2223A Oxygen Transmitter Functional Safety Manual
2.7
Hardware fault tolerance (HFT)
The ability to continue to provide a safety function in the presence of faults and errors. A
hardware fault tolerance of N means that N+1 faults could cause the loss of a safety
function.
2.8
Safe failure fraction (SFF)
The fraction of failures that does not have the potential to put the safety instrumented
system in a dangerous or non-functioning state. In other words, for each failure mode the
ratio of the diagnosed dangerous failures and the safe failures to the total failures. This
figure is sometimes expressed as a percentage.
2.9 PFD
AVG
The probability of a dangerous failure on demand. This is intended to apply to systems
operating in a low demand mode where the safety function is required on average a
maximum of once per year.
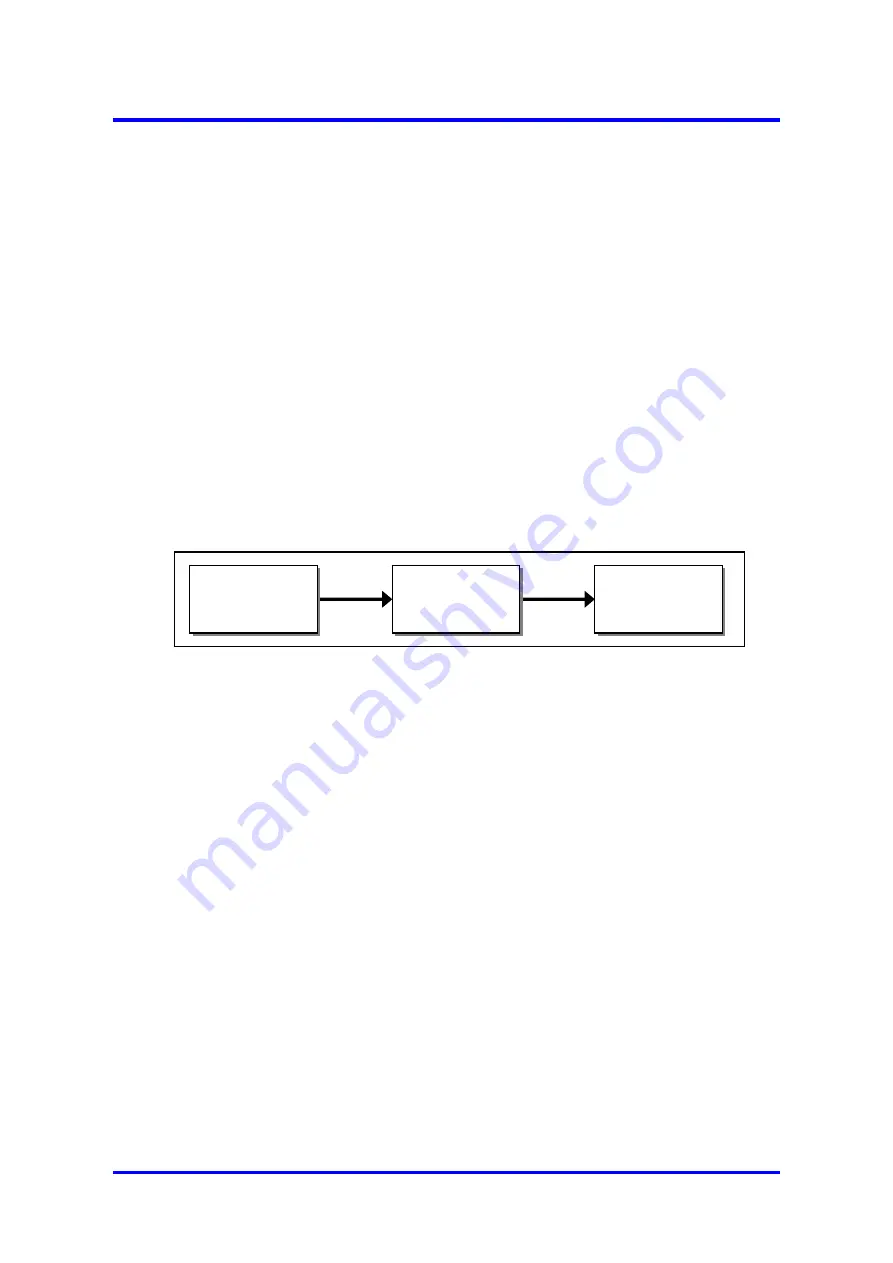
A typical safety instrumented system normally consists of three subsystems as follows:-
It can be seen that the analyser will typically be a part of the overall system and is therefore
only entitled to a fraction of the total PFD
AVG
range associated with the specified SIL.
Sensor
e.g. Analyser
Logic System
e.g. PLC
Final Elements
e.g. Valve
2.10 Mean time to repair (MTTR)
This is the average time taken to restore the safety instrumented system to a working state.
2.11 Proof
test
Periodic tests that are performed to detect failures so that, if necessary, the system can be
restored to a fully working state.
4
02223006A / Revision 0

















