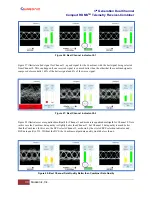
3
rd
Generation Dual Channel
Compact RDMS
TM
Telemetry Receiver-Combiner
42
Quasonix, Inc.
5.4.2.7
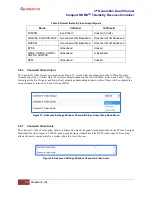
Differential Decoding Settings (SOQPSK Only)
The Differential Decoding option is set to On or Off by clicking on the check box (Figure 48) to enable or disable
the differential decoding. Differential Decoding defaults to enabled.
Differential decoding is available in all PSK modes (SOQPSK and legacy BPSK, QPSK, OQPSK, AQPSK,
AUQPSK, and UQPSK). Legacy modes often use differential forms of PCM encoding (e.g., NRZ-M) instead, and
only one or the other form of differential encoding should be used at a time.
In SOQPSK-TG mode, differential encoding and decoding eliminates the phase ambiguity inherent with the
received data. The differential decoder can be enabled or disabled through the Main Menu by pressing Enter when
the parameter is selected. The Enter key acts as a toggle switch. Normal SOQPSK operation requires the differential
decoder to be On. The default value is On.
Differential encoding results in two differentially-decoded bit errors for each received bit error. This doubling
negatively impacts subsequent error-correction capability for block forward error correction. Since the Attached
Sync Marker used to identify block boundaries can also be used to resolve the phase ambiguity inherent in PSK
modulation, differential encoding is unnecessary for block forward error correction. Therefore, differential decoding
is automatically disabled when Reed-Solomon encoding is enabled.
Figure 48: Configure Basic Settings Window-SOQPSK Mode
5.4.3
Configure Advanced Settings
The Configure screen also includes a secondary window for Advanced Settings. These include Measured Bit Rate,
IF Filter, Output Muting, Muting Timeout, AFC Mode, Best Channel Selector, Time Aligner, and PCM Encoding,
as shown in Figure 49. Additionally, the Advanced Settings window shows Video Output parameters, Channel A
and Channel B Output, Channel A and Channel B Scale, Tape Output Frequency, and FM De-emphasis (when in
PCM/FM mode).