3
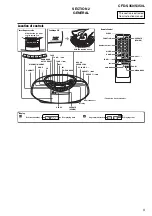
CFD-S350/S350L
•
UNLEADED SOLDER
Boards requiring use of unleaded solder are printed with the lead-
free mark (LF) indicating the solder contains no lead.
(Caution: Some printed circuit boards may not come printed with
the lead free mark due to their particular size.)
: LEAD FREE MARK
Unleaded solder has the following characteristics.
• Unleaded solder melts at a temperature about 40
°
C higher than
ordinary solder.
Ordinary soldering irons can be used but the iron tip has to be
applied to the solder joint for a slightly longer time.
Soldering irons using a temperature regulator should be set to
about 350
°
C.
Caution: The printed pattern (copper foil) may peel away if
the heated tip is applied for too long, so be careful!
• Strong viscosity
Unleaded solder is more viscous (sticky, less prone to flow)
than ordinary solder so use caution not to let solder bridges
occur such as on IC pins, etc.
• Usable with ordinary solder
It is best to use only unleaded solder but unleaded solder may
also be added to ordinary solder.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. SERVICING NOTES
......................................................... 4
2. GENERAL
............................................................................ 5
3. DISASSEMBLY
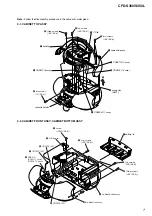
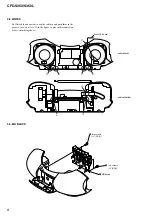
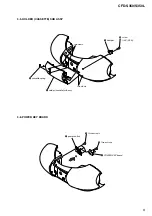
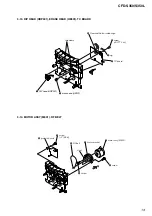
3-1. Cabinet Top Assy ................................................................ 7
3-2. Cabinet Front Assy, Cabinet Bottom Assy .......................... 7
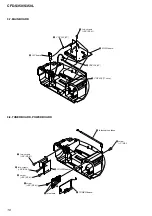
3-3. Wires ................................................................................... 8
3-4. MD Block ............................................................................ 8
3-5. Holder (Cassette) Sub Assy ................................................. 9
3-6. Power Key Board ................................................................ 9
3-7. Main Board ....................................................................... 10
3-8. Tuner Board, Power Board ................................................ 10
3-9. CD Lid ............................................................................... 11
3-10. LCD Block Assy ............................................................... 11
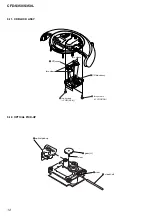
3-11. CD Block Assy .................................................................. 12
3-12. Optical Pick-up ................................................................. 12
3-13. R/P Head (HRP301), Erase Head (HE301), TC Board ..... 13
3-14. Motor Assy (M801), RF Belt ............................................ 13
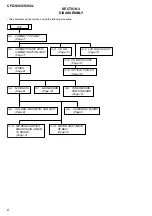
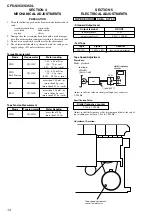
4. MECHANICAL ADJUSTMENTS
............................... 14
5. ELECTRICAL ADJUSTMENTS
Tape Section .......................................................................... 14
Tuner Section ......................................................................... 15
CD Section ............................................................................ 17
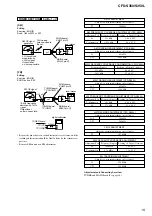
6. DIAGRAMS
6-1. Block Diagram – CD Section – ......................................... 19
6-2. Block Diagram – Tuner Section (CFD-S350 Model) – .... 20
6-3. Block Diagram – Tuner Section (CFD-S350L Model) – .. 21
6-4. Block Diagram – Main Section – ...................................... 22
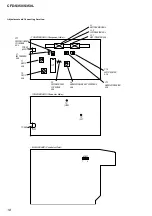
6-5. Circuit Boards Location .................................................... 23
6-6. Printed Wiring Board – CD Section – ............................... 24
6-7. Schematic Diagram – CD Section – .................................. 25
6-8. Printed Wiring Board
– Tuner Section (CFD-S350 Model) – ............................. 26
6-9. Schematic Diagram
– Tuner Section (CFD-S350 Model) – ............................. 27
6-10. Printed Wiring Board
– Tuner Section (CFD-S350L Model) – ........................... 28
6-11. Schematic Diagram
– Tuner Section (CFD-S350L Model) – ........................... 29
6-12. Schematic Diagram – Main Section (1/2) – ...................... 30
6-13. Schematic Diagram – Main Section (2/2) – ...................... 31
6-14. Printed Wiring Boards – Main Section – .......................... 32
6-15. Printed Wiring Board – TC Section – ............................... 33
6-16. Schematic Diagram – TC Section – .................................. 34
6-17. Printed Wiring Boards – Control Section – ....................... 35
6-18. Schematic Diagram – Control Section – ........................... 36
6-19. Printed Wiring Boards – Power Supply Section – ............ 37
6-20. Schematic Diagram – Power Supply Section – ................. 38
7. EXPLODED VIEWS
7-1. Cabinet Section ................................................................. 44
7-2. Cabinet (Front) Section ..................................................... 45
7-3. Cabinet (Top) (1) Section .................................................. 46
7-4. Cabinet (Top) (2) Section .................................................. 47
7-5. Cabinet (Bottom) Section .................................................. 48
7-6. Tape Mechanism Section .................................................. 49
7-7. CD Mechanism Section .................................................... 50
8. ELECTRICAL PARTS LIST
......................................... 51
SAFETY CHECK-OUT (US MODEL)
After correcting the original service problem, perform the following
safety check before releasing the set to the customer:
Check the antenna terminals, metal trim, “metallized” knobs, screws,
and all other exposed metal parts for AC leakage.
Check leakage as described below.
LEAKAGE TEST
The AC leakage from any exposed metal part to earth ground and
from all exposed metal parts to any exposed metal part having a
return to chassis, must not exceed 0.5 mA (500 microampers.).
Leakage current can be measured by any one of three methods.
1. A commercial leakage tester, such as the Simpson 229 or RCA
WT-540A. Follow the manufacturers’ instructions to use these
instruments.
2. A battery-operated AC milliammeter. The Data Precision 245
digital multimeter is suitable for this job.
3. Measuring the voltage drop across a resistor by means of a
VOM or battery-operated AC voltmeter. The “limit” indica-
tion is 0.75 V, so analog meters must have an accurate low-
voltage scale. The Simpson 250 and Sanwa SH-63Trd are
examples of a passive VOM that is suitable. Nearly all battery
operated digital multimeters that have a 2 V AC range are
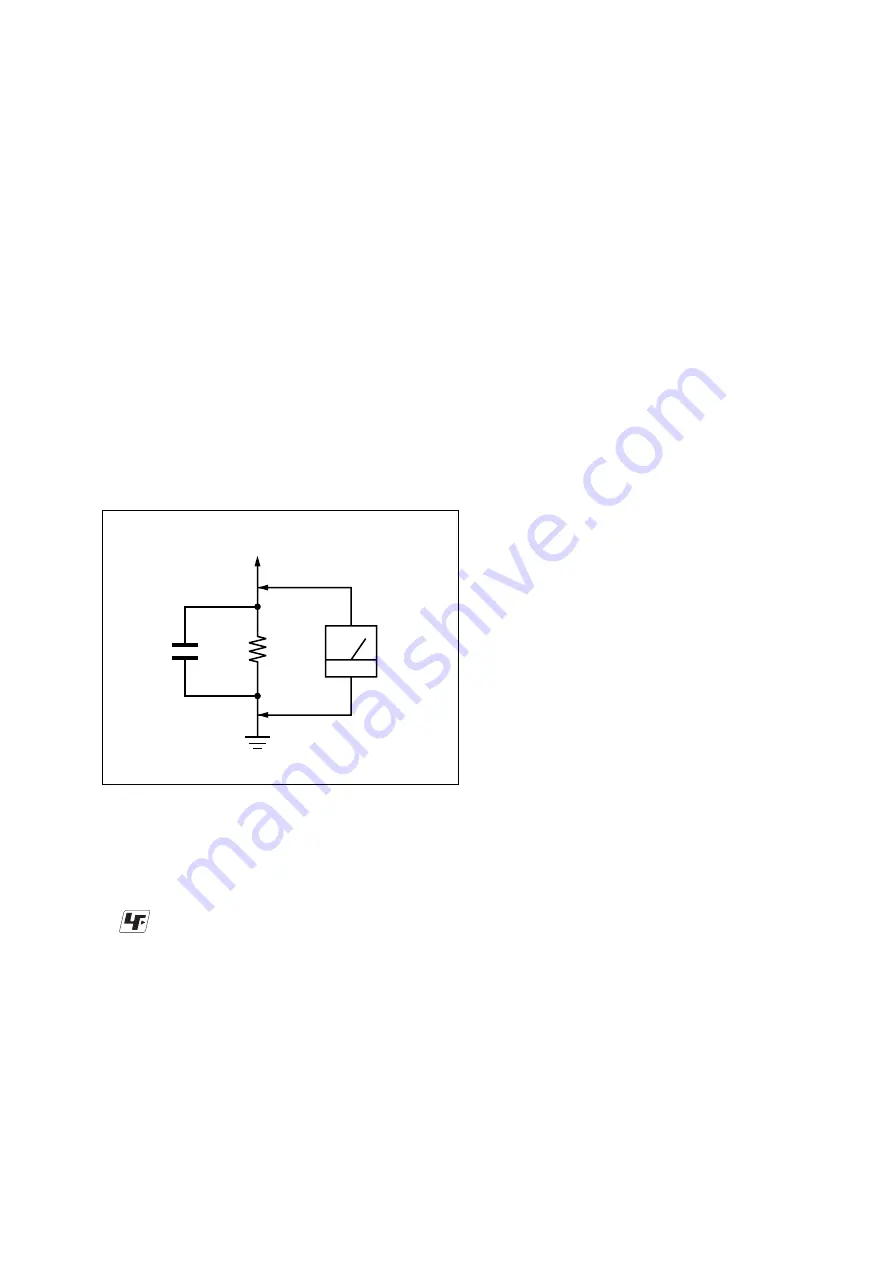
suitable. (See Fig. A)
1.5 k
Ω
0.15
µ
F
AC
voltmeter
(0.75 V)
To Exposed Metal
Parts on Set
Earth Ground
Fig. A. Using an AC voltmeter to check AC leakage.