6
Ion Optics and Detector Components
MP0 Ion Optics and Beam Blocker
24
TSQ Altis, Quantis, and Fortis Hardware Manual
Thermo Scientific
MP0 Ion Optics and Beam Blocker
The MP0 ion optics (
) transmits ions from the MP00 ion optics to the quadrupoles.
The multipole MP0 ion optics includes multipole MP0 and lenses EL11 and EL12. The
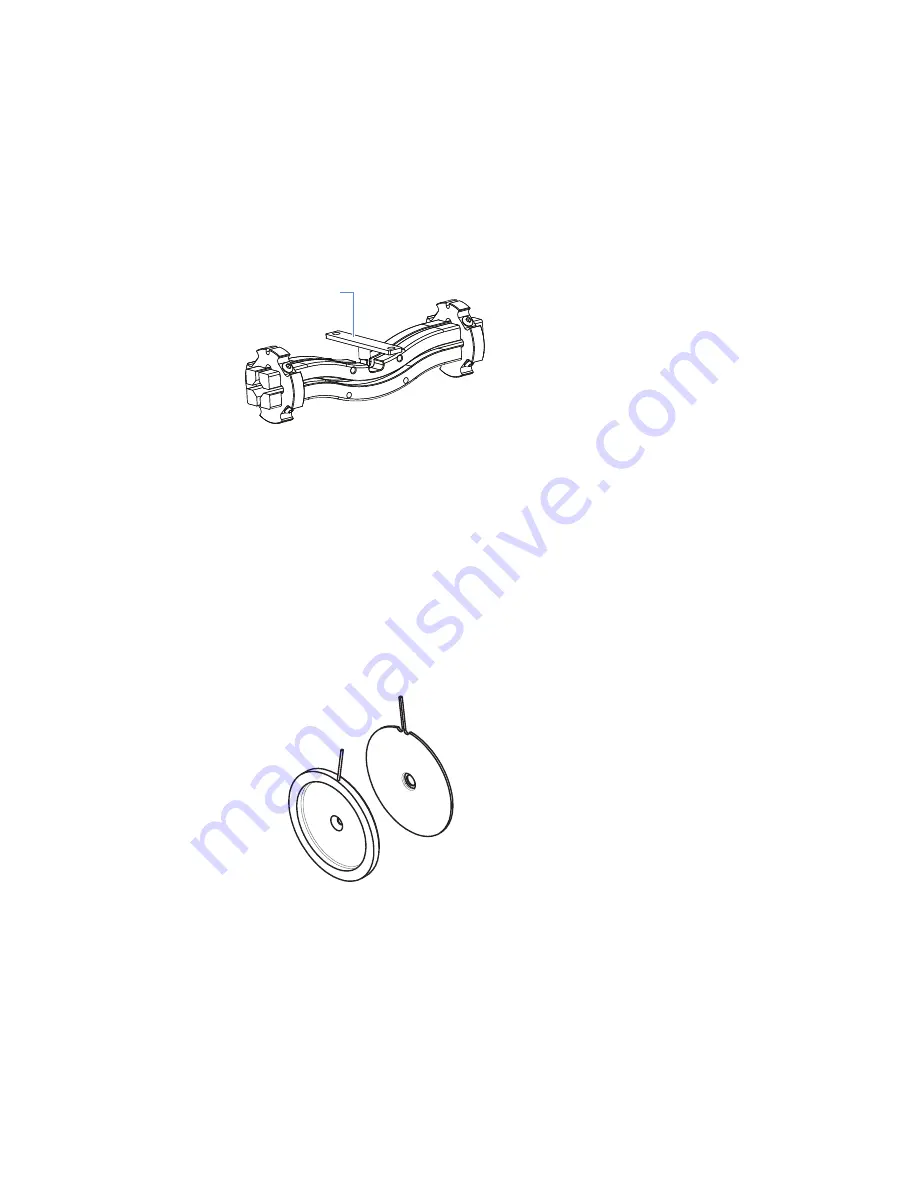
beam blocker (1 in
) is attached to the MP0 multipole.
Figure 14.
MP0 multipole with neutral beam blocker (1)
Multipole MP0 is an array of square-metal rods that transmit ions. The MS applies an RF
voltage to the elements to generate an electric field that guides the ions along the axis of the
multipole. The MP0 offset voltage increases the translational kinetic energy of the ions as they
leave MP00. The voltage causes the charged ions to follow the curve of the rods. Neutral
species do not follow the curve; instead, they strike the neutral beam blocker and are removed
from the beam.
The EL11 and EL12 lenses are metal disks with a circular hole in the center through which
the ion beams passes (
). They act as a two-element cone lens. The MS applies an
electrical potential to the lens to accelerate (or decelerate) ions as they approach each lens. The
EL11 and EL12 lenses are also a vacuum baffle between multipole MP0 and quadrupole Q1.
Figure 15.
EL11 (left) and EL12 (right) lenses
Dual-Mode, Discrete-Dynode Ion Detection System
The ion detection system includes a high-voltage conversion dynode (11 in
electron multiplier. Typically, the electron multiplier is set to a gain of about 5 × 10
5
(that is,
for each ion or electron that enters, 5 × 10
5
electrons exit) in MS mode and 2 × 10
6
in
MS/MS mode. The electrometer circuit converts the current that leaves the electron
multiplier through the anode to a voltage, and the data system records the voltage.
1






























