53
Earth Loop (Ground Loop): The result when the equipment sees more than one path to the system earth. Current flows because
a resistive loop susceptible to radio and mains interference is formed. In severe cases this can result
in audible hum or buzz in the system. Breaking the loop by removing all but one path to earth usually
solves the problem.
EQ (Equaliser):
This provides cut or boost of selected frequencies (equalisation) for tonal shaping of the sound.
Feedback:
Also known as ‘howlround’ or ‘ringing’, this is the rapidly increasing tone produced when a
microphone picks up its own signal from the speakers. It is usually a shrill and annoying squeal that
should be quickly dealt with by repositioning the microphone or speakers, reducing mic gain or
equalising the system to notch out the offending frequencies.
Gain:
This is the boost or attenuation applied to the source signal in the channel preamp stage to match it to
the console operating level. For example, a large amount of gain is needed to match low microphone
signals. It is set using the console meters. Gain is not used for level (volume) control.
Headroom:
The amount of level available expressed in dB to handle peaks above the normal 0dB operating level.
Hz (Hertz):
The measurement of frequency. The audio spectrum ranges from a low (bass) frequency of 20Hz to a
high (treble) 20kHz.
Highpass filter (HPF):
A filter that attenuates frequencies below the cut-off frequency.
Hum:
This is the audible noise that usually results from mains interference pickup, earth loops, bad
interconnections and induced power supply and lighting fields. It is usually at mains frequency (50/
60Hz) or a related harmonic.
Impedance:
A technical term for the resistance of a signal conductor to ground. Low impedance (Low Z) usually
refers to microphones of 200 ohms or less, and line signals typically less than 100 ohms. Low Z
sources are less prone to interference pickup. Inputs are usually high impedance (High Z) so that one
source can connect to more than one channel without signal loss. Note that the operating impedance
of a connection is set by the impedance of the source, not that of the unconnected input.
Limiter:
A signal processor that limits the maximum level possible by preventing the signal going over a
predetermined threshold level. This is very useful in club installations where it is inserted between the
console and house system amplifiers to prevent the DJ exceeding the maximum allowable volume.
Lowpass filter (LPF):
A filter that attenuates frequencies above the cut-off frequency.
Mono:
A single source with no stereo content, or the left and right stereo signals summed together as one.
Mono Sum:
A mono signal which is the sum of the left and right parts of a stereo pair.
Mute (Cut):
To turn off the signal. Transform is a mute, or cut effect.
Noise:
Generic term for an unwanted signal. This may be residual electronic hiss, hum, buzz, clicks and
pops.
Noise Floor:
This is the term for the residual electronic noise produced by all powered audio equipment. It usually
sounds like a constant hiss, although some equipment may suffer from residual hum as well.
Omni-directional:
The response of a microphone which picks up sounds equally all round. Not suited to live vocal
applications as they are more prone to feed back.
Pad:
Another term for attenuator.
Pan (Panoramic):
A control that adjusts the balance of the signal in the left and right speakers.
Peak Meter:
A type of signal meter that has a very fast attack and slower release. This picks up the fast signal
transients and holds them long enough for the operator to see the activity on the display. These
meters typically use led (light emitting diode) displays.
Phono:
Abbreviation for phonograph as in ‘turntable’. Usually means RIAA equipped input when marked on
console inputs. Can also refer to the RCA ‘phono’ type connector found on turntables and CD players.
Summary of Contents for UREI 1601E
Page 1: ...1...
Page 8: ...8...
Page 15: ...15...
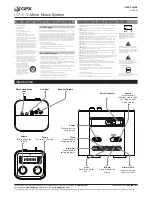
Page 16: ...16 DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION DESCRIPTION TOP PANEL...
Page 48: ...48 CONNECTING LEADS CONNECTING LEADS CONNECTING LEADS CONNECTING LEADS CONNECTING LEADS...
Page 55: ...55...
Page 56: ...56...