2/22/2018
XM540-W150
http://support.robotis.com/en/product/actuator/dynamixel_x/xm_series/xm540-w150.htm
14/17
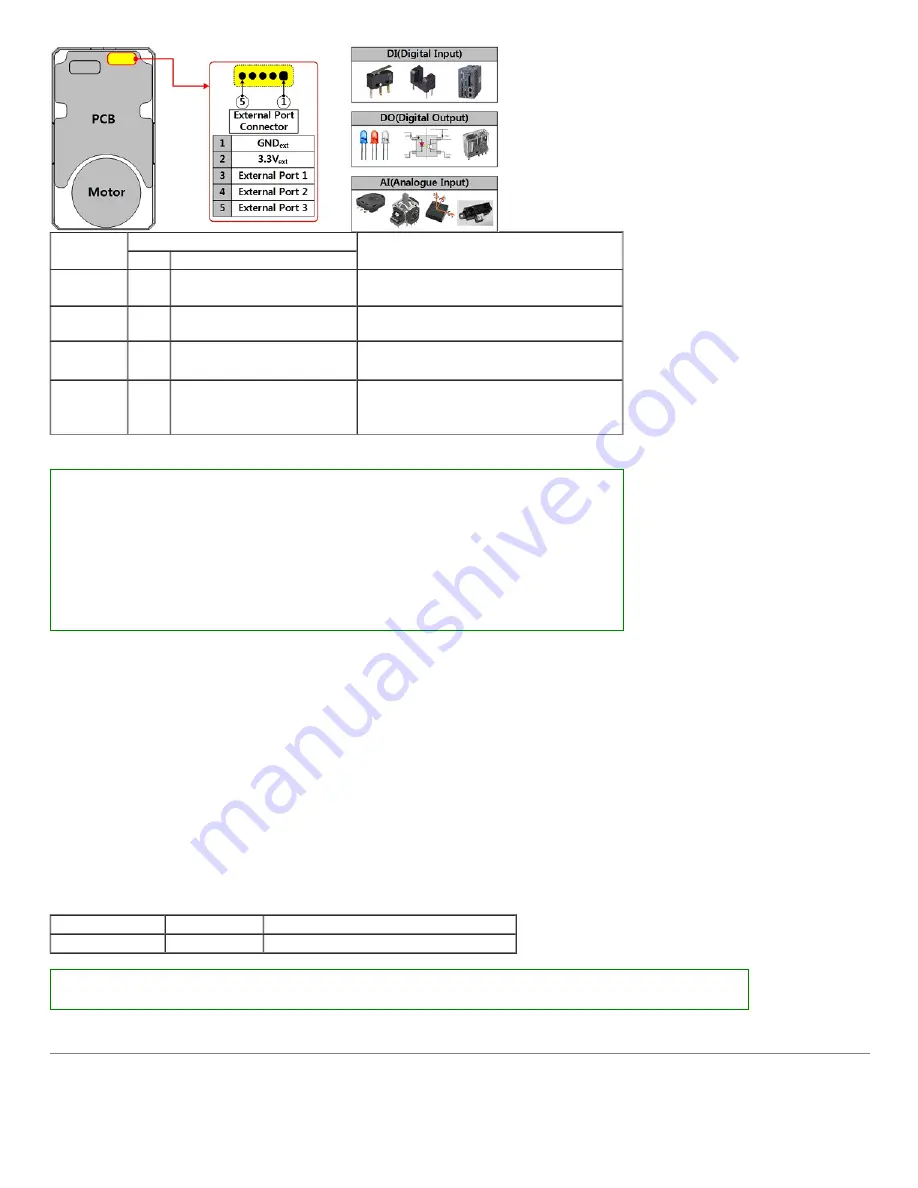
External Port
Mode
External Port Data
External Port
Electrical Characteristics
Access
Details
Common
-
-
0 ~ 3.3[V], 0 ~ 5[mA]
V
ESD(HBM)
: 2[kV]
0(AI)
Read
Converts External Port signal to digital value
External Data = signal x (4,095 / 3.3)
Resolution : 12[bit] (0 ~ 4,095)
1(DO_PP)
Write
0 : Set External Port output to 0[V]
1 : Set External Port output to 3.3[V]
Output High level(VOH) : 2.4 [V] (min)
Output Low level(VOL) : 0.5 [V] (max)
2(DI_PU)
3 (DI_PD)
Read
0: External Port input is 0[V]
1 : External Port input is 3.3[V]
Input High level(VIH) : 2.3 [V] (min)
Input Low level(VIL) : 1.0 [V] (max)
Pull-Up/Down : 40 [kΩ] (typ)
※
V
ESD(HBM)
: ESD(Electrostatic Discharge) Voltage(human body model)
The External Port is not electrically insulated, therefore, abide by the electrical specifications.
If the electrical specification is exceeded or there is a problem with the signal connection, special caution is required because
DYNAMIXEL can be damaged.
1. Be careful not to cause electric shock by static electricity (ESD), short circuit, open circuit.
2. Be careful not to let water or dust get into the External Port connector.
3. If you are not using the External Port, remove the cable.
4. To connect or disconnect the External Port, proceed with power off.
5. Do not connect the GNDext pin of External Port directly to the GND pin of DYNAMIXEL connector. Noise from power may affect
on the External Port.
Indirect Address 1 ~ 28 (168, 170 ~ 220, 222), Indirect Address 29 ~ 56 (578, 580 ~ 630, 632)
Indirect Data 1 ~ 28 (224, 225 ~ 250, 251), Indirect Data 29 ~ 56 (634, 635 ~ 660, 661)
Indirect Address and Indirect Data are useful when accessing two remote addresses in the Control Table as sequential addresses. Sequential addresses increase Instruction Packet efficiency. Addresses
that can be defined as Indirect Address is limited to RAM area(Address 64 ~ 661).
If specific address is allocated to Indirect Address, Indirect Address inherits features and properties of the Data from the specific Address. Property includes Size(Byte length), value range, and Access
property(Read Only, Read/Write). For instance, allocating 65(Address of LED) to Indirect Address 1(168), Indirect Data 1(224) can perform exactly same as LED(65).
①
Example 1) Allocating Size 1[byte] LED(65) to Indirect Data 1(224)
A. Indirect Address 1(168) : change the value to '65' which is the address of LED
B. Set Indirect Data 1(224) to ‘1’ -> LED(65) also becomes '1' and LED is turned on.
C. Set Indirect Data 1(224) to ‘0’ -> LED(65) also becomes ‘0’ and LED is turned off.
②
Example 2) Allocating Size 4[byte] Goal Position(116) to Indirect Data 2(225), all 4[byte] has to be allocated.
A. Indirect Address 2(170) : change the value to '116' which is the first address of Goal Position.
B. Indirect Address 3(172) : change the value to '117' which is the first address of Goal Position.
C. Indirect Address 4(174) : change the value to '118' which is the first address of Goal Position.
D. Indirect Address 5(176) : change the value to '119' which is the first address of Goal Position.
E. Set 4[byte] value '1024' to Indirect Data 2 -> Goal Position(116) also becomes '1024 and Dynamixel moves.
Indirect Address
Values
Description
Range
64~661
Indirection Address can't be allocated with EEPROM area
Note 1) : In order to allocate Data in the Control Table longer than 2[byte] to Indirect Address, all address must be allocated to Indirect Address like the above Example 2.
Note 2) : Indirect Address 29 ~ 56 and Indirect Data 29 ~ 56 can only be accessed with Protocol 2.0.
Wiring Instructions through hollow back case



































