Functions
106
7UM62 Manual
C53000-G1176-C149-3
2.14
Underexcitation (Loss-of-Field) Protection (ANSI 40)
General
The underexcitation or loss of field protection protects a synchronous generator/motor
from asynchronous operation in the event of a malfunction in the excitation system
and from local overheating of the rotor. Furthermore, it ensures that the network sta-
bility is not endangered due to the underexcitation of large synchronous generators.
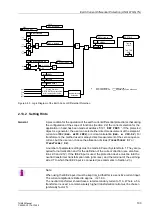
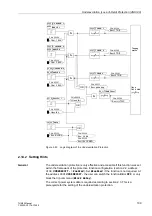
2.14.1 Functional Description
Underexcitation
Determination
In order to detect underexcitation, the unit processes all three terminal phase currents
and all three terminal voltages to form the stator circuit criterion. It also processes the
excitation voltage and/or the signal from an external excitation voltage monitor to form
the rotor circuit criterion.
For the stator circuit criterion, the reciprocal of the impedance (equal the admittance)
is calculated from the positive sequence system of the currents and voltages. In the
admittance plane, the stability limit of the machine is independent of the voltage: thus,
the protection characteristic can be optimally matched to the stability characteristic of
the machine. By evaluating the positive sequence system, underexcitation conditions
are reliably detected even during asymmetrical faults within or outside of the machine.
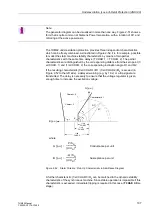
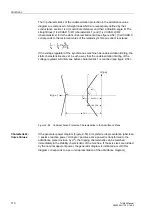
Characteristics
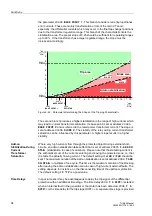
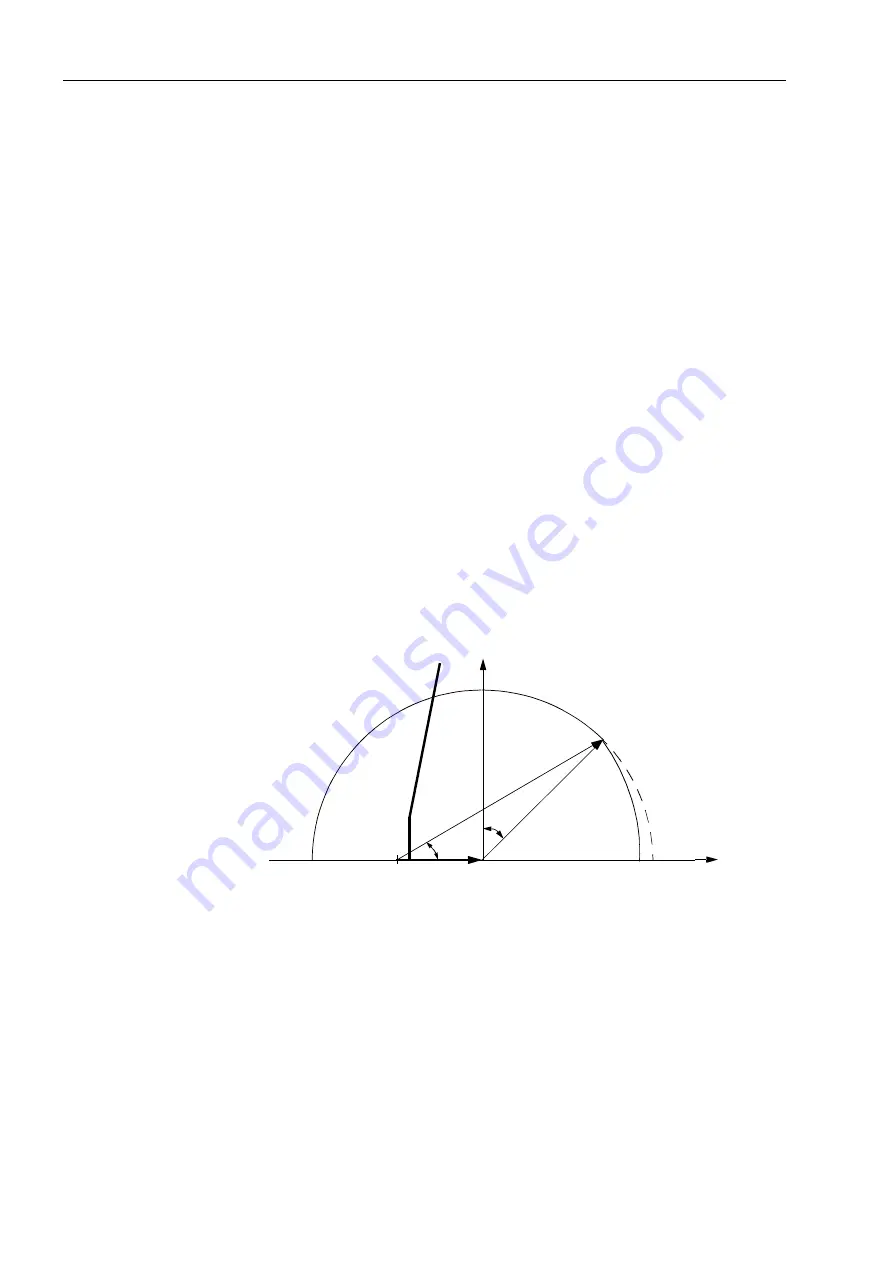
Figure 2-51 shows the loading diagram of the synchronous generator in the admit-
tance plane (P/U
2
; Q/–U
2
) with the steady-state stability limit which intersects the re-
active axis in close proximity to 1/X
d
(reciprocal value of the synchronous direct reac-
tance).
Figure 2-51
Admittance Diagram of Turbo Generators
I
w
U
-------
P
U
2
-------
G
=
=
I
EN
U
N
--------
I
N
U
N
--------
1
X
d
---------
–I
b
U
-------
–Q
U
2
--------
–B
=
=
ϑ
N
ϕ
N
U
N
Rated voltage
I
w
Active current
I
N
Nominal Current
I
b
Reactive current
I
EN
Rated excitation current
G
Conductance
ϑ
N
Rated pole angle (rotor angle)
B
Susceptance
ϕ
N
Rated load angle
P
Active power
X
d
Synchronous reactance
Q
Reactive power
U
Terminal voltage
underexcited
overexcited