XEROX WorkCentre
5735/5740/5745/5755/5765/5775/5790
Information Assurance Disclosure Paper
Ver. 2.00, March 2011
Page
22 of 50
3.
System Access
3.1.
Authentication Model
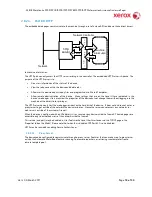
The authentication model allows for both local and network authentication and authorization. In the
local and network cases, authentication and authorization take place as separate processes: a user must
be authenticated before being authorized to use the services of the device.
If the device is set for local authentication, user account information will be kept in a local accounts
database (see the discussion in Chapter 4 of Xerox Standard Accounting) and the authentication process
will take place locally. The system administrator can assign authorization privileges on a per user basis.
User access to services will be provided based on the privileges set for each user in the local accounts
database. .
When the device is set for network authentication, the user’s network credentials will be used to
authenticate the user at the network domain controller.
Users can be authorized on an individual basis to access one or any combination of the following services:
Copy, Fax, Server Fax, Reprint Saved Jobs, Email, Internet Fax, Workflow Scanning Server.
Also users can be authorized to access one or any combination of the following machine pathways:
Services, Job Status, or Machine Status.
Assignment of users to the System Administrator role or the Accounting Administrator is managed by
groups set up at the LDAP or Active Directory server. Any user listed in the System Administrator group
will be granted sys admin privileges at the device. Likewise any user listed in the Accounting
Administrator group will be granted the privileges for that role. Use of network credentials for system
administrator login provides more security than the legacy model based on a sys admin PIN, allowing for
better tracking of sys admin logins by individual users.
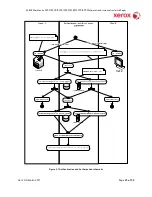
Figure 3-1 provides a schematic view of the authentication and authorization subsystem. Use of the local
accounts database or the network can be set independently for both authentication and authorization,
meaning that it is possible to enable network authentication and local authorization, or vice versa.
Usually the device will be set for both authentication and authorization to take place against the same
database, either local or network.