Measured Value Monitoring Functions
241
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.38
Measured Value Monitoring Functions
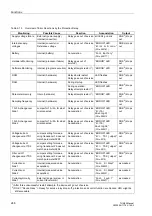
The device is equipped with extensive monitoring capabilities - both for hardware and
software. In addition, the measured values are also constantly monitored for
plausibility, therefore, the current transformer and voltage transformer circuits are
largely integrated into the monitoring.
2.38.1 Functional Description
2.38.1.1 Hardware Monitoring
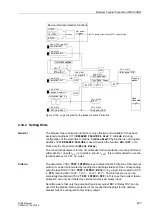
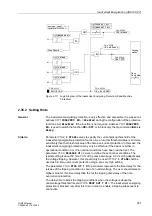
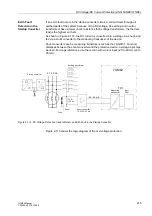
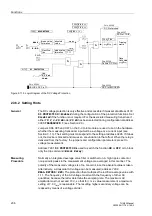
The device is monitored from the measurement inputs to the output relays. Monitoring
circuits and processor check the hardware for malfunctions and disallowed conditions
(see Table 2-13 in Section 2.38.1.5).
Auxiliary and
Reference Voltages
The processor voltage of 5 V DC is monitored, and if the voltage decreases below the
minimum value, the device is removed from operation. When the cross-polarized
voltage returns, the processor system is restarted.
Removal of or switching off the supply voltage removes the device from operation and
a message is immediately generated by a dead contact. Brief voltage interruptions of
less than 50 ms do not disturb the readiness of the device (for nominal auxiliary
voltage
≥
110 V DC).
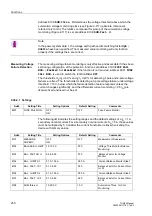
The processor monitors the offset and reference voltage of the AD (analog-digital)
converter. The protection is suspended if the voltages deviate outside an allowable
range, and lengthy deviations are reported (”
”).
Buffer Battery
The buffer battery, which ensures the operation of the internal clock and the storage
of counters and messages if the auxiliary voltage fails, is periodically checked for
charge status. If it is less than an allowed minimum voltage, then the ”
message is issued.
If the power supply voltage is cut off for 1 or 2 days, the internal buffer battery is auto-
matically switched off, i.e. the internal clock will stop, whereas the buffered annuncia-
tions and fault event data will be preserved.
Memory
Components
The working memory (RAM) is tested when the system is started up. If a malfunction
occurs then, the starting sequence is interrupted and an LED blinks. During operation,
the memory is checked using its checksum.
For the program memory, the cross sum is formed periodically and compared to the
stored program cross sum.
For the settings memory, the cross sum is formed periodically and compared to the
cross sum that is freshly generated each time the setting process takes place.
If a malfunction occurs, the processor system is restarted.
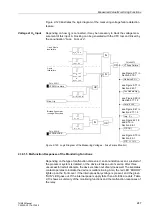
Sampling
Sampling and the synchronization between the internal buffer components are
constantly monitored. If any deviations cannot be removed by renewed
synchronization, then the processor system is restarted.