English
82
Pompes Salmson 05/2015
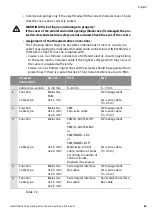
Drinking water circulation
systems with resistance in
the generator circuit
≤
50%
of the resistance in the
ascending section
5. Drinking water circulation systems
with thermostatically controlled line
shut-off valves
Δ
p-c
Heating systems
1. Two-pipe systems
• Pump is installed in the feed pipe.
• The feed temperature is controlled
by atmospheric conditions.
An increasing feed temperature
increases the flow rate.
2. One-pipe systems
• Pump is installed in the return pipe.
• The feed temperature is constant.
A falling feed temperature reduces
the flow rate.
3. Primary circuits with condensing
boiler
• Pump is installed in the return pipe.
A falling feed temperature reduces
the flow rate.
Δ
p-T
Drinking water circulation
systems
4. Drinking water circulation systems
with thermostatically controlled line
shut-off valves or constant flow rate.
If the temperature is increased in the
circulation pipe, the flow rate is
reduced.
Heating-ventilation/air-
conditioning systems
Drinking water circulation
systems
1. Constant flow rate
Manual
control mode
Heating systems
1. All systems
• Pump is installed in the feed pipe.
• The feed temperature falls during
low load periods (e.g. at night).
• The pump runs 24 hours without
external control at the mains.
Setback
operation
System type
System conditions
Recommended
control mode