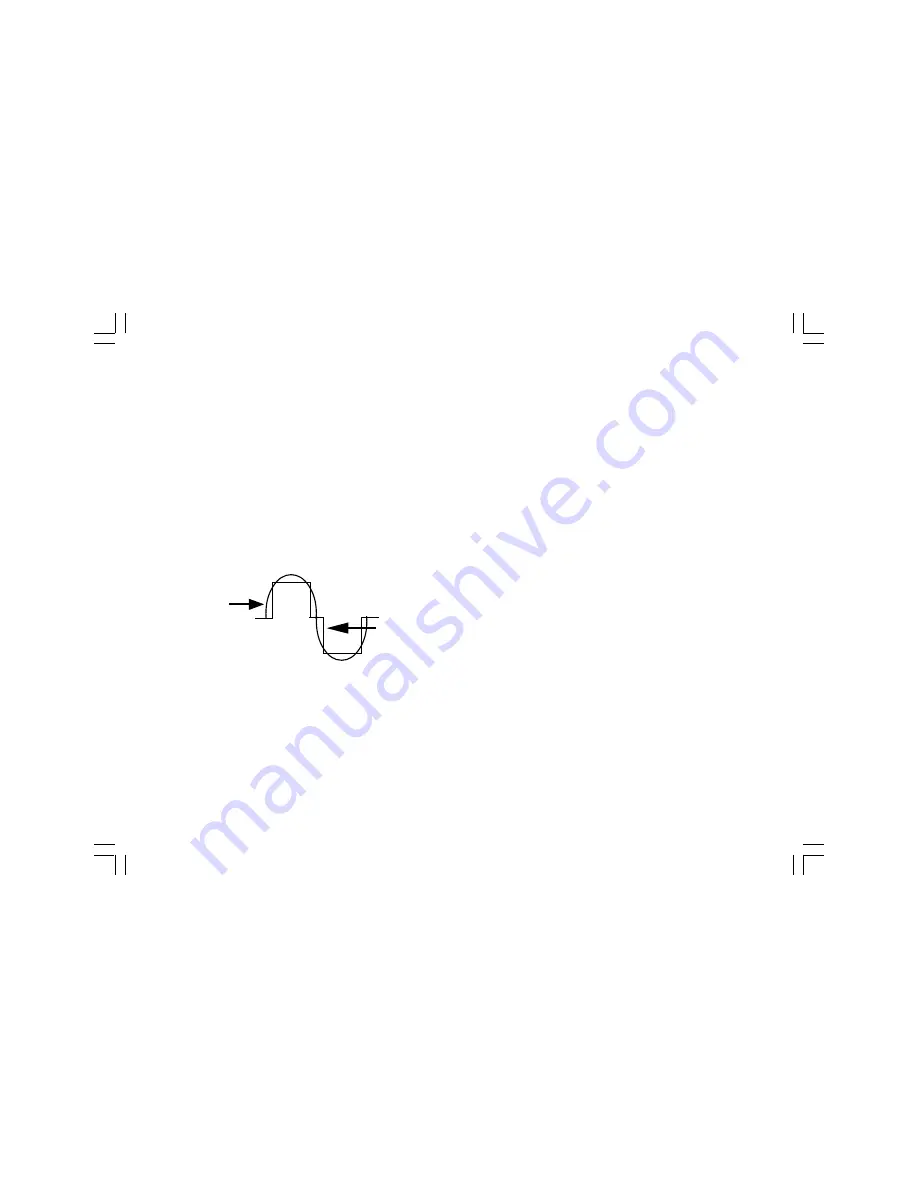
3.2 THE SAMLEX SI-750HP OUTPUT WAVEFORM
The AC output waveform of the SI-750HP is known as “modified sine
wave”. It is a waveform that has characteristics similar to the sine wave
shape of utility power. This type of waveform is suitable for most AC loads,
including linear and switching power supplies used in electronic equipment,
transformers, and motors.
The modified sine wave produced by the SI-750HP inverter has an RMS
(root mean square) voltage of 110 volts, which is the same as standard
household power. Most AC voltmeters (both digital and analog) are sensitive
to the average value of the waveform rather than the RMS value. They are
calibrated for RMS voltage under the assumption that the waveform
measured will be a pure sine wave. These meters will not read the RMS
voltage of a modified sine wave correctly. They will read about 20 to 30 volts
low when measuring the output of the inverter. For accurate measurement
of the output voltage of this unit,
use a true RMS reading voltmeter
such
as a Fluke 87, Fluke 8060A, Fluke 77/99 series, Beckman 4410, or Triplett
4200.
FIGURE 4
Modified Sine Wave and Sine Wave Comparison
4. INSTALLATION
4.1 POWER SOURCE REQUIREMENTS
The power source must provide between 10.6 and 15.5 volts DC and
must be able to supply the necessary current to operate the load. The
power source may be a battery or a well-regulated DC power supply. To
obtain a rough estimate of the current (in amperes) the power source
must deliver, simply divide the power consumption of the load (in watts
AC) by 10.
Example: If a load is rated at 750 watts AC, the power source must be
able to deliver: 750 divided by 10 = 75 amperes
Modified
Sine Wave
110 VAC
Sine Wave
110 VAC
6.
Your SI-750HP monitors the following potentially hazardous condi-
tions:
Low Battery Voltage
- This condition is not harmful to the inverter
but could damage the power source. An audible alarm will sound when
input voltage drops to 10.6. The SI-750HP automatically shuts down
when input voltage drops to 10.0 volts. When the condition is corrected,
the unit may be restarted.
Over Voltage Protection
- The SI-750HP will automatically shut
down when the input voltage exceeds 15 volts DC.
However,
voltages higher thatn 15V may cause damage.
Short Circuit Protection
- Reverse polarity or
a short circuit
condition will usually result in an external or internal fuse being
blown.
Overload Protection
- The inverter will automatically shut down when
the continuous draw exceeds 750 Watts. When the overload is removed
the inverter will self-start.
Over Temperature Protection
-
The inverter is cooled by a fan.
When the temperature sensor inside the SI-750HP reaches 150 de-
grees F, the unit will automatically shutdown. Allow the unit to cool for
at least 15 minutes before restarting after a heat-related shutdown.
Unplug unit while cooling.
Low Battery Alarm
- An alarm will sound when the voltage from the
battery drops to 10.6 volts. This is an indication that the battery needs
to be recharged. The user should stop operation of the electronic device
at this time, since the inverter will shut down automatically shortly there-
after, when the battery voltage drops to 10 volts.
If the low voltage alarm sounds when the battery is fully charged, fol-
low the steps for solving lack of output power in the Troubleshooting
Guide. The alarm will sound when the inverter is overloaded, in thermal
shutdown, or if there is an excessive voltage drop between the battery
and inverter.
NOTE:
It is normal for the alarm to sound while the unit is being
connected to, or disconnected from, the power source. This is not
indicative of a problem
11.








