YASKAWA
TOEPYAIGA8002B GA800 Drive Programming
427
A pulse train signal with a maximum frequency of 32 kHz can be output from the drive output terminal MP as the
monitor value. Sinking mode and sourcing mode are supported.
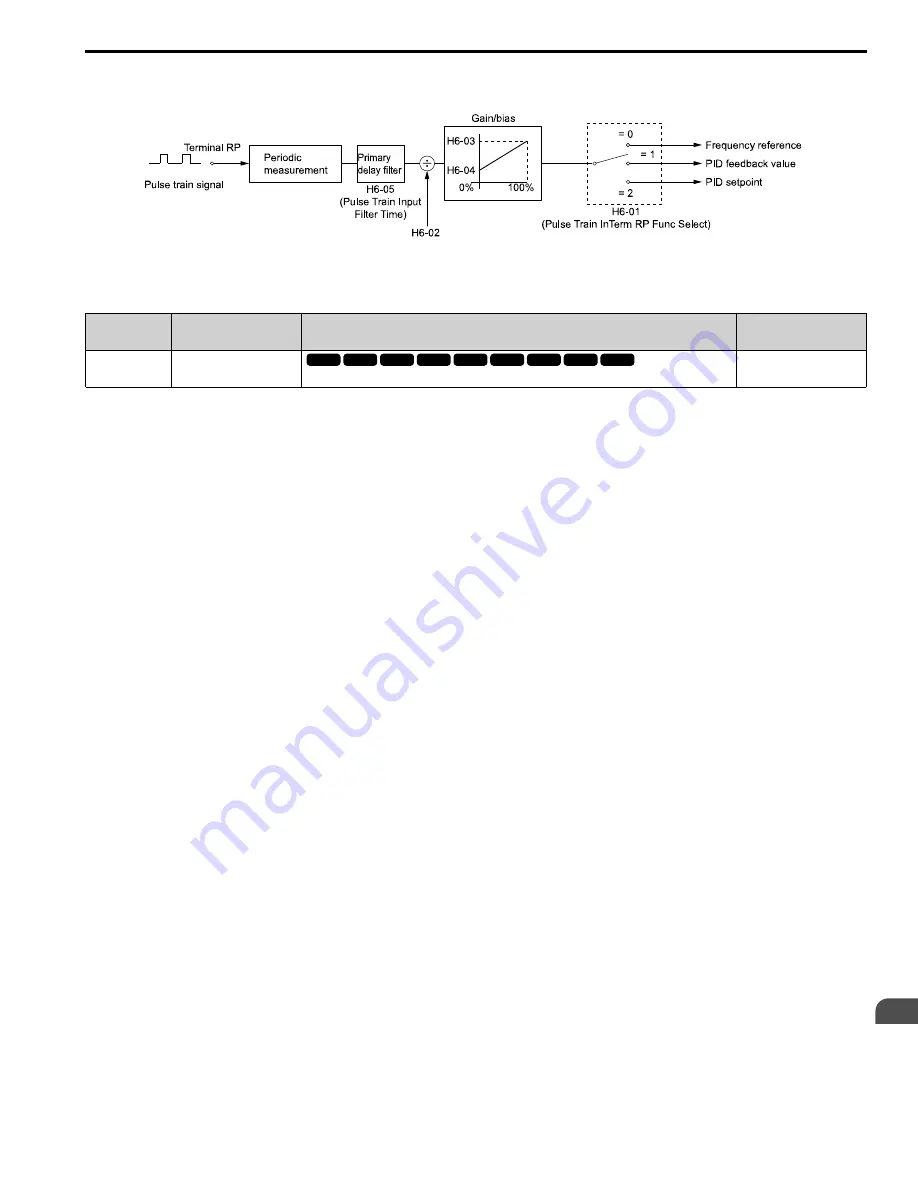
Figure 2.113 Pulse Train Input Block Diagram
■
H6-01: Terminal RP Pulse Train Function
No.
(Hex.)
Name
Description
Default
(Range)
H6-01
(042C)
Terminal RP Pulse Train
Function
Sets the function for pulse train input terminal RP.
0
(0 - 3)
0 : Frequency Reference
When
b1-01 [Frequency Reference Selection 1]
or
b1-15 [Frequency Reference Selection 2]
=
4 [Pulse Train Input]
,
the drive inputs the frequency reference received from terminal RP.
1 : PID Feedback Value
The drive inputs the PID control feedback value received from terminal RP.
2 : PID Setpoint Value
The drive inputs the PID control target value received from terminal RP.
3 : Speed Feedback (V/F Control)
Select V/f Control method to enable simple encoder feedback.
Use motor speed feedback for better speed control precision. The drive compares the frequency reference to the motor
speed feedback received from the encoder, and uses the ASR function to compensates for motor slip. You cannot use
input terminal RP used for the simple encoder to detect the direction of motor rotation. Use a different method to
detect motor rotation.
Use these methods to detect the direction of motor rotation.
•
Use MFDI
Set MFDI
H1-xx = 7E [Reverse Rotation Identifier]
. When the configured terminal is activated, the motor operates
in Reverse run. When the terminal is deactivated, the motor operates in Forward run.
Use an encoder that outputs 2-tracks (phase A, B) to detect the direction of motor rotation.
•
Use the frequency reference
When the you do not use the MFDI, the Forward/Reverse run command is the same as the direction of motor
rotation.
shows speed control in Simple Closed Loop V/f Mode.
V/f
CL-V/f
OLV
CLV
AOLV
OLV/PM
OLV/PM AOLV/PM CLV/PM
EZOLV
















































