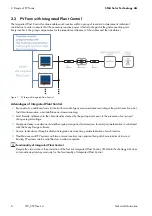
SMA Solar Technology AG
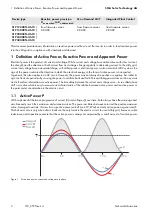
1 Definition of Active Power, Reactive Power and Apparent Power
Technical Information
IPC_STP-TI-en-14
3
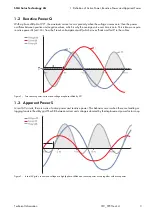
1.2 Reactive Power Q
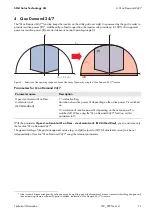
With a phase shift phi of 90°, the maximum current occurs precisely when the voltage crosses zero; then the power
oscillates between positive and negative values, which is why the average value over time is zero. This is known as pure
reactive power Q (unit: Var, from the French volt-ampère-réactif) which moves "back and forth" in the cables.
Figure 2: Pure reactive power: current and voltage are phase-shifted by 90°
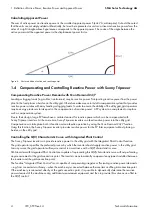
1.3 Apparent Power S
In real AC circuits, there is a mix of active power and reactive power. This behavior occurs when there are leading or
lagging loads in the utility grid. The shift between current and voltage is denoted by the displacement power factor cos φ.
Figure 3: In real AC grids, current and voltage are slightly phase-shifted and reactive power occurs together with active power.