Looping techniques
Depending upon the source material, creating a natural-sounding loop can be a difficult task. Many factors beyond your control may
produce distracting pops and glitches, thereby calling unwanted attention to the loop. Although looping skill is largely the product of
practice and experimentation, there are some guidelines to consider.
Match endpoint amplitudes
One of the easiest ways to minimize the occurrence of glitches when creating loops is to select loop endpoints that have an amplitude
of zero. These points are known as zero-crossings.
Match endpoint waveform slope
Another technique for reducing loop glitches is to avoid matching loop endpoints where the waveform slope does not match. If the
waveform slope changes drastically, a pop plays when the sample is looped.
Non-matching slope
Matching slope
Match endpoint sound levels
The overall amplitude (or loudness) approaching the loop’s endpoints should be as similar as possible to prevent distracting glitches.
Unfortunately, it is frequently difficult to avoid this problem, particularly with rapidly decaying source material.
Avoid very short loops
If the loop is shorter than ~50 ms (1/20 Hz), the pitch of the loop may not equal the sample pitch. Pitch-tuning a loop is accomplished by
creating short loops with a length equal to 1/frequency. For example, a sample of pitch 440 Hz corresponds to A5 on the keyboard,
meaning the loop can be pitch-tuned 2.27 ms. However, pitched loops do not sound like the original sample.
Editing loops
The loop you initially create in any situation is rarely perfect. Frequently, loops require some degree of editing before they are usable.
Once you create a loop, you can quickly edit its beginning and end (and subsequently its length) by dragging the markers to a new
location.
Editing a loop without the Loop Tuner
After you create a loop, you can quickly edit its beginning and end (and subsequently its length) by dragging the markers to a new
location. However, this method frequently does not provide the control required to create seamless loops. In this case, you should edit
the loop using the Loop Tuner.
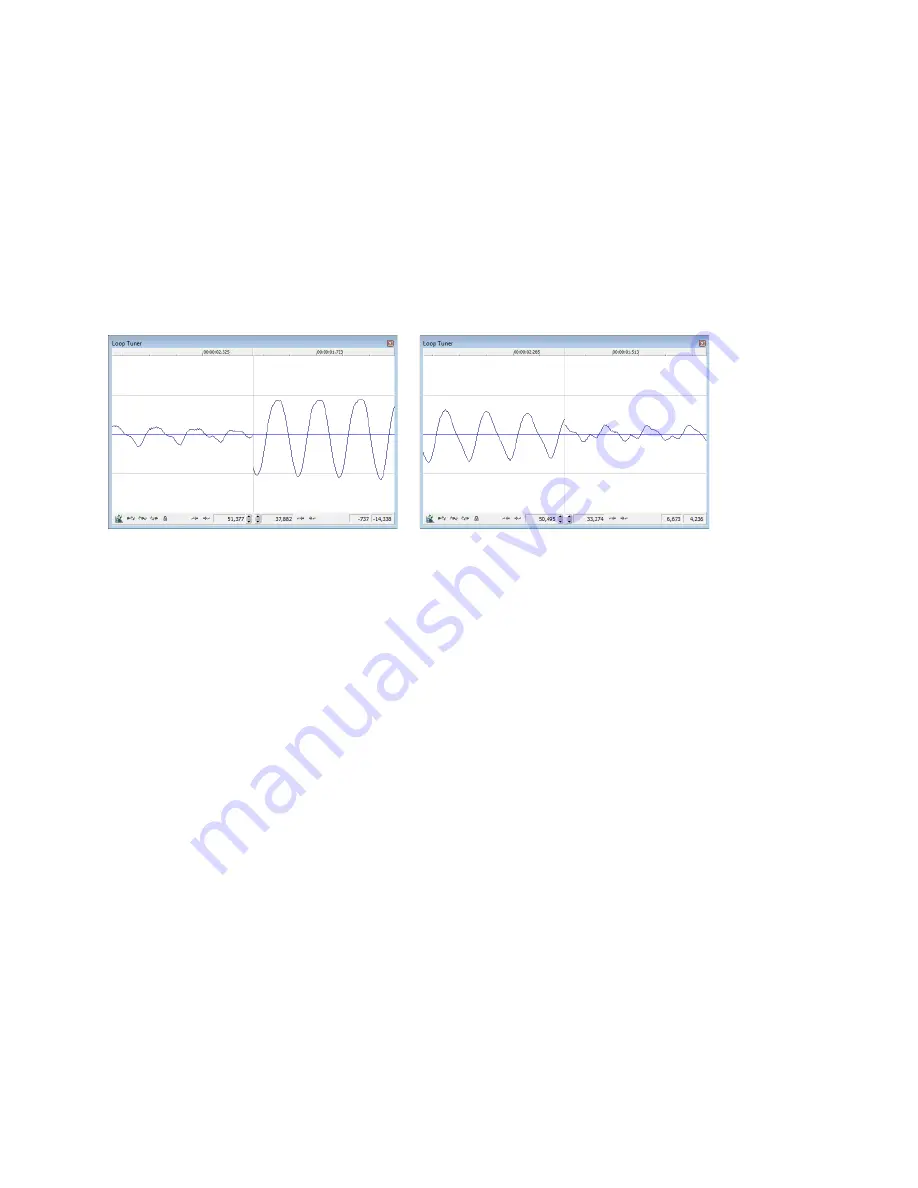
Editing a loop with the Loop Tuner
The Loop Tuner allows you to precisely edit loop points in order to prevent distracting audio glitches. This is accomplished by greatly
magnifying the waveform and displaying the loop tags in relation to one another. You can also use the Loop Tuner to adjust the starting
and ending points of a loop (or selection) to create smooth transitions.
LOOPING
|
263
Summary of Contents for Pro 10
Page 1: ...Pro 10 Sound Forge User Manual ...
Page 2: ......
Page 26: ...20 CHAPTER 1 ...
Page 60: ...54 CHAPTER 2 ...
Page 152: ...146 CHAPTER 8 ...
Page 166: ...160 CHAPTER 9 ...
Page 176: ...170 CHAPTER 10 ...
Page 200: ...194 CHAPTER 11 ...
Page 220: ...214 CHAPTER 12 ...
Page 236: ...230 CHAPTER 13 ...
Page 266: ...260 CHAPTER 16 ...
Page 278: ...272 CHAPTER 17 ...
Page 312: ...306 CHAPTER 20 ...
Page 346: ...340 APPENDIX C ...
Page 366: ...360 APPENDIX E ...
















































