5
5.2
WELDING ALUMINIUM
The welder must be prepared as for welding mild steel
with gas protection, but with the following differences:
- 100% ARGON as the shielding gas for welding.
- A wire having a composition suited to the base material
to be welded.
For welding ALLUMAN: 3÷5% silicon wire
- For welding ANTICORODAL: 3÷5% silicon wire
- For welding PERALUMAN: 5% magnesium wire
- For welding ERGAL: 5% magnesium wire
Use grinding wheels and brushes specifically designed
for aluminium, and never use them on other materials.
REMEMBER that cleanliness is quality!
The wire reels must be stored in nylon bags with dehu-
midifying packets.
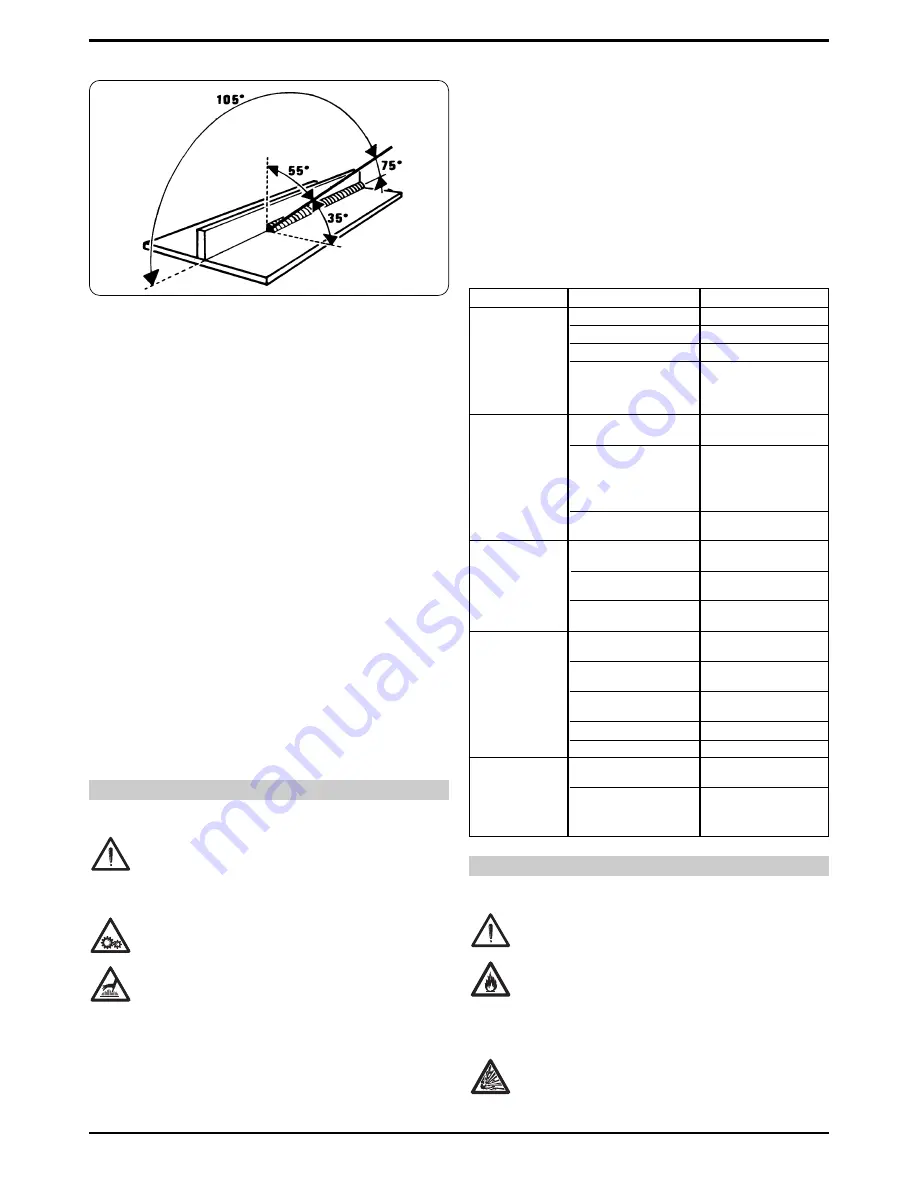
For the correct welding angle see figure 3.
5.3 WELDING STAINLESS STEEL
The welder must be prepared as for welding mild steel
with gas protection, but with the following differences:
- Reel of stainless steel wire compatible with the compo-
sition of the material to be welded.
- Cylinder containing 98% ARGON + 2% 02 (recom-
mended composition)
The recommended torch angle and welding direction are
shown in figure 3.
6 MAINTENANCE AND CHECKS
6.1
GENERAL NOTES
WARNING!
Turn off the welder and unplug the power cord from the
socket before each checking and maintenance operation.
Moving parts can cause serious injuries.
Keep away from moving parts.
GLOWING HOT SURFACES can cause serious
burns.
Let the unit cool before servicing.
Periodically remove any dust or foreign matter that may
have deposited on the transformer or diodes; to do so,
use a jet of clean, dry air.
When replacing the wire roller, make sure the groove is
aligned with the wire and corresponds to the diameter of
the wire used.
Always keep the interior of the gas nozzle clean to avoid
metal bridges created by welding dross between the gas
nozzle and the contact tip. Make sure the outlet hole of
the contact tip has not expanded excessively; if so,
replace.
Strictly avoid striking the torch or allowing it to suffer
violent impact.
6.2 TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
7 SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
7.1 FIRE
WARNING!
Avoid causing fire because of sparks, slag, hot
metal or pieces.
Make sure that suitable fire-fighting equipment
is available close to welding area.
Remove all flammable and combustible material from
the welding area and its surrounding (32 ft minimum).
Do not weld containers of combustible or flam
mable material, even when empty.
Fig. 3
TROUBLE
The welding machi-
ne supplies limited
current
Welding with a lot
of metal spatter
The wire jams or
entangles between
the drive rolls and
the torch infeed wire
guide
No wire feed or irre-
gular wire feed
Porosity in the wel-
ding seam
PROBABLE CAUSE
Line fuse blown
Burnt out diode or diodes
Burnt out electronic board
Loose torch or ground
connections or any other
electrical power connec-
tions
Voltage adjustment switch
has a loose contact
Improper adjustment of
welding parameters
Poor ground connection
Contact tip with wrong dia-
meter
Misalignment of the drive
roll groove
Obstructed or clogged
liner
Drive roll with too large a
groove
Obstructed or clogged
liner
Wire holding roller not
completely tightened
Clogged contact tip
Insufficient shielding gas
Excess oxidation of the
edges to be welded
Gas nozzle partially or
completely clogged by
spatter
REMEDY
Replace line fuse
Replace
Replace
Tighten all connections
Replace the switch
Select the correct parame-
ters through the welding-
voltage switch and the
wire-speed adjustment
potentiometer
Check grounding connec-
tions
Replace
Realign
Remove and clean
Replace the drive roll
Remove and clean
Tighten all the way
Replace
Increase gas delivery
Thoroughly clean the
edges with a metal brush
Remove and clean or
replace being careful not
to clog the gas outlets






























