Motor Starting Time Supervision (ANSI 48)
213
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.32
Motor Starting Time Supervision (ANSI 48)
General
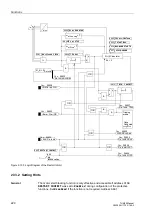
When the 7UM62 relay is used to protect a motor, the starting time monitoring feature
supplements the overload protection described in Section 2.9 by protecting the motor
against the potential damage that might result from frequent starting or extended
starting durations. In particular, rotor-critical high-voltage motors can quickly be
heated above their thermal limits when multiple starting attempts occur in a short
period of time. If the durations of these starting attempts are lengthened by excessive
voltage surges during motor starting, by excessive load moments, or by locked rotor
conditions a tripping signal will be initiated by the device.
2.32.1 Functional Description
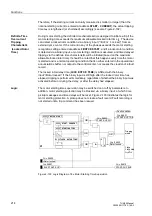
The motor starting time monitoring is initiated by the motor starting recognition setting
entered at address
. This current releases the calculation of
the tripping characteristic.
One characteristic is definite time while the other one is inverse time.
Inverse Time-
Overcurrent
Tripping
Characteristic
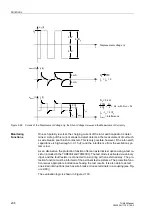
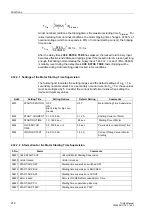
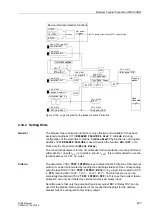
The inverse time-overcurrent characteristic is designed to operate only when the rotor
is not blocked. The inverse time characteristic allows motor starting time monitoring to
adjust for those situations where high starting voltages result in decreased starting
currents. The tripping time is calculated based on the following formula:
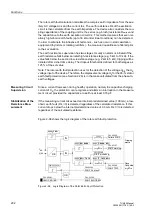
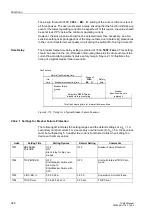
Figure 2-102 Inverse Time Characteristic Tripping Curve for Motor Starting Current
t
TRIP
I
StartCurrent
I
--------------------------------
è
ø
æ
ö
2
⋅
=
where
I
>
I
Motor Start
t
Startmax
where
t
TRIP
– Actual tripping time for flowing current I
t
Startmax
– Tripping time for nominal start-up current
I
A
(set at address
,
I
– Current actually flowing (measured value)
I
StartCurr.
– Nominal starting current of the motor (set at address
I
MotorStart
– Pickup value for recognition of motor starting (set at address
)
t
TRIP
I
I
MotorStart
I
StartCurr.
t
Startmax
[s]