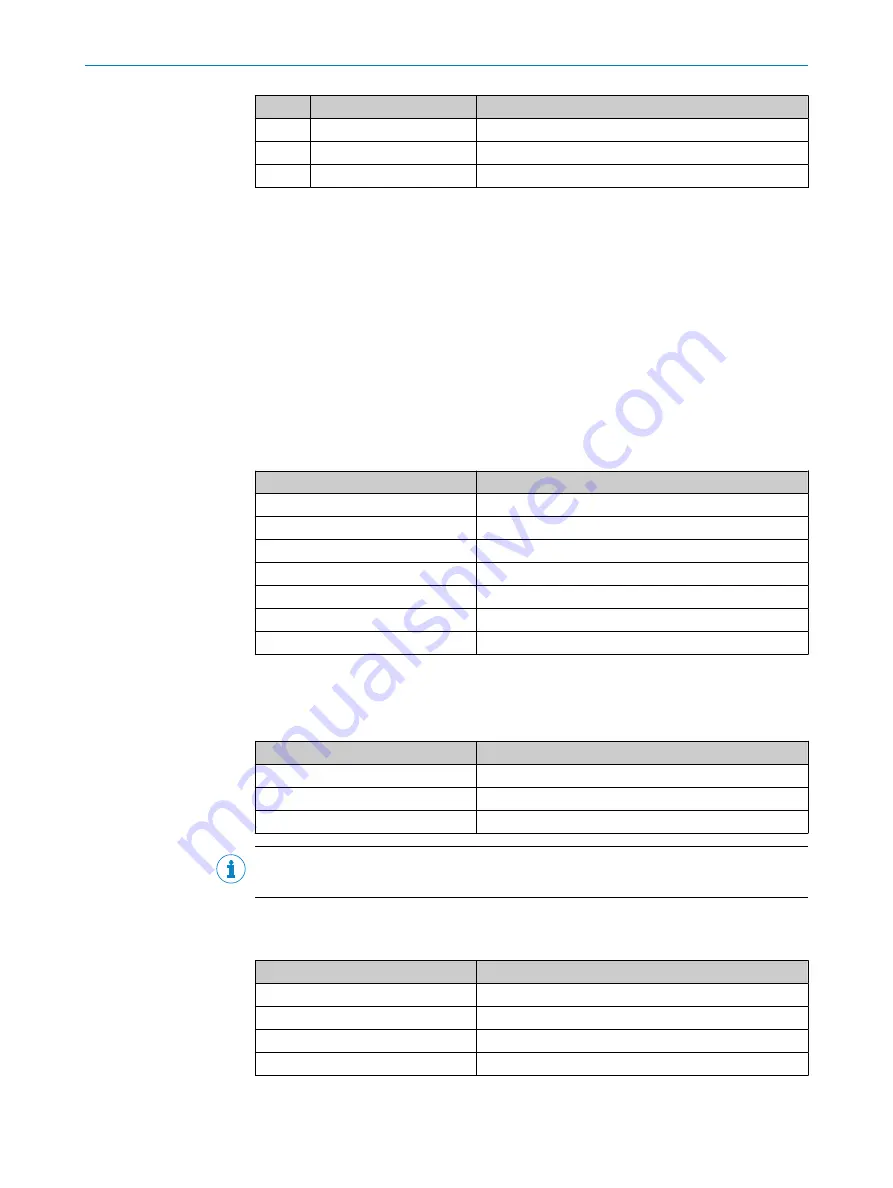
Pin
Signal
Function
3
CAN GND
Ground
4
CAN_H
CAN-Bus High (IN/OUT)
5
CAN_L
CAN-Bus Low (IN/OUT)
1)
The CAN V
S IN
supply voltage is galvanically isolated from the supply voltage for the device. The device is
supplied with voltage via the "PWR IN" connection.
6.4
Wiring the CAN interface
Framework Conditions for the CAN Interface
The SICK-specific CAN-SENSOR network is based on the CAN bus. The CAN bus is set
up in line topology.
Data transmission rate
The maximum allowable length of cable between the device and the host computer
depends on the selected physical type of the host interface and the data transmission
rate set in the device.
Table 14: Maximum length of cable as a function of the data transmission rate
Data transmission rate
Maximum data cable length
10 kbit/s
4,976 m
20 kBit/s
2,476 m
50 kBit/s
976 m
100 kBit/s
576 m
125 kBit/s
476 m
250 kBit/s
1)
226 m
500 kBit/s
76 m
1)
Device default.
Total length of the stub cables
Table 15: Permissible total length of all stubs
Data transmission rate
Maximum total of all stub cables
125 kBit/s
156 m
250 kBit/s
78 m
500 kBit/s
39 m
NOTE
Do not exceed this total length. Each stub cable may be a maximum of 6 m long.
Wire cross-section of the data cable
Table 16: Wire cross-section as a function of the data transmission rate
Data transmission rate
Required wire cross-section
0 m ... 40 m
≥ 0.25 mm
2
40 m ... 300 m
≥ 0.34 mm
2
300 m ... 600 m
≥ 0.5 mm
2
600 m ... 1,000 m
≥ 0.75 mm
2
The required wire cross-section for the data cable depends on the total length of the
network. The table shows the overview as per ISO 11898.
6
ELECTRICAL INSTALLATION
28
T E C H N I C A L I N F O R M A T I O N | Camera ICD880/890 Generation 4
8023775/1A4I/2020-12-01 | SICK
Subject to change without notice
















































