21
EN
Additional Information
3-856-761-11(2)
Guide to the Serial Copy
Management System
This deck uses the Serial Copy Management System,
which allows only first-generation digital copies to be
made of premastered software via the deck’s digital
input jack. An outline of this system appears below:
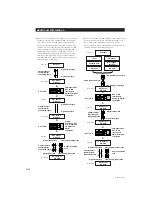
1
You can record from digital program sources (CDs,
premastered MDs or DATs) onto a DAT or recordable MD
via digital input jack on the DAT or MD deck. You
cannot, however, record from this recorded DAT or MD
onto another DAT or recordable MD via the digital input
jack on the DAT or MD deck.
CD player
DAT deck
MD deck
Optical cable or coaxial
digital connecting cable
Recording
DAT deck or
MD deck
v
First-generation
DAT or MD
recorded via
digital-to-digital
connection
v
Playing
Digital output jack
Digital input jack
DAT or MD
Digital output jack
Digital input jack
Recording
DAT deck or
MD deck
DAT deck or
MD deck
Playing
Optical cable or
coaxial digital
connecting cable
Audio connecting
cord
Line (analog) output jack
Line (analog) input jack
Applying the principle of human hearing
The SBM function applies the principle of human
hearing in the reintegration of signal information. The
auditory range of the human ear is generally
considered to be 20 Hz to 20 kHz; hearing sensitivity,
however, shows greater sensitivity to the range
between 3 kHz and 4 kHz, and lower sensitivity to
frequencies above and below this range. This principle
applies also to quantizing noise as well. By reducing
quantizing noise in this particular range, signals can be
recorded to produce more expansive sound than is
possible by a uniform reduction of noise over the entire
audible range.
Noise-shaping filter
The SBM function uses a noise-shaping filter (see Fig.
B) with a frequency response similar to that of the
human ear to reduce quantizing noise within the most
sensitive frequency range, and to feed back the
quantizing error (that is normally lost) back to the
input signal, re-integrating the low-end bit information
with the high-end bit information (see Fig. A).
Fig. A
24-bit information
input
Noise-shaping
filter
16-bit SBM
output
/
/
Fig. B shows the improvement in the quantizing noise
level when the SBM switch is on (theoretical values).
Given a noise level of 0 dB when the SBM switch is off,
the improvement in noise level for sampling
frequencies lower than 3 kHz exceeds 10 dB when the
SBM is activated.
Fig. B
SBM
ON
SBM
OFF
Noise
level
(dB)
Sampling frequency (Hz)
The SBM function operates only during recording. The
improved sound produced by the SBM function,
however, can be enjoyed during playback, regardless
of the SBM switch position or the DAT deck being
used.
-10
-5
0
5
10
15
20
25
20
100
50
200
1k
500
2k
15k
5k
10k
(Continued)