Chapter 2: Math, Angle, and Test Operations
36
Keyboard Math Operations
Using Lists with Math Operations
Math operations that are valid for lists return a list calculated element by element. If you use two
lists in the same expression, they must be the same length.
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication, Division
You can use + (addition,
Ã
),
N
(subtraction,
¹
),
…
(multiplication,
¯
), and
à
(division,
¥
) with real
and complex numbers, expressions, lists, and matrices. You cannot use
à
with matrices. If you
need to input A/2, enter this as A
†
1/2 or A
†
.5.
Trigonometric Functions
You can use the trigonometric (trig) functions (sine,
˜
; cosine,
™
; and tangent,
š
) with real
numbers, expressions, and lists. The current angle mode setting affects interpretation. For
example,
sin(30)
in radian mode returns
L
.9880316241; in degree mode it returns .5.
You can use the inverse trig functions (arcsine,
y ?
; arccosine,
y @
; and arctangent,
y A
) with real numbers, expressions, and lists. The current angle mode setting affects
interpretation.
Note:
The trig functions do not operate on complex numbers.
Power, Square, Square Root
You can use
^
(power,
›
),
2
(square,
¡
), and
‡
(
(square root,
y C
) with real and complex
numbers, expressions, lists, and matrices. You cannot use
‡
(
with matrices.
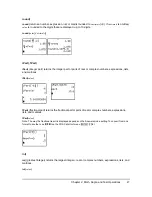
valueA
+
valueB
valueA
…
valueB
valueA
N
valueB
valueA
à
valueB
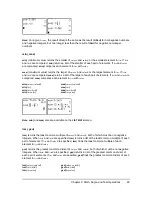
sin(
value
)
cos(
value
)
tan(
value
)
sin
L
1
(
value
)
cos
L
1
(
value
)
tan
L
1
(
value
)
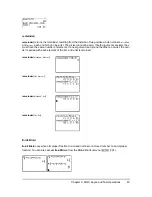
MathPrint™:
value
power
Classic:
value
^
power
È
value
2
‡
(
value
)
È