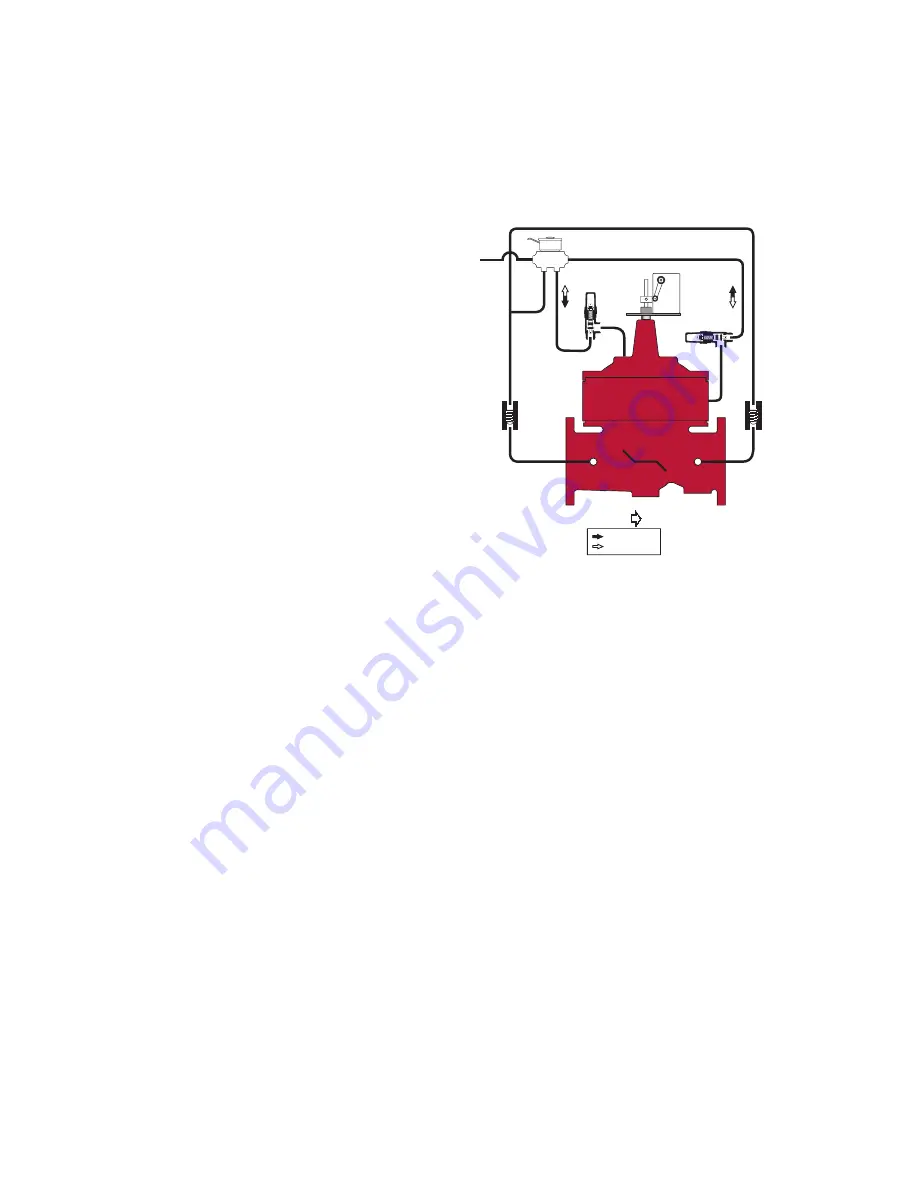
980-16GD (Globe) Pump Control Control Valve with Mechanical Check Feature
2 IOM-A-ACV-980-16_680-16 2115
EDP# 1917100
© 2021 Watts
Standard Components
1
X
3
6
3
2
X
X
Y/FC
Y/FC
4(L)
CLOSES VALVE
OPENS VALVE
FLOW
5
X
Installation
1. Prior to installation, flush line to remove debris.
2. Install valve so the flow arrow matches flow through the line, and gauges to monitor valve inlet and outlet pressures.
3. Install isolation valves upstream and downstream of the main valve.
4. Provide adequate clearance for valve servicing and maintenance. Refer to valve servicing dimensions on next page. Avoid installing
valves 6" and larger in the vertical position (main valve stem horizontal). Automatic Control Valves (ACVs) are designed for horizon-
tal in-line installation, with the cover facing up (main valve stem vertical). Slow operation or premature stem and guide wear may
occur if valve is not installed according to factory recommendations. Consult factory for detailed engineering review prior to order-
ing if valve is to be installed other than horizontally in-line.
5. If valve is equipped with a pilot control system, extra precautions should be made during installation to protect the piping circuit
from damage. Only remove the pilot control system from the valve if necessary. Tubing and fittings should be kept clean and
replaced exactly as removed. Consult appropriate hydraulic schematic to ensure proper re-assembly.
6. Connect solenoid wiring leads to desired switching device, using safe, standard electrical practices.
7. Wire the limit switch contacts to the proper relay connections, using safe, standard electrical practices. Adjust the limit switch collar
to the approximate make/break contact position.
8. After installation, vent entrapped air from valve cover and pilot system by following instructions on Technical Bulletin.
Start-up of an automatic control valve requires that proper procedures be followed. Time must be allowed for the valve to react to adjustments and the
system to stabilize. The objective is to bring the valve into service in a controlled manner to protect the system from damaging over-pressure.
Operation
The Pump Control Valve is designed to minimize the surges associ-
ated with the starting and stopping of pumps. The valve slowly opens
and closes as required to control pumping related surges. The pump
starts and stops against a closed valve.
Pump start up:
When the pump is signaled to start, the 4-Way
Solenoid is energized and directs fluid and pressure into the power
chamber (below the diaphragm), and relieves fluid and pressure from
the cover chamber (above the diaphragm). The fluid and pressure
relieved from the cover chamber is vented to atmosphere or available
floor drain. The valve opens at an adjustable rate, gradually admitting
pumping pressure into the distribution system. Rate of valve opening
is controlled by the adjustable opening speed control, which restricts
the speed at which fluid and pressure evacuate the cover chamber.
The valve remains fully open during the pumping cycle.
Pump shutdown:
When the pump is signaled to shut-off, the 4-Way
Solenoid is de-energized, and directs fluid and pressure into the cover
chamber (above the diaphragm), and relieves fluid and pressure from
the power chamber (below the diaphragm). The fluid and pressure
relieved from the power chamber is vented to atmosphere or available
floor drain. The valve closes at an adjustable rate, gradually reducing
pumping pressure. Rate of valve closure is controlled by the adjust-
able closing speed control, which restricts the speed at which fluid
and pressure evacuate the power chamber. When the valve reaches
the closed position, the limit switch is actuated, turning the pump off.
Emergency Closure:
The valve is equipped with a Mechanical Check
Feature, which acts independent of diaphragm position, and provides
immediate closure when flow ceases.
Manual Operation:
Engaging the Solenoid Manual operator simulates
power to the solenoid, manually opening the main valve. Disengaging
the Solenoid Manual operator returns the valve to the closed position.
1 – Main Valve (900GD-16 - Dual Chamber with Lift-Check)
2 – 4-Way Solenoid
3 – Check Valve
4 – Limit Switch
5 – Adjustable Opening Speed
6 – Adjustable Closing Speed
Y – Y-Strainer
X – Isolation Cocks






























