18
In the POWRE ON box,Input : be, ef, 03, 06, 00, ba, d2, 01, 00, 00, 60, 01,
00. Then use the same input rule to input other code.
b. If the data is in the character string format, input
„character string‟.
For example:
the “POWER ON” code in the SHARP C40/50 projector
manual is :
P
O
W
R
-
-
-
1
(
“-” is space
,
is enter.
)
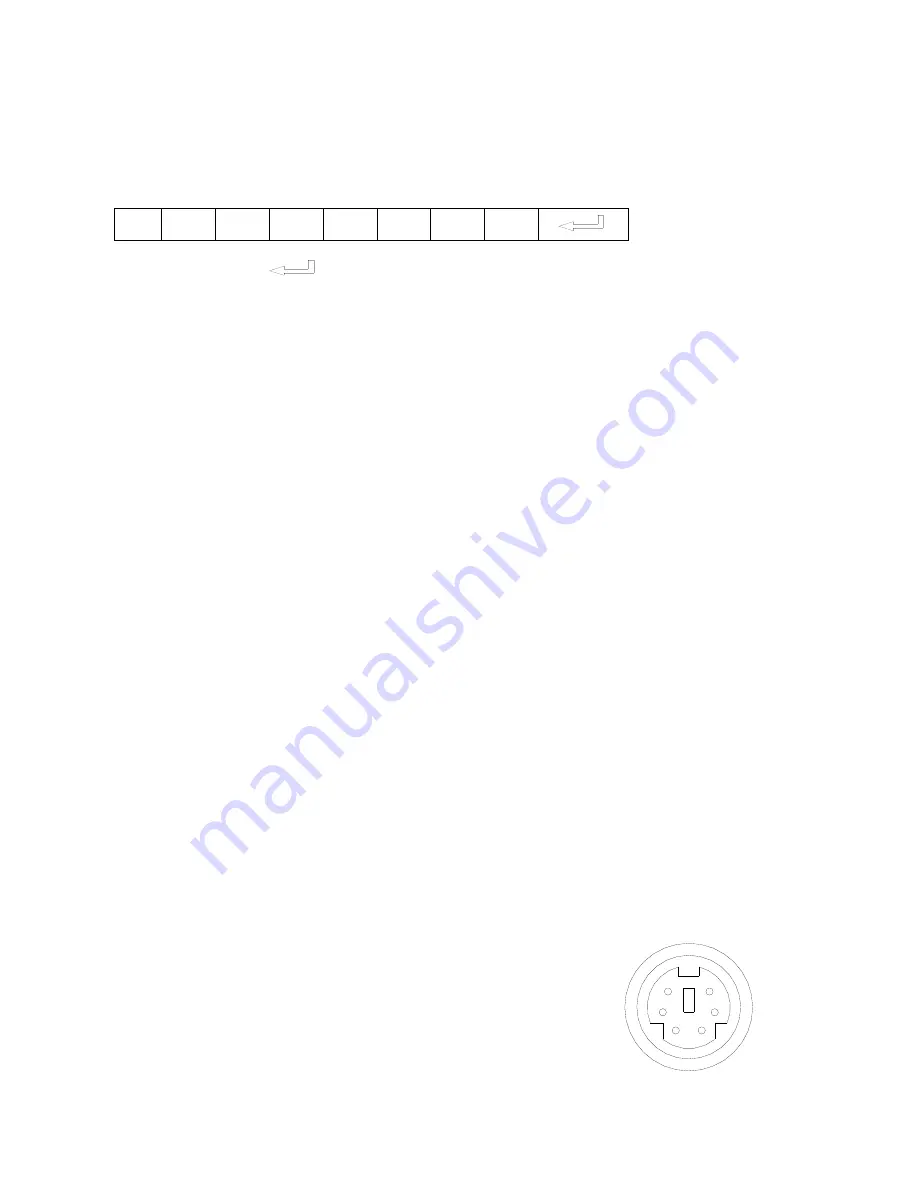
In the POWER ON box, input
‟POWR 1‟, 0d, 0a
(Remarks: There are 3 spaces after POWER, 0d, 0a is enter.)
Input other codes in the same way.
c. If the data is in the numerical value and character format, then
synthesize the above-mentioned formats.
3)
.
Once done, click
“Add” to add your projector model, then Click “Send”.
Afterward, click
“Ok”. Now, you can use the visualizer to control your
projector.
4. Connect the visualizer
‟s projector control port to the RS232 port with a
RS232 cable
(
Please disconnect the computer from the RS232 port first
)
.
Then use buttons on the operation panel to control the projector.
The visualizer provides a 6-pin to 9-pin RS232 cable. If this cable does not
match to your projector
‟s RS232 port, an additional RS232 cable is needed.
This additional RS232 cable can be made based on the pin location of the
projector
‟s RS232 control port. The pin locations of the visualizer are: the
pin 1 is RXD (Received Data); the pin 5 is TXD (Transmitted Data); the pin
4 is GND (Ground). Other pins are not defined. The pin location information
of the projector is provided by the projector
‟s manufacturer. The projector‟s
RS232 control port normally has RXD pin, TXD
pin and GND pin, the name may be different. The
parallelism of each data pin is shown as follows:
Visualizer
‟s RXD pin------------Projector‟s TXD pin
Visualizer
‟s TXD pin------------Projector‟s RXD pin
Visualizer
‟s GND pin------------Projector‟s GND pin
6
5
4
3
2 1





































