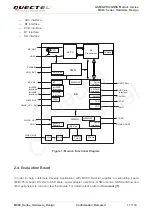
GSM/GPRS/GNSS Module Series
MC60 Series Hardware Design
MC60_Series_Hardware_Design Confidential / Released 27 / 114
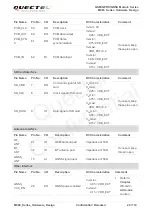
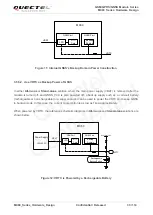
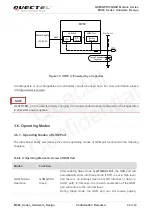
Table 8: Comparison between All-in-one and Stand-alone Solution
3.5. Power Supply
3.5.1. Power Features
3.5.1.1. Power Features of GSM Part
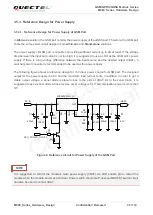
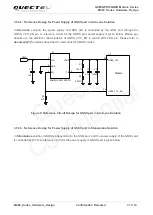
The power supply of the GSM part is one of the key issues in MC60 design. Due to the 577us radio burst
in GSM part every 4.615ms, the power supply must be able to deliver high current peaks in a burst period.
During these peaks, drops on the supply voltage must not exceed the minimum working voltage of the
GSM part.
The maximum current consumption of GSM part could reach 1.6A during a burst transmission. It will
cause a large voltage drop on the VBAT. In order to ensure stable operation of the part, it is
recommended that the maximum voltage drop during the burst transmission does not exceed 400mV.
All-in-one
Stand-alone
Remarks
Firmware upgrade
Firmware upgrade via UART
Port (GSM and GNSS parts
share the same firmware
package)
Firmware
upgrade
via
UART Port (GSM and
GNSS parts share the
same firmware package)
Refer to
Chapter
3.9.1.3
for details
Data transmission
Both GSM and GNSS data
are transmitted through the
GSM UART Port
GSM data is transmitted
through the GSM UART
Port.
GNSS data is transmitted
through the GNSS UART
Port.
GNSS TURN
ON/OFF
By AT command through
GSM UART Port
Through
the
external
switch of MCU
Refer to
Chapter
3.7
and
3.8
for
details
GNSS wake up GSM
GNSS can wake up GSM by
interrupts
N/A
GNSS
’s EPO data
download
EPO data is downloaded
directly through the GSM
part.
MCU receives the EPO
data which is downloaded
through the GSM part, and
then transmit it to the
GNSS part.
Refer to
Chapter
3.18
for details
Quectel
Confidential