12
3.4
The Main Screen
When performing leak detection, one of the difficulties faced by
operators is how to identify and measure the sound made by a leak
when other interfering sounds are also present. The HL 5000
utilizes a feature called Dual Segment Analysis (DSA) to differentiate
between the two types of sounds. Leak sounds, when present, do
not change or go away; they are constant. Other sounds (wind
blowing, passing cars, dogs barking) within range of the microphone
will vary and show changes in volume and intensity or disappear
altogether. DSA allows the HL 5000
to analyze all the sounds
detected by the microphone and separate those sounds that are
constant and unchanging (like those caused by a water leak) from
those that are caused by elements of the surrounding environment.
The levels of each type of sound are then displayed by separate bar
graphs on the main screen.
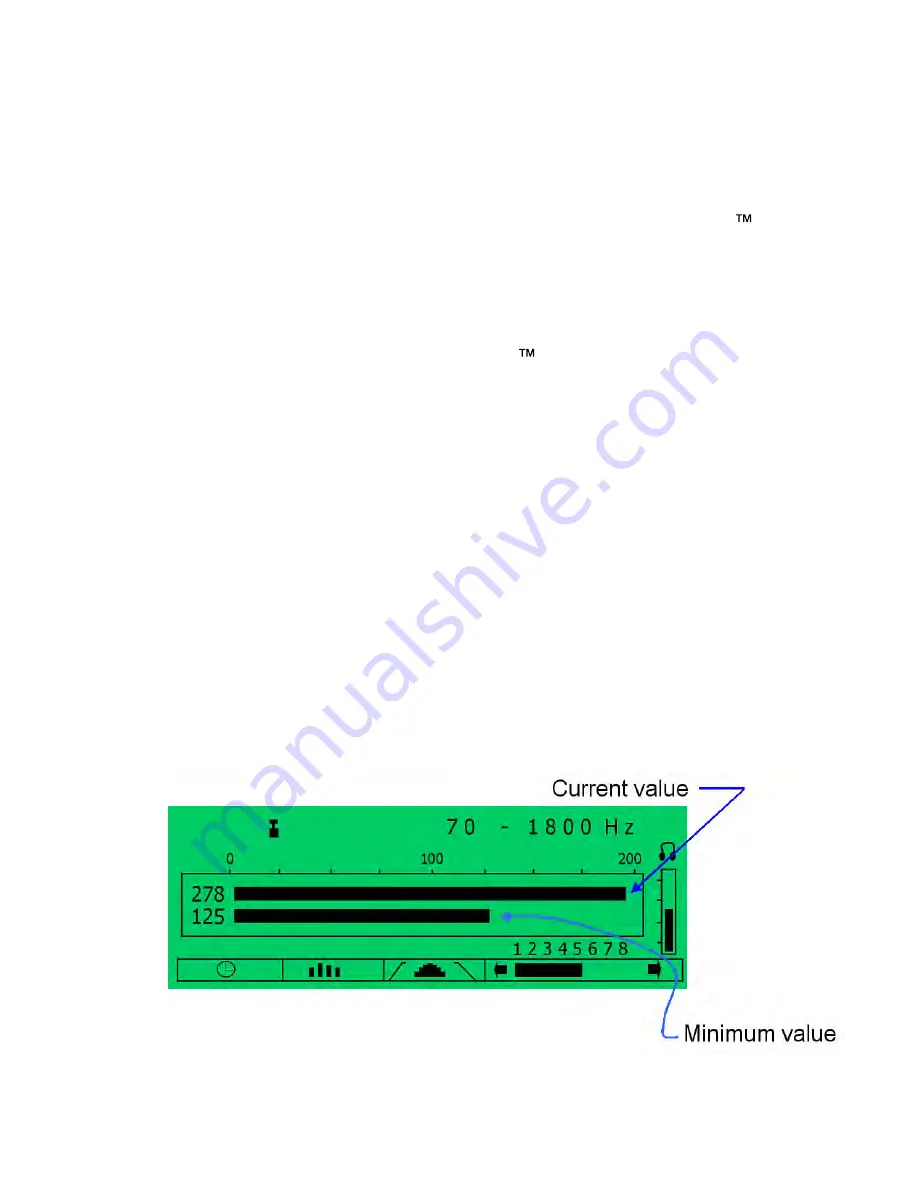
The Main Screen (Fig. 11) reveals both the current total sound
level (top bar) and the minimum constant leak sound level
(bottom bar) for all sound frequencies currently selected by the user
(see Section 3.5 on Filter Selection). Measurement of sound levels
takes place when the unit is on and the headphones are not muted.
When the headphones are muted, the unit is placed in stand-by
mode and the last measured sound levels remain displayed. When
the unit is returned to measurement mode (un-muted) the
measurement cycle begins again and any changes in the two sound
levels are re-calculated and displayed.
Fig 11 : Current Total and Minimum Leak Sound Values















































