8-6
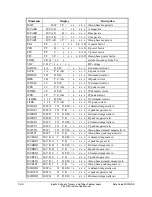
Breaker Monitor and Metering Functions
Date Code 20011205
SEL-311A Instruction Manual
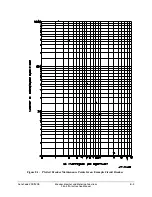
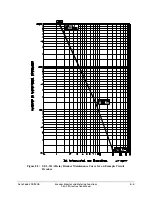
In Figure 8.2, note that the breaker maintenance curve levels off horizontally to the left of set
point KASP1, COSP1. This is the close/open operation limit of the circuit breaker (COSP1 =
10000), regardless of interrupted current value.
Also, note that the breaker maintenance curve falls vertically below set point KASP3, COSP3.
This is the maximum interrupted current limit of the circuit breaker (KASP3 = 20.0 kA). If the
interrupted current is greater than setting KASP3, the interrupted current is accumulated as a
current value equal to setting KASP3.
Operation of SEL
OGIC
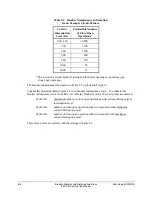
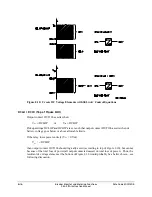
Control Equation Breaker Monitor Initiation Setting BKMON
The SEL
OGIC
control equation breaker monitor initiation setting BKMON in Table 8.2
determines when the breaker monitor reads in current values (Phases A, B, and C) for the breaker
maintenance curve and the breaker monitor accumulated currents/trips (see
BRE Command
[Breaker Monitor Data]
in
Section 10: Serial Port Communications and Commands
).
The BKMON setting looks for a rising edge (logical 0 to logical 1 transition) as the indication to
read in current values. The acquired current values are then applied to the breaker maintenance
curve and the breaker monitor accumulated currents/trips.
For example, the SEL
OGIC
control equation breaker monitor initiation setting may be set:
BKMON = TRIP
(TRIP is the logic output of Figure 5.1)
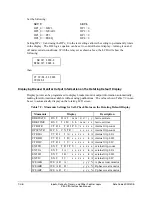
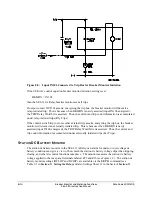
Refer to Figure 8.3. When BKMON asserts (Relay Word bit TRIP goes from logical 0 to
logical 1), the breaker monitor reads in the current values and applies them to the breaker
monitor maintenance curve and the breaker monitor accumulated currents/trips.
As detailed in Figure 8.3, the breaker monitor actually reads in the current values 1.5 cycles after
the assertion of BKMON. This helps especially if an instantaneous trip occurs. The
instantaneous element trips when the fault current reaches its pickup setting level. The fault
current may still be “climbing” to its full value, after which it levels off. The 1.5-cycle delay on
reading in the current values allows time for the fault current to level off.
Figure 8.3: Operation of SEL
OGIC
Control Equation Breaker Monitor Initiation Setting
See Figure 8.8 and accompanying text for more information on setting BKMON. The operation
of the breaker monitor maintenance curve, when new current values are read in, is explained in
the following example.
Breaker Monitor Operation Example
As stated earlier, each phase (A, B, and C) has its own breaker maintenance curve. For this
example, presume that the interrupted current values occur on a single phase in Figure 8.4
Summary of Contents for SEL-311A
Page 6: ......
Page 8: ......
Page 10: ......
Page 24: ......
Page 40: ......
Page 66: ......
Page 96: ......
Page 98: ......
Page 112: ......
Page 114: ......
Page 122: ......
Page 170: ......
Page 202: ......
Page 204: ......
Page 246: ......
Page 248: ......
Page 286: ......
Page 290: ......
Page 304: ......
Page 306: ......
Page 334: ......
Page 384: ......
Page 386: ......
Page 394: ......
Page 398: ......
Page 402: ......
Page 404: ......
Page 410: ......
Page 412: ......
Page 426: ......
Page 444: ......
Page 460: ......
Page 474: ......