Spectrum Measurements
R&S
®
ESR
322
User Manual 1175.7068.02 ─ 12
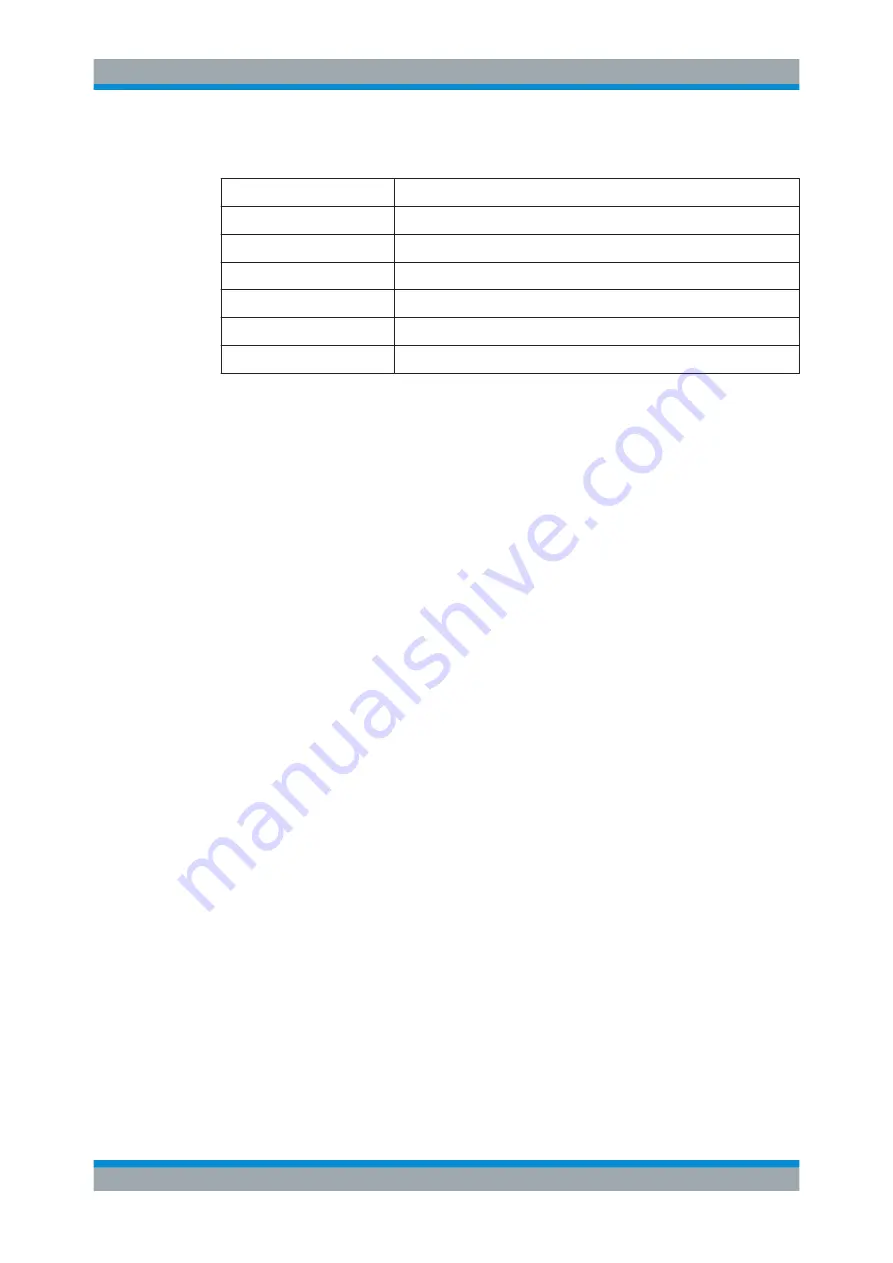
After a CCDF measurement, the results are displayed in a table beneath the diagram.
Mean
Mean power
Peak
Peak power
Crest
Crest factor (peak power – mean power)
0,01 %
Level values over 0,01 % above mean power
0,1 %
Level values over 0,1 % above mean power
1 %
Level values over 1 % above mean power
10 %
Level values over 10 % above mean power
In addition, a red reference line indicating the calculated Gauss distribution is dis-
played.
Remote command:
CALCulate<n>:STATistics:CCDF[:STATe]
Activates the CCDF measurement.
CALCulate<n>:STATistics:CCDF:X<Trace>
Reads out the level values for 1 % probability.
Percent Marker ← CCDF
Opens an edit dialog box to enter a probability value and to position marker 1. Thus,
the power which is exceeded with a given probability can be determined very easily. If
marker 1 is deactivated, it will be switched on automatically.
As all markers, the percent marker can be moved simply by touching it with a finger or
mouse cursor and dragging it to the desired position.
Remote command:
CALCulate<n>:MARKer<m>:Y:PERCent
Res BW ← CCDF
Opens an edit dialog box to set the resolution bandwidth directly.
For correct measurement of the signal statistics the resolution bandwidth has to be
wider than the signal bandwidth in order to measure the actual peaks of the signal
amplitude correctly. In order not to influence the peak amplitudes the video bandwidth
is automatically set to 10 MHz. The sample detector is used for detecting the video
voltage.
Remote command:
[SENSe:]BANDwidth|BWIDth[:RESolution]
# of Samples ← CCDF
Opens an edit dialog box to set the number of power measurements that are taken into
account for the statistics.
Apart from the number of measurements the overall measurement time depends also
on the set resolution bandwidth as the resolution bandwidth directly influences the
sampling rate.
For details see
"Selecting the number of samples"
Measurements






























