AM 320-01-808
8
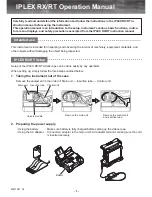
Fig. 2: Block diagram of a slave processor
2. The Slave Processor (5L5)
The slaves can be thought of as digital
sound generators. Each SL5 board can
produce 4 sounds, each consisting of two
sound components; the organ can be
equipped with a total of 8 slave boards.
The slave receives its information from
the master via the 2-port RAM, located on
the slave. According to the
information it receives from the master, the
slave then produces the sounds. The output of
the sounds is done automatically by the timer,
the DMA controller and the slave CPU after
the CPU has made the correct timer and
DMA settings. The CPU is responsible only
for the amplitude envelope for the 8
components. Each of the B Digital to Analog
Converters (DAC) receives an envelope
voltage. The Audio signal, after being
produced by the DAC, can then be routed to
one of the 5 output channels by the
"crosspoint matrix."
Summary of Contents for CD 600
Page 1: ...AM 320 01 808 1 assembly manual Technical Data CD 600 700 800 900 AM 320 1st Edition ...
Page 2: ...AM 320 01 808 2 ...
Page 4: ...AM 320 01 808 4 ...
Page 7: ...AM 320 01 808 7 Block Diagram CD Series ...
Page 12: ...AM 320 01 808 12 Backplane board MB4O edge connector pin layout view from back of card rack ...
Page 13: ...AM 320 01 808 13 MB4O Male connector pin layout ...
Page 14: ...AM 320 01 808 14 MB4O Component layout ...
Page 15: ...AM 320 01 808 15 MB4O Schematic diagram ...
Page 17: ...AM 320 01 808 17 MST8 Component layout ...
Page 18: ...AM 320 01 808 18 MST8 Schematic diagram ...
Page 19: ...AM 320 01 808 19 ...
Page 21: ...AM 320 01 808 21 5L5 Component layout ...
Page 22: ...AM 320 01 808 22 SL5 Schematic diagram ...
Page 23: ...AM 320 01 808 23 ...
Page 25: ...AM 320 01 808 25 C0l Component layout ...
Page 26: ...AM 320 01 808 26 C0l Schematic diagram ...
Page 27: ...AM 320 01 808 27 ...
Page 30: ...AM 320 01 808 30 ...
Page 31: ...AM 320 01 808 31 ...
Page 33: ...AM 320 01 808 33 DH11 Component layout ...
Page 34: ...AM 320 01 808 34 DH 11 Schematic diagram ...
Page 35: ...AM 320 01 808 35 ...
Page 37: ...AM 320 01 808 37 DH 100 Component layout ...
Page 38: ...AM 320 01 808 38 ...
Page 39: ...AM 320 01 808 39 ...
Page 41: ...AM 320 01 808 41 IF 40 Component layout ...
Page 42: ...AM 320 01 808 42 ...
Page 43: ...AM 320 01 808 43 ...
Page 45: ...AM 320 01 808 45 EF 40 Component layout ...
Page 46: ...AM 320 01 808 46 ...
Page 47: ...AM 320 01 808 47 ...
Page 49: ...AM 320 01 808 49 WV 30 Component layout ...
Page 50: ...AM 320 01 808 50 ...
Page 51: ...AM 320 01 808 51 ...
Page 53: ...AM 320 01 808 53 AF 40 Component layout ...
Page 54: ...AM 320 01 808 54 ...
Page 55: ...AM 320 01 808 55 ...
Page 57: ...AM 320 01 808 57 pedal KD 11 Component layout ...
Page 58: ...AM 320 01 808 58 ...
Page 59: ...AM 320 01 808 59 ...
Page 60: ...AM 320 01 808 60 KD 11 b Schematic diagram ...
Page 61: ...AM 320 01 808 61 ...
Page 62: ...AM 320 01 808 62 KD 4 Schematic diagram ...
Page 63: ...AM 320 01 808 63 PK 40 Schematic diagram Pedalboard matrix ...
Page 65: ...AM 320 01 808 65 CB 41 Component layout ...
Page 66: ...AM 320 01 808 66 ...
Page 67: ...AM 320 01 808 67 ...
Page 68: ...AM 320 01 808 68 CB 42 Schematic diagram ...
Page 69: ...AM 320 01 808 69 ...
Page 70: ...AM 320 01 808 70 CB 43 Schematic diagram ...
Page 71: ...AM 320 01 808 71 ...
Page 73: ...AM 320 01 808 73 EM 1 Schematic diagram ...
Page 75: ...AM 320 01 808 75 ...
Page 76: ...AM 320 01 808 76 CB 40 Schematic diagram ...
Page 79: ...AM 320 01 808 79 CB 49 Schematic diagram ...
Page 80: ...AM 320 01 808 80 CB 44 Schematic diagram ...
Page 81: ...AM 320 01 808 81 ...
Page 84: ...AM 320 01 808 84 PS 21 Component layout ...
Page 85: ...AM 320 01 808 85 PS 21 Schematic diagram ...
Page 87: ...AM 320 01 808 87 CB 45 Component layout CB 46 Component layout ...
Page 88: ...AM 320 01 808 88 CB 45 Schematic diagram ...
Page 89: ...AM 320 01 808 89 CB 46 Schematic diagram ...
Page 92: ...AM 320 01 808 92 ...
Page 94: ...AM 320 01 808 94 ...
Page 95: ...AM 320 01 808 95 Power chassis NE 60 schematic diagram ...
Page 96: ...AM 320 01 808 96 Power Connections ...