Functions
2.5 Distance Protection
SIPROTEC, 7SD5, Manual
C53000-G1176-C169-5, Release date 02.2011
154
Resistance tolerance
The resistance setting R allows a reserve for fault resistance which appears as an additional resistance at the
fault location and is added to the impedance of the line conductors. It comprises, for example, the resistance
in arcs, the earth distribution resistance of earth points and others. The setting must consider these fault resis-
tances, but should at the same time not be larger than necessary. On long heavily loaded lines, the setting may
extend into the load impedance range. Fault detection due to overload conditions is then prevented with the
load trapezoid. Refer to margin heading „Load range (only for impedance pickup)“ in Subsection 2.5.1. The re-
sistance tolerance may be separately set for the phase-to-phase faults on the one hand and the phase-to earth
faults on the other hand. It is therefore possible to allow for a larger fault resistance for earth faults for example.
Most important for this setting on overhead lines, is the resistance of the fault arc. In cables on the other hand,
an appreciable arc can not exist. On very short cables, care must however be taken that an arc fault on the
local cable termination is inside the set resistance of the first zone.
The standard value for the arc voltage U
Arc
is approx. 2.5 kV per meter of arc length.
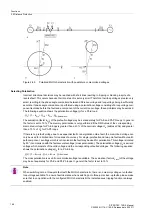
Example:
A maximum arc voltage of 8 kV is assumed for phase-to-phase faults (line data as above). If the minimum
primary short-circuit current is assumed to be 1000 A this corresponds to 8
Ω
primary. The resistance setting
for the first zone, including a safety margin of 20%, would be
primary:
R1
Prim
= 0.5 · R
Arc
· 1.2 = 0.5 · 8
Ω
· 1.2 = 4.8
Ω
or secondary:
Only half the arc resistance was applied in the equation, as it is added to the loop impedance and therefore
only half the arc resistance appears in the
per phase
impedance. Since an arc resistance is assumed to be
present in this case, infeed from the opposite end need not be considered.
The resistance R
L
of the line itself can be ignored with SIPROTEC 4 devices. It is taken into account by the
shape of the polygon, provided that the inclination angle of the polygon
Distance Angle
(address
1511
) is
not set greater than the line angle
Line Angle
(address
1105
).
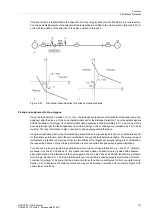
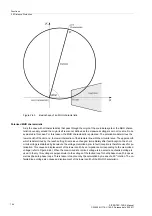
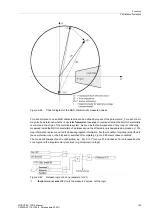
A separate resistance tolerance can be set for earth faults. Figure 2-60 illustrates the relationships.
Figure 2-60
Resistance measurement of the distance protection in the presence of arc faults
The maximum arc resistance R
Arc
must be determined for setting the distance zone in R direction. The
maximum arc fault resistance is attained when the smallest fault current at which an arc is still present flows
during an earth fault.