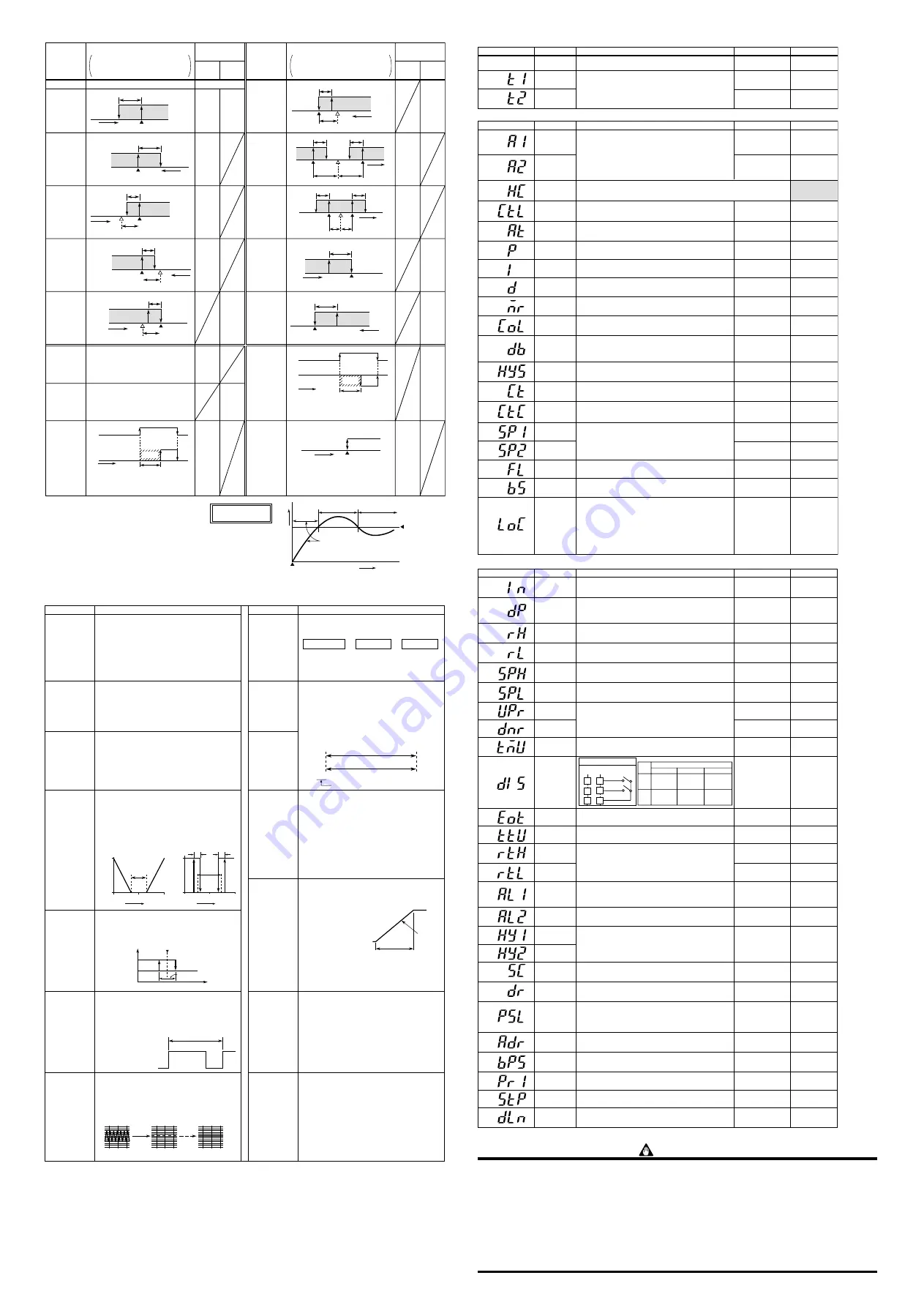
Hysteresis
Temperature setpoint
Deviation setting
Measured value
Opn (on)
Cls (off)
Hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis
Hysteresis
Temperature setpoint
Temperature setpoint
Deviation setting
Measured value
Cls
(on)
Opn
(off)
Cls
(on)
Hysteresis
Alarm setting
Measured value
Opn (off)
Opn (off)
Cls (on)
Hysteresis
Alarm setting
Measured value
Opn (off)
Cls (on)
7
17
(See note.)
6
16
(See note.)
De-energized
on deviation
low limit
1
11
(See note.)
PV
high limit
No alarm
Deviation
high and low
limit
2
12
(See note.)
PV
low limit
8
18
(See note.)
Deviation
within high-
and -low-
limit
3
13
(See note.)
Deviation
high limit
9
19
(See note.)
De-energized
on PV
high limit
4
14
(See note.)
Deviation
low limit
10
20
(See note.)
25
24
De-energized
on PV
low limit
Break timer
function
Heater
disconnection
alarm
23
Timer
function
5
15
(See note.)
De-energized
on deviation
high limit
21
The contact is closed at input
burnout.
Fault
diagnosis
alarm
22
FAIL
output
OFF
Measured value
Opn (off)
Opn (off)
Cls (on)
Deviation setting
Hysteresis
Cls (on)
Measured value
Temperature setpoint
Deviation setting
Cls (on)
Hysteresis
Opn (off)
Measured value
Temperature setpoint
Deviation setting
Hysteresis
Opn (on)
Cls
(off)
Alarm setting
Measured value
Hysteresis
Cls (off)
Opn (on)
Alarm setting
Measured value
Measured value
Temperature setpoint
Hysteresis
Deviation setting
Opn (on)
Cls (off)
The output contact is opened in the following events:
• Program error
• ROM error
• RAM error
• power failure
External contact
(TMR) Opn
Opn
(off)
Opn
Opn
(off)
Cls (on)
Timer setting
Time
The output contact closes when the timer setting has passed
since external contact was closed. Then, the output contact
opens immediately when external contact is opened.
External contact
(TMR) Opn
Cls (off)
Opn
Cls
(off)
Opn (on)
Timer setting
Time
The output contact opens when the timer setting has passed
since the contact was closed. Then, the output contact closes
immediately when external contact is opened.
The controller starts measuring the current from
the heater disconnection detector when 100
milliseconds have passed after turning on the
output.
Cls
Cls
(on)
Heater current
Alarm setting
Opn (off)
Abnormal
Alarm output = ON
Normal
Low limit alarm
setpoint
In this area, the alarm output is turned
off even when a measured value falls
below the low limit alarm setpoint.
Time
Power-on
°
C
Taken as
normal.
Waiting action
Cls
Blinking
• A/D converter error
• RJC error
• EEPROM error
Blinking
Alarm type
Alarm
type code
Closed contact
during alarm
Open contact
during alarm
■
Alarm Function List
Action
“Opn” and “Cls” indicate that the relay contact is
opened and closed; “(on)” and “(off)” indicate that
the lamp is on and off; and white triangles indicate
temperature control setpoints.
Alarm
type code
Closed contact
during alarm
Open contact
during alarm
Action
“Opn” and “Cls” indicate that the relay contact is
opened and closed; “(on)” and “(off)” indicate that
the lamp is on and off; and white triangles indicate
temperature control setpoints.
Alarm type
(SP value display)
Target
setpoint
Minimum value (SPL) to maximum value (SPH) of target setpoint range
Unit:
°
C/
°
F
SPL
CTL
Control mode
ONF(0): On/off control
PID(1): PID control
SLF(2): Dynamic auto tune control (cannot be set for heating/cooling control)
SLF(2) :for standard type;
PID(1) : for
heating/cooling type
AT
Auto-tuning
OFF(0): Stop auto-tuning
ON(1): Start auto-tuning
OFF(0)
P
Proportional
band
1
°
C/
°
F to the temperature that corresponds to 100% of the
measured input range (scale) span
5% of measured
input range (scale)
span
I
Integral time
1 to 3600 seconds;
OFF(0): no integral action
240 seconds
D
Derivative
time
1 to 3600 seconds;
OFF(0): no derivative action
60 seconds
MR
Manual reset
–100 to 100%
50.0% for standard type;
0.0% for
heating/cooling type
COL
Cooling-side
gain
0.01 to 9.99 times
1.00 times
DB
Deadband
0% of measured
input range (scale)
span
HYS
Hysteresis for
on/off control
0
°
C/
°
F to the temperature that corresponds to 100% of the
measured input range (scale) span
0.5% of measured
input range (scale)
span
CT
Control output
cycle time
1 to 240 seconds
30 seconds
CTC
Cooling-side
control output
cycle time
1 to 240 seconds
30 seconds
SP1
Target
setpoint 1
Minimum value (SPL) to maximum value (SPH) of target
setpoint range
Unit:
°
C/
°
F
There are also optional engineering units for voltage input.
SPL
SP2
Target
setpoint 2
SPL
FL
PV input filter
OFF(0), 1 to 120 seconds
OFF(0)
BS
PV input bias
–100 to 100% of measured input range (scale) span
0% of measured
input range (scale)
span
LOC
Key lock
T1
Timer
setting 1
0.0 to 99.59
Unit: minutes and seconds or hours and minutes
Set the timer time unit using parameter TTU.
For example, 15.25 sets 15 minutes and 25 seconds.
(T1 is for AL1, and T2 is for AL2)
0.00
T2
Timer
setting 2
0.00
(2) Operating Parameters : Parameters changed rather frequently during operation.
HC
Heater disconnection
current measured
value
“HC” is not a parameter to be set. The current value (0 to 80) of heater disconnection
detector is displayed. Unit: A (ampere)
Settings: When the display value is – – – –, the heater current is not being measured.
A1
Alarm 1
setpoint
Max. value of
measured input range
(scale) (PV alarm)
A2
Alarm 2
setpoint
Min. value of
measured input range
(scale) (PV alarm)
IN
Measured
input type
1 to 23, 31 to 48 (See input range code list.)
OFF(0): No input
(If no input type is specified at the time of ordering, you must set the input type.)
OFF(0), or the input
range code specified
with order
DP
Decimal point
position of
measured input
0: No decimal place (nnnn)
1: One decimal place (nnn.n)
2: Two decimal places (nn.nn)
3: Three decimal places (n.nnn)
1
RH
Maximum value
of measured
input scale
(RL + 1) to 9999
100.0
RL
Minimum value
of measured
input scale
–1999 to (RH –1)
0.0
SPH
Maximum value
of target setpoint
range
(SPL+1
°
C) to the maximum value of the measured input range
(scale) ; Unit:
°
C/
°
F
Maximum value of
measured input
range (scale)
SPL
Minimum value
of target setpoint
range
Minimum value of measured input range (scale) to (SPH –1
°
C)
Unit:
°
C/
°
F
Minimum value of
measured input
range (scale)
UPR
Setpoint ramp-
up-rate
OFF(0)
or a value from the minimum to the maximum value of the
measured input range (scale)
Unit:
°
C/min or
°
C/hour,
°
F/min or
°
F/hour
Set the ramp-rate time unit using parameter TMU.
OFF(0)
DNR
Setpoint ramp-
down-rate
OFF(0)
AL1
Alarm 1 type
OFF(0) or a value from 1 to 22 (see the table of alarm function
list), and either
23 or 24 (if the timer function [/EX option] is included), and
25 (if the heater disconnection function [/HBA option] is included)
1
(PV high limit alarm)
AL2
Alarm 2 type
OFF(0) or a value from 1 to 22 (see the table of alarm function
list), and either
23 or 24 (if the timer function [/EX option]) is included)
2
(PV low limit alarm)
HY1
Alarm 1
hysteresis
0 to 100% of measured input range (scale) span
Unit:
°
C/
°
F
0.5% of measured
input range (scale)
span
HY2
Alarm 2
hysteresis
SC
SUPER
function
ON(1): Uses the SUPER function
OFF(0): Does not use SUPER function
Note: Not displayed when on/off control
OFF(0)
DR
Direct/reverse
action
0: Reverse action
1: Direct action
Note: Not displayed for heating/cooling type
0
ADR
Controller
address
1 to 99
However, the number of controllers that can be connected per
host device is 31 at the maximum.
1
BPS
Baud rate
2.4(0): 2400 bps
4.8(1): 4800 bps
9.6(2): 9600 bps
9.6(2)
PRI
Parity
NON(0): Disabled
EVN(1); Even parity
ODD(2): Odd parity
EVN(1)
STP
Stop bit
1 or 2 bits
1 bit
DLN
Data length
7 or 8 bits
• 8 bits when ladder, MODBUS (RTU)
• 7 bits when MODBUS (ASCII)
8 bits
PSL
Protocol
selection
0: PC-link communication
1: PC-link communication with sum check
2: Ladder communication
3: MODBUS in ASCII mode
4: MODBUS in RTU mode
0
(3) Setup Parameters : Parameters rarely changed in normal use after once having been set.
0: No key lock
1: Prevents operations from being changed except for the
changing of SP in the operating display
2: Prevents all parameter changing operations
–1: Set
⬙
-1
⬙
to enter the setup parameter setting display.
But if
⬙
LOC=1 or 2
⬙
is already set, the parameter value can
not be changed by setting
⬙
LOC=-1
⬙
only. To change the
parameter value, set
⬙
LOC=0
⬙
at first (for disabling keylock),
then set
⬙
LOC=-1
⬙
once again.
0
TMU
Setpoint ramp-
rate time unit
0 :
°
C or
°
F / hour
1 :
°
C or
°
F / min
1
DIS
EOT
TTU
RTH
RTL
External Contact Inputs
21
22
23
SP2
STOP
TMR
STOP
COM
TMR
STOP
SP2
STOP
Parameter DIS
0
1
2
SP1/SP2
switching
SP2
when DI=ON
Timer starts
when DI=ON
Timer stops
when DI=OFF
Timer starts
when DI=ON
Timer stops
when DI=OFF
RUN/STOP
switching
STOP
when DI=ON
SP1/SP2
switching
SP2
when DI=ON
RUN/STOP
switching
STOP
when DI=ON
3
4
5
UT150 UT152
UT155
DI-function
selection
Output in STOP
mode
Timer time unit
Maximum value
of retransmission
output
Minimum value
of retransmission
output
In STOP mode by contact input, fixed control output can be
generated.
0 : 0%, 1 : 100%
0 : hour.minute
1 : minute.second
(Displayed at voltage input)
(Displayed at voltage input)
(Displayed at voltage input)
Temperature input : Within measured input range
Voltage input : RTL+1digit to max. value of measured input
(scale)(RH)
Min. value of measured input (scale)(RL) to RTH-1digit
However, RTL<RTH
Maximum value of
measured input range
(scale)
Minimum value of
measured input range
(scale)
0
0
1
■
Parameter Lists
(1) Target Setpoint (SP) and Timer Setting 1 and 2
Code
Name
Setting range and unit
Default
User setting
Code
Setting range and unit
Default
User setting
Code
Name
Setting range and unit
Default
User setting
■
PV alarm Unit:
°
C/
°
F
Setting range: minimum value to maximum value of
measured input range (scale)
■
Deviation alarm Unit:
°
C/
°
F
Setting range: –100 to 100% of the measured input range (scale) span
■
Heater disconnection alarm Unit: A (ampere)
Setting range: OFF(0), 1 to 80
(can be set for the alarm 1 setpoint only)
■
PID control Unit:
°
C/
°
F
Setting range: –(proportional band setting) to +(proportional band setting)
■
On/off control Unit:
°
C/
°
F
Setting range: –50 to +50% of measured input range (scale)span
Name
Numbers in ( ) are the parmeter setpoints that apply when the
communication function is used. Ex. OFF(0), ON(1)
■
What is Dynamic Auto Tune Control?
Dynamic auto tune control is one of the features offered by the temperature controller.
When the controller is turned on or the measured input value (PV) starts “hunting”, this mode of control monitors
the behavior of the PV and/or OUT (control output value) to automatically determine the optimum PID constants.
This means that the PID constants may be changed automatically. If this is not desirable for your system, operate the
controller in the normal “PID control”.
If you want to automatically determine the PID constants at the initial startup of the controller, first define the target
setpoint (SP) and then turn the controller off once and then back on again. Do not use dynamic auto tune control for
a system where there is interference or continual disturbances.
■
Description of Parameters
This section describes the parameter functions specific to the UT150/UT152/UT155 temperature controllers.
(The functions described in other sections of this manual and the general functions are not discussed.)
Parameter
Function
Parameter
Function
Control mode
CTL
Select one from the following:
a. Dynamic auto tune control (SLF)
(See note)
b. PID control (PID)
c. On/off control (ONF)
Note: Dynamic auto tune control is not available
for heating/cooling control.
Read the section below this table to find out more
about dynamic auto tune control.
PV input bias
BS
This function adds a bias value to the measured input value,
and the result is used for display and control computation.
This function is useful for carrying out fine adjustment when
the PV value is within the required accuracy but it differs
from the value obtained by other equipment.
Manual reset
MR
You can set this parameter only for control
without an integral action (when registered as
CTL=PID and I=OFF). The controller outputs the
manual reset (MR) value when PV=SP. For
example, if you set MR=50%, the controller
outputs (OUT) 50% when PV=SP.
Cooling-side
gain
COL
Maximum/minimum
value of measured
input scale
RH,
RL
For heating/cooling control, you can set the ratio
between the cooling-side output and heating-side
output.
For example, if you set COL=2.0 and the heating-
side output is 10% at a certain deviation (SP-PV),
then the cooling-side output will be 20% when the
cooling-side also reaches that deviation.
Deadband
DB
You can only set a deadband for heating/cooling
control. In a positive deadband, there are neither
heating-side nor cooling-side outputs. In a
negative deadband, there are both heating-side and
cooling-side outputs, which overlap each other.
Maximum/minimum
value of
target setpoint range
SPH,
SPL
Using the SPH and SPL parameters, you can limit
the setting range of the target setpoint (SP) within
the measured input range(scale).
This function prevents SP from being mistakenly
set at too large or too small a value (beyond the
setting range).
Hysteresis for
on/off control
HYS
For on/off control (CTL=ONF), you can set a
hysteresis around the on/off point (SP) to prevent
chattering.
Setpoint ramp
up/ramp-down
rate
UPR,
DNR
To prevent a sudden change in SP, or to change SP at a
constant rate, ramp-up and ramp-down rates can be set
separately. This function operates at the following events.
a. SP change
b. SP1/SP2 switching
c. Power-on
At power-on, SP starts from
the current PV value.
Set the ramp-rate time unit using parameter TMU.
The cycle time is the period of on/off repetitions
of a relay or voltage pulse output in time
proportional PID control. The ratio of the ON time
to the cycle time is proportional to the control
output value.
Hysteresis for
alarm 1 and 2
HY1,
HY2
The alarms are output as relay outputs. Since a
relay has a limited life, excessive on/off actions
will shorten the life of the alarm. To prevent this,
you can set a hysteresis to prevent excessive
on/off actions for both alarm 1 and alarm 2.
PV input filter
FL
This function should be used when the PV display value
may fluctuate greatly, for example, when the measured
input signal contains noise. The filter is of the first-
order lag type, and FL sets the time constant. If a larger
time constant is set, the filter can remove more noise.
SUPER
function
selection
SC
The SUPER function is effective in the following cases:
a. An overshoot must be suppressed.
b. The rise-up time needs to be shortened.
c. The load often varies.
d. SP is changed frequently.
Note 1: The SUPER function will not work when
on/off control is selected, or I or D
constants is set at OFF in PID control.
Note 2: For some types of systems, the SUPER
function may not be so useful. If this is
the case, turn off the function.
Decimal point
of measurement
input
DP
For DC voltage input, the input signal can be scaled for the
particular engineering unit. For example, if you set the input
type (IN) at range code 22, the initial range is 0.0 to 100.0.
a. Using DP, set the decimal point position fit for the
engineering unit you want to use. (In the example below,
the 2 digits to the right of the decimal point)
b. Next, register the scale values of the measured input scale using
RH and RL. (In the example below, RH=10.00 and RL=0.00)
Initial scale
100.0 (5V)
0.0 (1V)
10.00 (RH)
0.00 (RL)
Measured input scale
(after being scaled)
Register the decimal point position using DP.
On/off point (SP)
Hysteresis
ON
OFF
Cycle time
t ON
t OFF
Input
HYS
HYS
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Deadband
DB (+)
Deadband
DB (+)
0
SP
PV
100%
100
0
SP
100
PV
100%
Cooling
side
Heating
side
100%
0%
1. When the deadband of a heating/
cooling type is positive
(Proportional band [P] control)
2. When both the heating and cooling
sides are under on-off control
PV value inside the controller
measured input value
PV bias
+
=
Ramp-rate
for n
°
C/min.
or n
°
C/h.
Control output
/ cooling-side
control output
cycle time
CT
CTC
2-seconds filter
10-seconds filter






















