Functions
6-90
7SA522 Manual
C53000-G1176-C119-2
If there is a disturbance in the signal transmission path the overreaching zone can be
blocked via a binary input. The distance protection operates with the usual time grad-
ing characteristic (non delayed trip in Z1). The overreaching zone Z1B can then be ac-
tivated by an automatic reclose function via the binary input “
!(QDEOH$5]RQHV
” and
setting 1357 “
” set to “Yes” (refer also to Figure 6-39 bottom).
The occurrence of erroneous signals resulting from transients during clearance of ex-
ternal faults or from direction reversal resulting during the clearance of faults on par-
allel lines, is neutralized by the “Transient Blocking”. It prolongs the blocking signal by
the transient blocking time
(address
), if it has been present
for the minimum duration equal to the waiting time
(address
).
It lies in the nature of the blocking scheme that single end fed short circuits can also
be tripped rapidly without any special measures, as the non feeding end cannot gen-
erate a blocking signal.
6.4.1.6
Transient Blocking
In the overreach schemes, the transient blocking provides additional security against
erroneous signals due to transients caused by clearance of an external fault or by fault
direction reversal during clearance of a fault on a parallel line.
The principle of transient blocking scheme is that following the incidence of an external
fault, the formation of a release signal is prevented for a certain (settable) time. In the
case of permissive schemes, this is achieved by blocking of the transmit and receive
circuit.
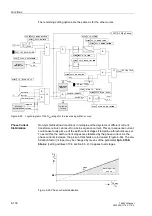
Figure 6-54 shows the principle of the transient blocking function.
If, following fault detection, a fault in the reverse direction is determined within the wait-
ing time
(address
), the transmit circuit and the release of
the overreaching zone Z1B are prevented. This blocking condition is maintained for
the duration of the transient blocking time
(address
) even
after reset of the blocking criterion.
In the case of the blocking scheme, the transient blocking prolongs the received block
signal as shown in the logic diagram Figure 6-53.
Figure 6-54 Transient blocking with POTT and Unblocking schemes
Dis. forward
&
Dis. PICKUP
7U%ON:DLW7LPH
7U%ON%ORFN7LPH
Dis Telep. off
>Dis.Telep. Blk
≥
1
&
transient
blocking
Figure 6-48
or 6-50
T
T
≥
1
Dis. reverse
Dis.T.Trans.Blk
4068
Summary of Contents for siprotec 7SA522
Page 20: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 64: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 89: ...SIPROTEC 4 Devices 4 25 7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 Figure 4 20 CFC Logic example ...
Page 408: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 456: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 516: ...7SA522 Manual C53000 G1176 C119 2 ...
Page 620: ...Appendix B 48 ...