• • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • •
22
I N S T R U C T I O N M A N U A L • M O D E L H 5 2 0 / H 5 4 0
A P P L I C A T I O N S – S T A K I N G
Ultrasonic staking, also referred to as ultrasonic “heading” or “riveting”,
controls the flow of the molten plastic used to capture or retain another
component in place. Ultrasonic staking provides an alternative to welding
when the two parts consist of dissimilar materials that cannot be welded or
when simple mechanical retention of one part relative to another is
inadequate (i.e. as distinct from molecular bonding). A common application is
the attachment of plastic to metal. Typically a metal part, with location holes,
is placed over a plastic part with molded bosses. The horn tip is then pressed
against the plastic boss and the vibratory motion creates friction and localized
heating. As the boss melts, the light pressure from the horn forms a head to
a shape determined by the horn tip configuration. When the vibrations stop,
the plastic material solidifies, and the dissimilar materials are fastened
together.
With staking, tight assemblies are possible because mating parts are
clamped under pressure of the horn until the rivet head solidifies. There is no
elastic recovery as is the case with heat staking or cold forming. A major
advantage of ultrasonic staking over heat staking is that the ultrasonic staking
tip remains relatively cool during the process, forming a clean head with no
sticking or stringing during assembly.
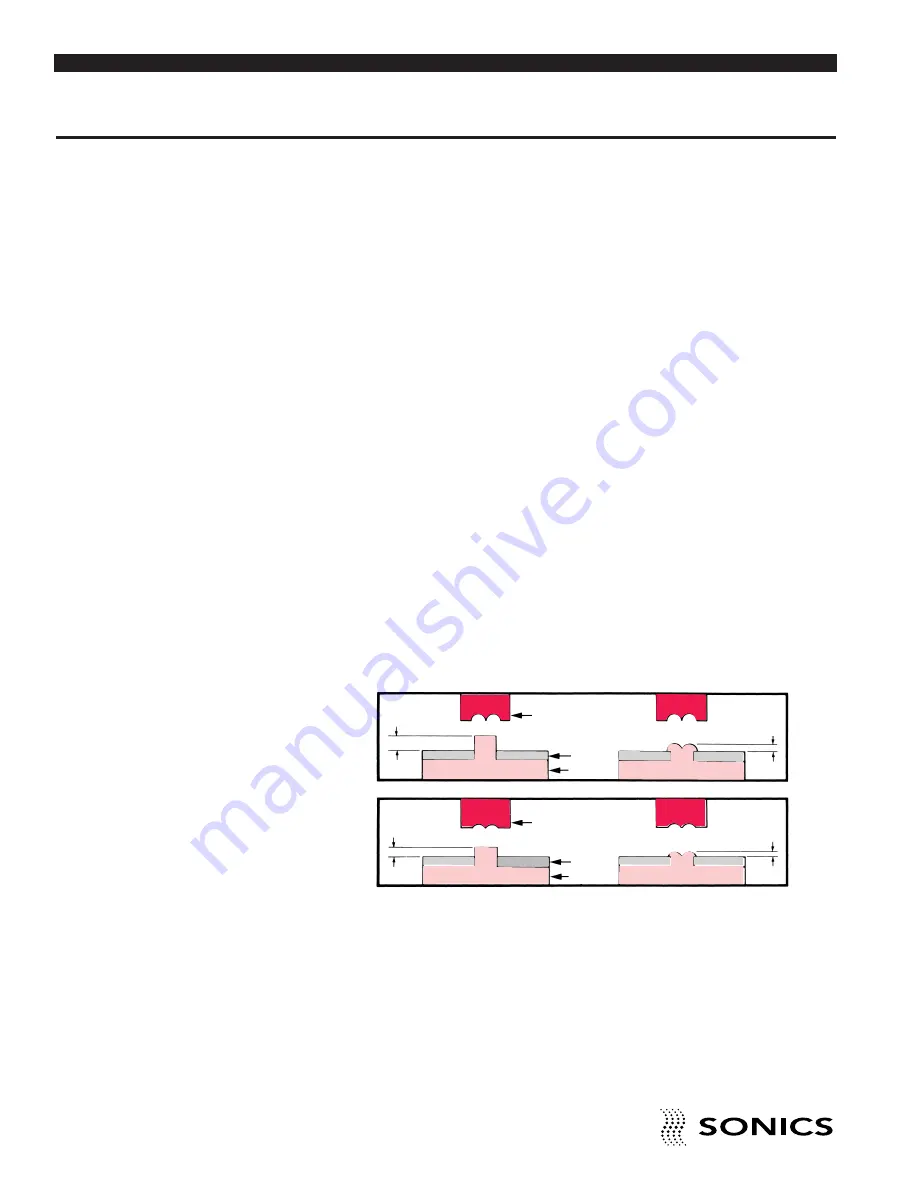
STANDARD FLARED STAKE
The standard flared stake satisfies the requirements of most applications.
This stake is recommended for bosses with an O.D. of 1⁄16 inch (1.6 mm) or
larger, and is ideally suited for low density, nonabrasive amorphous plastics.
BEFORE
HIGH PROFILE
AFTER
.6d
.5d
METAL
PLASTIC
HORN
METAL
PLASTIC
HORN
BEFORE
LOW PROFILE
AFTER
1.6d
.25d
d
2d
d
1.5d

























