5. Operation
5.1
Operating Conditions
Motor operating requirements have been established in order to prevent increases in motor temperature.
The temperature of the motor increase when the frictional load or inertial load is high, and when the motor is operated
with frequent start/stops or changes of direction. It is important,therefore,to operate the motor in accordance with the
requirements given below. (See Catalogue for the rated torque,starting torque and the permissible inertia load.)
Note
The temperature of the motor's casing and the driver's rear panel should not exceed 90
℃
and 80
℃
, respectively.
If the driver's internal heat sink exceeds 90
℃
, the overheat protection function will be activated,
causing the motor to stop.
(1) Conditions for Continuous Operation
The load torque converted into the motor shaft should not exceed the rated torque.
(2) Inertial Load Conditions
The Inertial load (GD
2
) converted into the motor shaft should be no greater than the permissible load inertia.
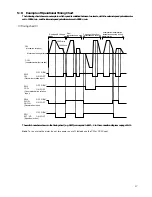
(3) Operating Patterns
When doing start/stops (instant stops) or direction reversals in short cycles, pay careful attention to motor and driver
temperature rises.
Note
To run or stop the motor, do not turn power on or off. Instead use the CW or CCW input.
5.2
Protection Functions
The
FBL
Ⅱ series has several protection functions.
When a protection function is activated, an alarm signal is output, the LED on the driver's front panel lights and the motor
comes to a natural stop. When an alarm signal is output, turn off power. To cancel the alarm, first resolve the cause and check for
safety, and then turn power on again. Once power has been turned off, wait at least 1 minute before turning it on again.
No alarm signal is output when the low-speed protection function activates, since the function adjusts the speed back to the
minimum or set speed.
16
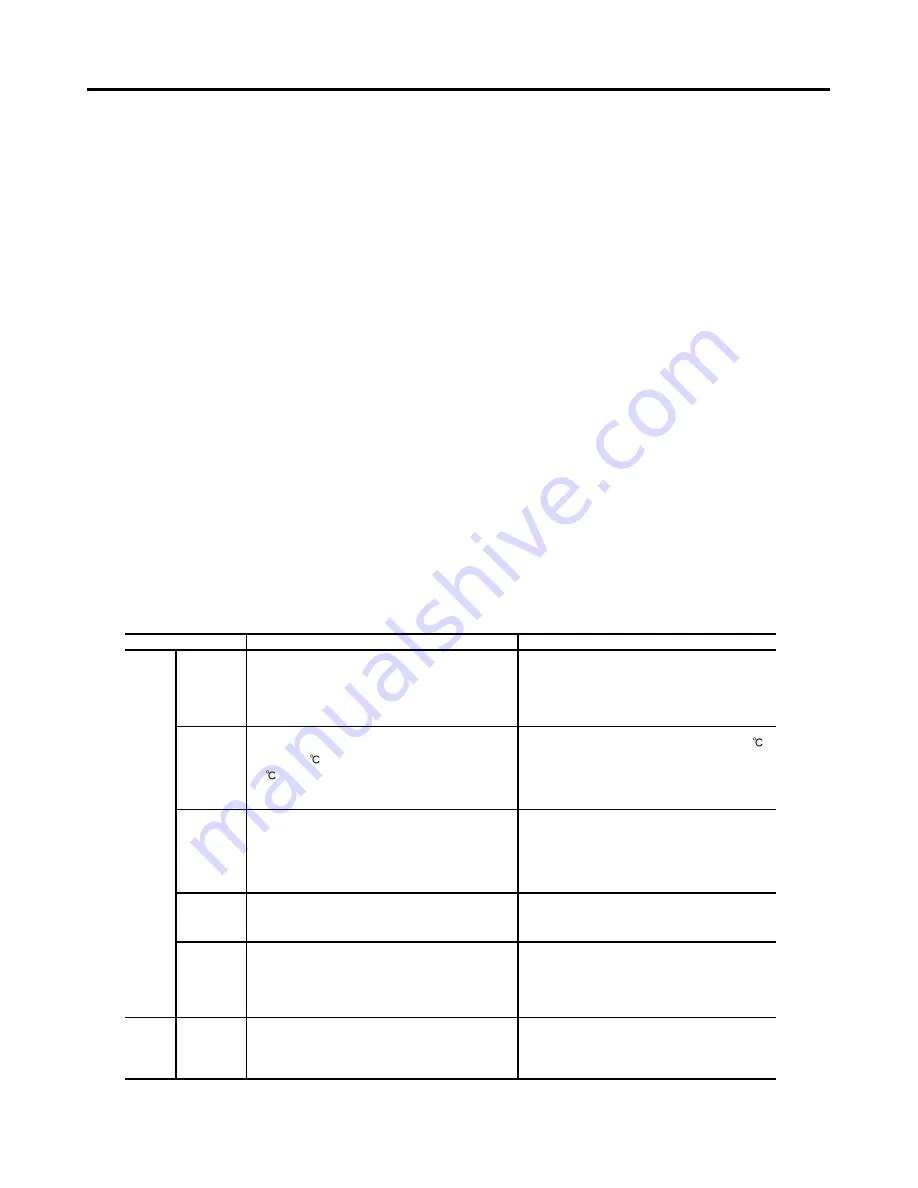
Alarm
Signal
Output
No Alarm
Signal
Output
Action
Activated when a load exceeding the rated torque
(load torque or motor current of 130% max. of rated
load or rated motor current) is applied to the motor for
5 seconds or more or when the motor is operated in
short cycles of stopping/starting or CW/CCW rotation.
Activated when the driver's ambient temperature
exceeds 50
, or when its internal heat sink exceeds
90
as a result of using short operating cycles of
starting/stopping or CW/CCW rotation.
Protects the driver against damage when the motor
is driving an inertial load exceeding the permissible
inertial load, or when the motor shaft is turned by the
load (during lowering operation).
Activated when a input voltage to the driver is less
than specified voltage.
Prevents motor malfunction when the sensor cable
within the motor cable is disconnected during motor
operation. (An alarm signal will not be output while
the motor is at a standstill.)
Activated when motor speed falls considerably below
the speed control range (less than 250r/min) due to
a reduction in the speed setting, an overload, etc.
Overload
protection
Overheating
protection
Overvoltage
protection
Under voltage
protection
Open-Phase
protection
Low-speed
Response
Check the load torque, referring to the load torque-
driver input current characteristics on page 21.
Reduce the load torque if it seems to exceed the
rated torque, or lengthen the operating cycle.
If the driver's ambient temperature exceeds 50
,
employ some cooling method to lower it; otherwise,
reduce the load torque or lengthen the operation
cycle.
Check to see that the inertial load does not exceed
the permissible value (see Catalogue) or that the
motor shaft is not being turned by the load.
Check to see that there is input voltage to the
driver.
Check to see that the motor cable has not been
disconnected.
Increase the speed setting to 300r/min or higher.
This function is not activated by an overload if
speed is above 300r/min.
Type of protection function