DCSG
U
SER
’
S
M
ANUAL
©
2007
V
IDERE
D
ESIGN
14
additional amplification of the video signal, for low-light situations. It is
settable from 0 to 18 dB (1x to 8x).
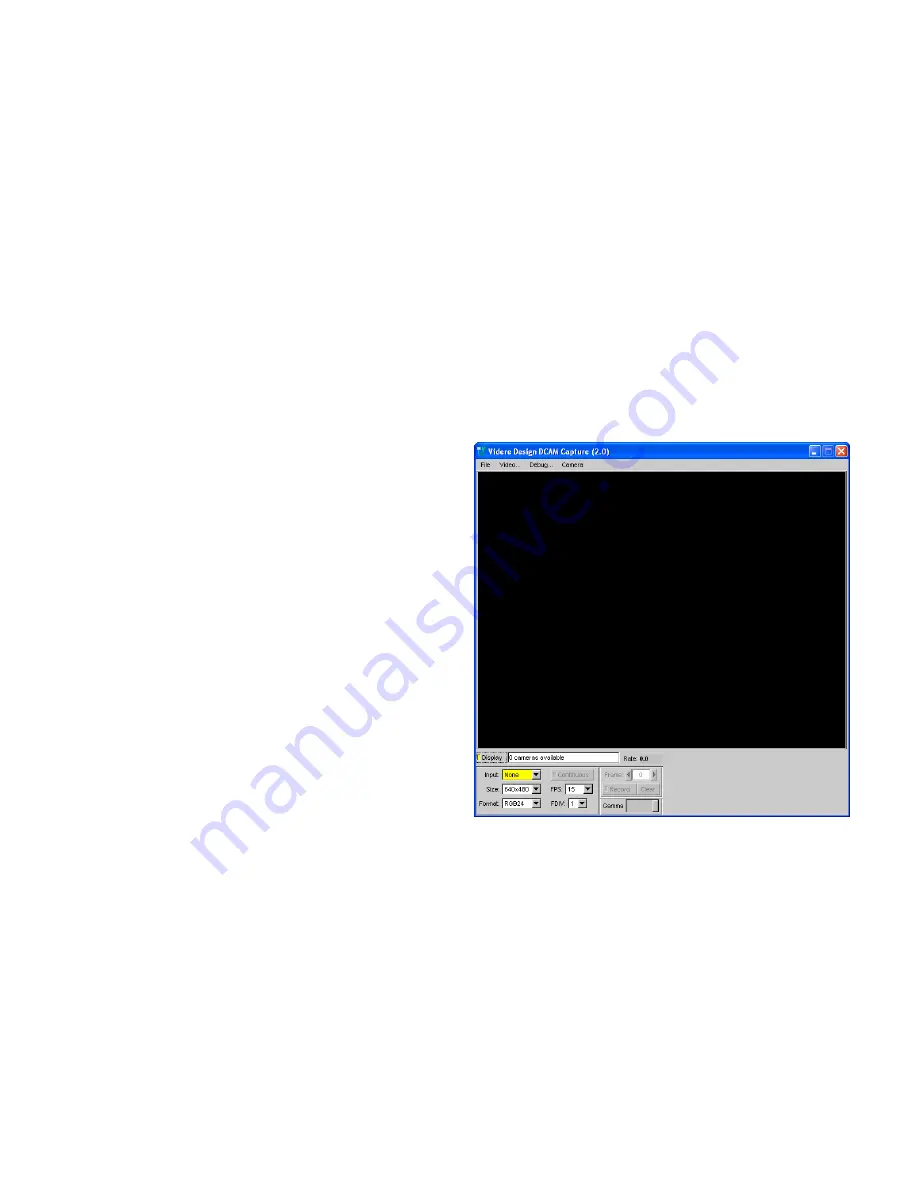
Digitization control can operate in either manual or automatic mode. Refer
to Figure 7-1 for the controls in the video capture program. Both manual
and automatic modes are available for the DCSG(-C) devices.
In manual mode, the user program sets the exposure and gain. The
exposure and gain are based on a 0 to 100 scale. Here are some tips for
setting exposure and gain.
•
In general, keep the gain as low as possible, since it introduces
additional noise into the system. Use it only if the exposure is set to
maximum, or if the exposure must be kept low to minimize motion
blur. Indoors, the gain is usually set higher because of the lower
light levels.
•
Adjust the manual iris of the lens to as small an opening as possible
for your application, without having to use gain. This will increase
the depth of field and give better optical performance. Indoors, the
iris usually is fully open. Outdoors, in bright conditions, the iris can
be partially closed.
There are automatic modes for both exposure and gain. In auto mode, gain
and exposure are controlled by the host PC, which samples the incoming
image and sends commands to the stereo device. The auto algorithm will
try to reduce gain as much as possible, while still maintaining overall light
levels in the image.
Auto mode for gain and exposure can be set separately. For the DCSG, it is
recommended to use a manual mode for gain, and auto mode for exposure.
Indoors, set the gain to a higher value; outdoors, set it to a low value. With
exposure in auto mode, the light on the image will be adjusted by changing
the exposure.
7.4 Subsampling
In many applications it is not necessary to work with the the full 640x480
image. The CMOS imagers are capable of sampling the pixels in the array.
Sampling allows the video stream to send less data, for faster frame rates or
less bus activity. A sampled image shows the same scene as the original
image, but it uses fewer pixels to do so, and has less detail.
Binning
is a subsampling technique in which several adjacent pixels are
averaged into one. Binning reduces video noise, sometimes quite
substantially. Binning is available on the host PC – the larger image is first
Figure 7-2 Frame size and sampling controls in the main capture window.





















