Should you have a problem with the inverter, check the following:
l
That the welding current is correct for the diameter and type of electrode being used.
l
That the mains switch is on, and illuminated. If this is not the case then there may be a mains supply problem.
l
That the yellow LED is not illuminated. If it is this indicates either a main under-voltage or a short circuit.
l
That the nominal intermittence ratio is correct, and that the fan is working correctly. In the case of a thermal protection interruption, wait for the machine to cool.
l
That you are using the correct voltage. If the supply is too high or too low the machine will cut out.
l
That the cables are undamaged and that there is nothing causing a short-circuit.
l
That all circuit connections are correct. In particular check that the work clamp is correctly attached to the workpiece. Ensure that there is no grease, paint etc on the contact surfaces.
l
That correct gas is being used.
7. TROUBLESHOOTING
9. ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY
9.1. THIS EQUIPMENT IS IN CONFORMITY WITH THE EUROPEAN STANDARD ON THE ELECTROMAGNETIC COMPATIBILITY
OF ARC WELDING EQUIPMENT AND SIMILAR PROCESSES (e.g. ARC AND PLASMA CUTTING)
9.2.
Protection against interference. (E.M.C.)
The emission limits in this standard may not, however, provide full protection against
interference to radio and television reception when the equipment is used closer than 30m to the receiving antenna. In special cases,
when highly susceptible apparatus is being used in close proximity, additional mitigation measures may have to be employed in order
to reduce the electromagnetic emissions. At the same time there could occur some potential difficulties in having electromagnetic
compatibility in a non-industrial environment (e.g. in residential areas). Therefore it is most important that the equipment is used and
installed according to the following instructions.
9 .3.
Installation and use.
The user is responsible for installing and using the equipment according to these instructions. If electromagnetic
disturbances are detected, then it shall be the responsibility of the user of the equipment to resolve the situation with the technical
assistance of the supplier. In some cases this remedial action may be as simple as earthing the circuit (see Note). In other cases it
could involve constructing an electromagnetic screen, enclosing the welding power source and the work, complete with associated input
filters. In all cases the electromagnetic disturbances shall be reduced to the point where they are no longer troublesome.
Note:
The
welding/cutting circuit may or may not be earthed for safety reasons. Changing the earthing arrangements should only be
authorised by a person who is competent to assess whether the changes will increase the risk of injury, e.g. by allowing
parallel welding/cutting circuit return paths which may damage the earth circuits of other equipment. Further guidance is given in IEC
974-13 Arc Welding Equipment - Installation and Use.
9.4.
Assessment of area.
Before installing the equipment the user shall make an assessment of potential electromechanical problems in the
surrounding area. The size of the surrounding area to be considered will depend on the structure of the building and other activities that
are taking place. The surrounding area may extend beyond the boundaries of the premises.
The following shall be taken into account :
a) Other supply cables, control cables, signalling and telephone cables, above, below and adjacent to the welding equipment.
b) Radio and television transmitters and receivers.
c) Computer and other control equipment.
d) Safety critical equipment, e.g. security monitoring of industrial equipment.
e) The health of people in the vicinity, e.g. persons fitted with a pacemaker or hearing aid.
f) Equipment used for calibration or measurement.
g) The immunity of other equipment in the environment. The user shall ensure that other equipment being used in the environment is
compatible. This may require additional protective measures.
h) The time of day that welding and other activities are to be carried out.
fig.9
fig.10
8. MAINTENANCE
p
WARNING! DISCONNECT FROM THE MAINS ELECTRICAL SUPPLY AND WAIT FOR CIRCUIT LIGHT TO GO OUT BEFORE ATTEMPTING TO OPEN THE UNIT.
l
Inspect the inverter internally with a frequency dependent on the amount of use and the dustiness of the environment and remove dust deposits from the
transformer, reactance and rectifier using a jet of dry compressed air (max 10bar). Do not direct compressed air onto the circuit boards. These should be
cleaned with a soft brush.
l
At the same time check that the electrical connections are tight and that there is no damage to the wiring insulation.
l
After inspection and cleaning ensure that the cover is correctly replaced and that the fixing screws are fastened right down.
l
Keep the outside of the machine clean by wiping with a soft dry cloth. For any other service or maintenance, contact your local Sealey service agent.
p
WARNING! NEVER OPERATE THE INVERTER WITH THE COVERS REMOVED.
6.3
TIG WELDING
6.3.1 THE TIG WELDING PROCESS: (Optional TIG welding accessory kit INV/TIG is available your Sealey dealer.)
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) welding uses an arc struck between a tungsten electrode and the work to fuse the joint. The electrode itself is not consumed
and filler metal may be required to build the weld profile.The process is protected from atmospheric oxidation by a shield of inert gas which flows from the
ceramic nozzle. This gas is normally pure argon, but helium by itself or a mixture of helium and argon may be used for special applications. For stainless
steel use a mixture of argon and hydrogen.
6.3.2 To achieve a good weld the pieces should be carefully cleaned and free of oxidation, oil, grease and solvents etc
6.4
TIG WELDING PROCEDURE:
p
p
WARNING! Keep the gas bottle away from sources of heat including sunlight.
p
p
WARNING! DO NOT hit the electrode on the workpiece, as this may damage the electrode.
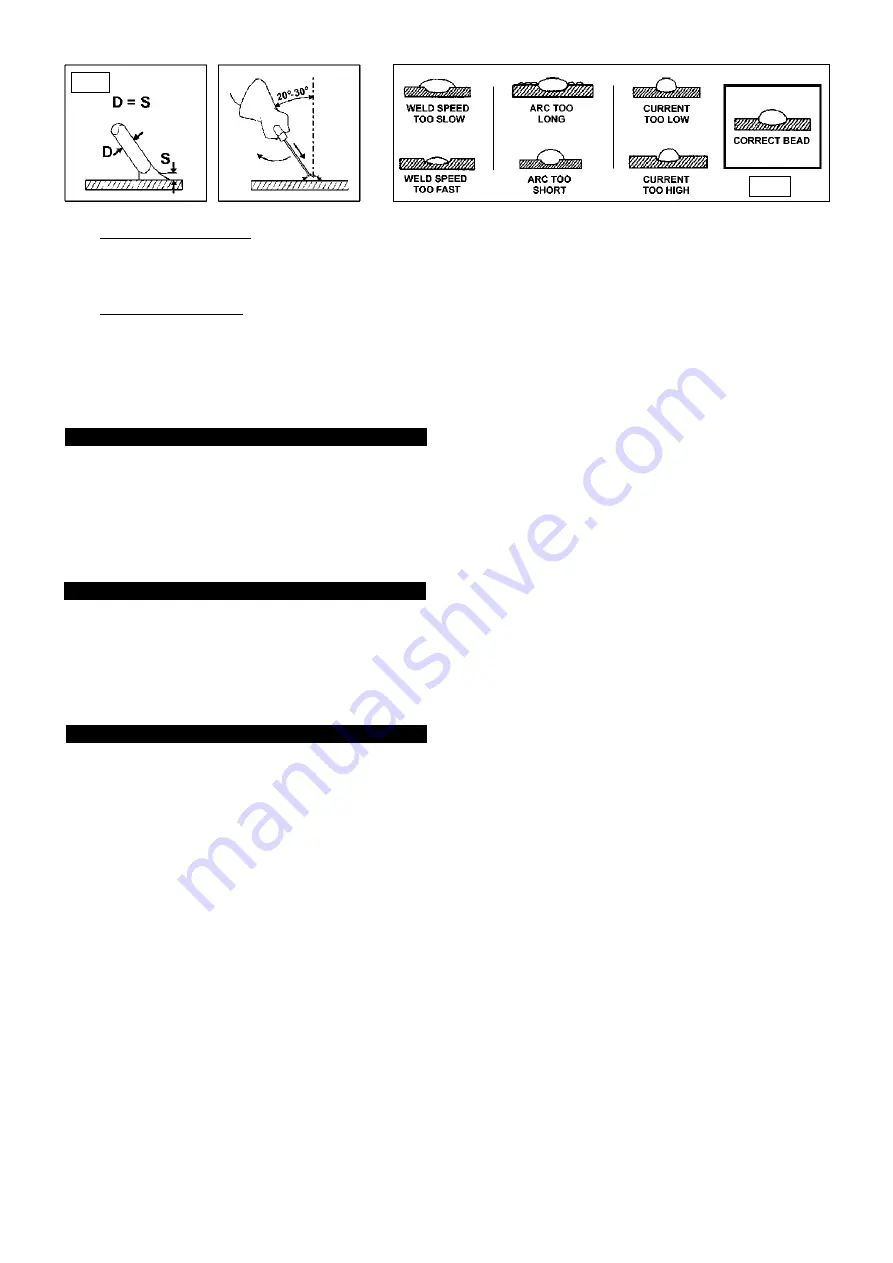
6.4.1. Strike the electrode tip on the workpiece as if you were striking a match.
6.4.2. Point the electrode in the direction of the weld at about 2.5mm distance from the surface and use the arc to melt the metal at the joint.
6.4.3. To increase or decrease flow of gas, use the control knob on the torch handle.
6.4.4. Filler metal may be added by using cut lengths of wire over 1.5mm diameter. To use filler metal (for example when making a fillet weld), add it to the
leading edge of the weld pool.
6.4.5 To end welding lift the electrode quickly away from the workpiece.
MW140.V3 - 1 - 220205







