53
Raveon Technologies Corp.
10. Diagnostic Provisions
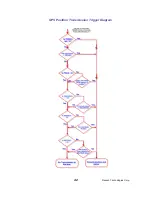
10.1. Overview of Diagnostics
Internal to the
M6
radio modem, is a powerful 32-bit microprocessor. Along with
handing all aspects of radio modulation and demodulation, the microprocessor
also maintains an extensive array of diagnostic information.
This section details the diagnostic information available, and describes how to us
the information to optimize or troubleshoot a
M6
radio network.
10.2. Reading the Diagnostic Information
M6
diagnostic information is read using AT commands, while the unit is in the
Command Mode. Refer to the section “User Serial Port Commands” to learn
how to put the
M6
modem into the Command Mode.
To see a general overview of how the modem has been operating, us the
ATST
command (status request command), without any parameter. The radio modem
will respond with a list of certain operation statistics that it maintains. All statistics
start counting at 0. The
ATST 1
command can be used to reset all statistics
back to 0, except the run-time timers.
Other operation and configuration statistics are available using the ATST
command, with a parameter to specify the desired statistic. The following table
describes the various statistics available.
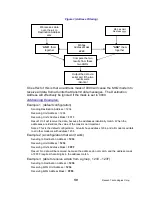
10.3. Status and Statistics Command
AT
Command
Command Description
Response
STAT
General Communication Statistics – This command will cause the
M6 to output a table of various operational statistics.
Statistics
overview screen
STAT 1
GPS Statistics – If device has the GPS option, it displays GPS and
TDMA related statistics.
GPS statistics
screen
STAT 2
Low-level internal statistics – Returns various low-level statistics.
These are subject to change in various firmware revisions.
Low-level
statistics screen
STAT 3
Compile date and time – Returns the data and the time that the
firmware was compiled.
Date and time
STAT 4
Run Time – Returns the amount of time that the modem has been
powered up and running.
Run time display
screen
STAT 9
Reset all statistics counters
OK