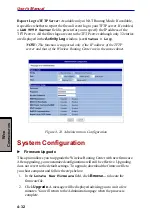
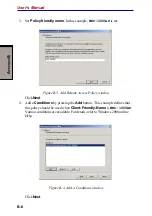
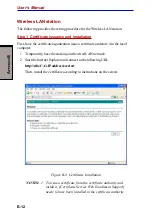
5-7
T
ROUBLESHOOTING
3. The following message, for example, indicates proper communica-
tion. Check the network settings of the computers.
C:\ping 192.168.10.100
Pinging 192.168.10.100 with 32 bytes of data
Reply from 192.168.10.100: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.10.100: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.10.100: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
Reply from 192.168.10.100: bytes=32 time<10ms TTL=128
4. The following message, for example, indicates improper commu-
nication. Check other items of Wireless LAN troubleshooting.
C:\ping 192.168.10.100
Pinging 192.168.10.100 with 32 bytes of data
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
Request timed out.
5. If you want to configure IP address, refer to the
section in Chapter 3, Setup, for more
information.
Application problems
Some network applications do not work.
Cause
The Wireless Routing Center uses NAT to convert the IP addresses and
port numbers in the headers of packets in communication between
LAN and WAN. Therefore, applications that use IP addresses and port
numbers kept in the data part of packets may not work as expected due
to differences between the packet header and packet data in terms of IP
addresses and port numbers.
Applications using a protocol other than TCP/UDP might not operate
properly due to non conversion of port numbers by NAT because there
is no port number in the header.
Remedy
These applications do not operate normally with the Wireless Routing
Center. If you know their port numbers, however, they might be usable
by registering the port numbers using Port Forwarding. For details, see
the
section in Chapter 4.
Application problems