Logical Command and Speed Reference
CFW300 | 7-13
7
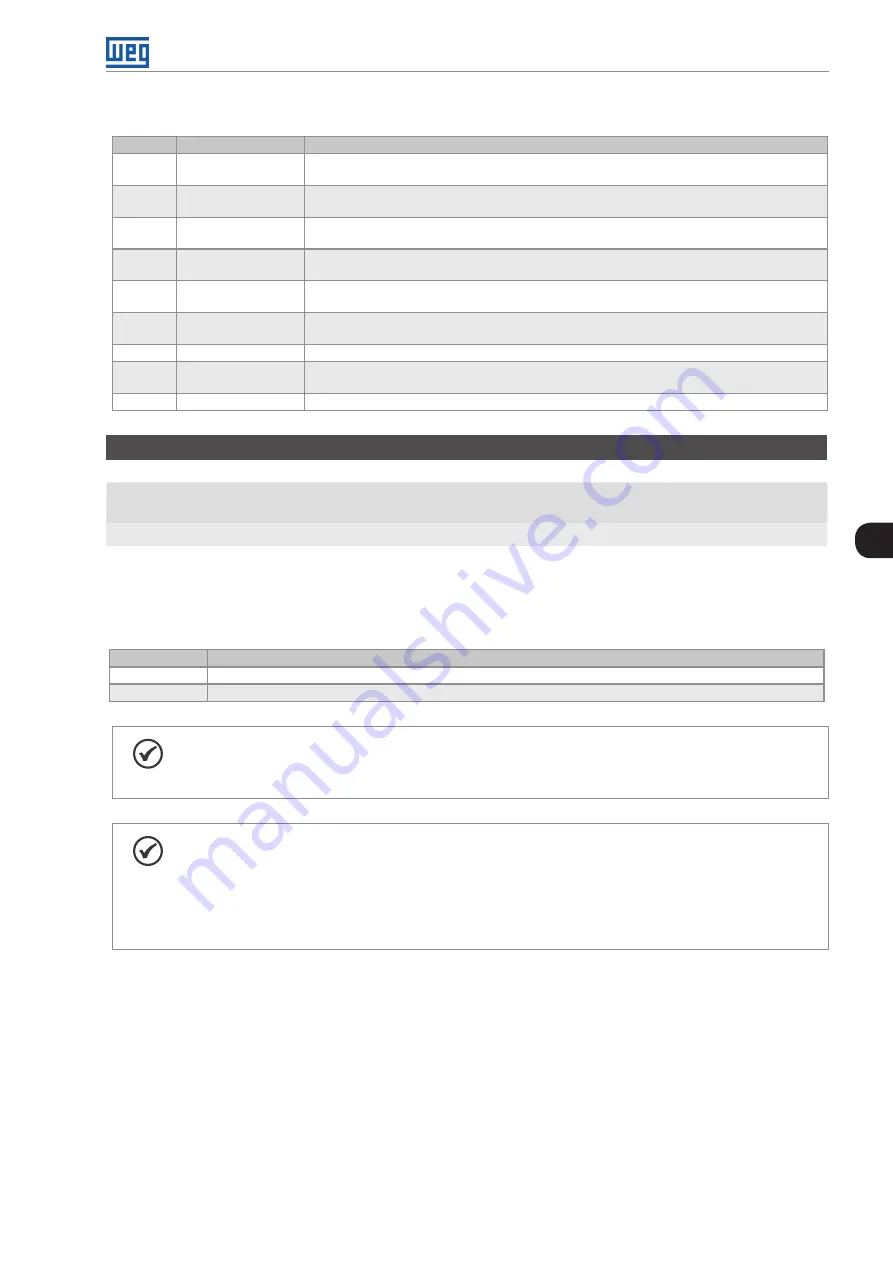
Table 7.5:
Control word
BIT
Function
Description
0
Ramp Enable
0:
stops the motor by deceleration ramp
1:
spins the motor according to the acceleration ramp until reaching the speed reference value
1
General Enable
0:
disables the inverter completely, interrupting the power supply to the motor
1:
enables the inverter completely, allowing the operation of the motor
2
Run Forward
0:
spins the motor in the opposite direction of the reference signal (reverse)
1:
spins the motor in the direction of the reference signal (forward)
3
Enable JOG
0:
disable JOG function
1:
enable JOG function
4
Remote
0:
inverter goes into Local mode
1:
inverter goes into Remote mode
5
2
nd
Ramp
0:
acceleration and deceleration ramp by P100 and P101
1:
acceleration and deceleration ramp by P102 and P103
6
Reserved
-
7
Fault Reset
0:
no function
1:
if in fault state, reset the fault
8 to 15
Reserved
-
P229 - Stop Mode
Adjustable
Range:
0 = Ramp to Stop
1 = Coast to Stop
Factory
Setting:
0
Properties:
cfg
Description:
This parameter defines the motor stop mode when the inverter receives the "Stop" command.
describes the options of this parameter.
Table 7.6:
Selection of stop mode
P229
Description
0
The inverter will apply the stop ramp programmed in P101 or P103
1
The motor will run free until it stops
NOTE!
When the Coast Stop mode is programmed and the Flying Start function is disabled, only activate
the motor if it is stopped.
NOTE!
This parameter is applied to all the inverter command sources, but it was created aiming at allowing
the command via HMI to be able to disable the motor by inertia instead of deceleration ramp. In this
way, when P229 = 1, Bit 0 of the control word (Ramp Enable) has a function similar to Bit 1 (General
Enable). The same way, the digital input functions such as: Run/Stop, Forward/Reverse Run stop
the motor by inertia in this condition of P229.
7.3.1 Control via HMI Inputs
Contrary to the network interfaces and SoftPLC, the HMI commands do not access the inverter control word
directly, because of limitations of key functions and HMI behavior. The HMI behavior is described in
HMI AND BASIC PROGRAMMING on page 4-1
.
7.3.2 Control via Digital Inputs
Contrary to the network interfaces and SoftPLC, the digital inputs do not access the inverter control word directly,
because there are several functions for DIx that are defined by the applications. Such digital input functions are
detailed in
Section 12.5 DIGITAL INPUTS on page 12-11
.
Summary of Contents for CFW300 V1.3X
Page 2: ......
Page 8: ...Contents...
Page 46: ...Identification of the Inverter Model and Accessories 6 4 CFW300 6...
Page 60: ...Logical Command and Speed Reference 7 14 CFW300 7...
Page 72: ...V f Scalar Control 9 10 CFW300 9...
Page 80: ...VVW Vector Control 10 8 CFW300 10...
Page 116: ...Digital and Analog Inputs and Outputs 12 24 CFW300 12...
Page 132: ...Reading Parameters 15 6 CFW300 15...






























